orthorhombic structure Crystalline polyethylene (PE) can be achieved in two different forms. The more common is described by an orthorhombic structure having lattice parameters provided in the image, where the unit cell contains 4 Carbon and 8 Hydrogen atoms. The second form is monoclinic (see image), where a=0.809nm, b=0.253nm and c=0.479nm. In this variant, a=7.41 A b= 4.95 A c= 2.55 A the chains are aligned slightly askew but the unit cell also contains 4 Carbon and 8 Hydrogen, resulting in a higher density of 998.1 kg/m. O Hydrogen O Carbon a) Determine the angle beta (B) that is associated with the monoclinic form of crystalline polyethylene. b) Compare the Atomic Packing factor in the orthorhombic vs monoclinic forms. Present your answer in the form of a ratio of the APF's. C) Considering that the monoclinic structure occurs in 41% of the crystalline formations and orthorhombic exists in the other 59%: Determine the percent crystallinity (having mixed forms) present in HDPE ("high- density" PE) when assuming amorphous solid (zero crystallinity) has a density of 0.8672g/cm?, and demonstrating the theoretical density of the orthorhombic structure. Monoclinic structure
orthorhombic structure Crystalline polyethylene (PE) can be achieved in two different forms. The more common is described by an orthorhombic structure having lattice parameters provided in the image, where the unit cell contains 4 Carbon and 8 Hydrogen atoms. The second form is monoclinic (see image), where a=0.809nm, b=0.253nm and c=0.479nm. In this variant, a=7.41 A b= 4.95 A c= 2.55 A the chains are aligned slightly askew but the unit cell also contains 4 Carbon and 8 Hydrogen, resulting in a higher density of 998.1 kg/m. O Hydrogen O Carbon a) Determine the angle beta (B) that is associated with the monoclinic form of crystalline polyethylene. b) Compare the Atomic Packing factor in the orthorhombic vs monoclinic forms. Present your answer in the form of a ratio of the APF's. C) Considering that the monoclinic structure occurs in 41% of the crystalline formations and orthorhombic exists in the other 59%: Determine the percent crystallinity (having mixed forms) present in HDPE ("high- density" PE) when assuming amorphous solid (zero crystallinity) has a density of 0.8672g/cm?, and demonstrating the theoretical density of the orthorhombic structure. Monoclinic structure
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter11: Liquids And Solids
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.87QE
Related questions
Question
Question attached
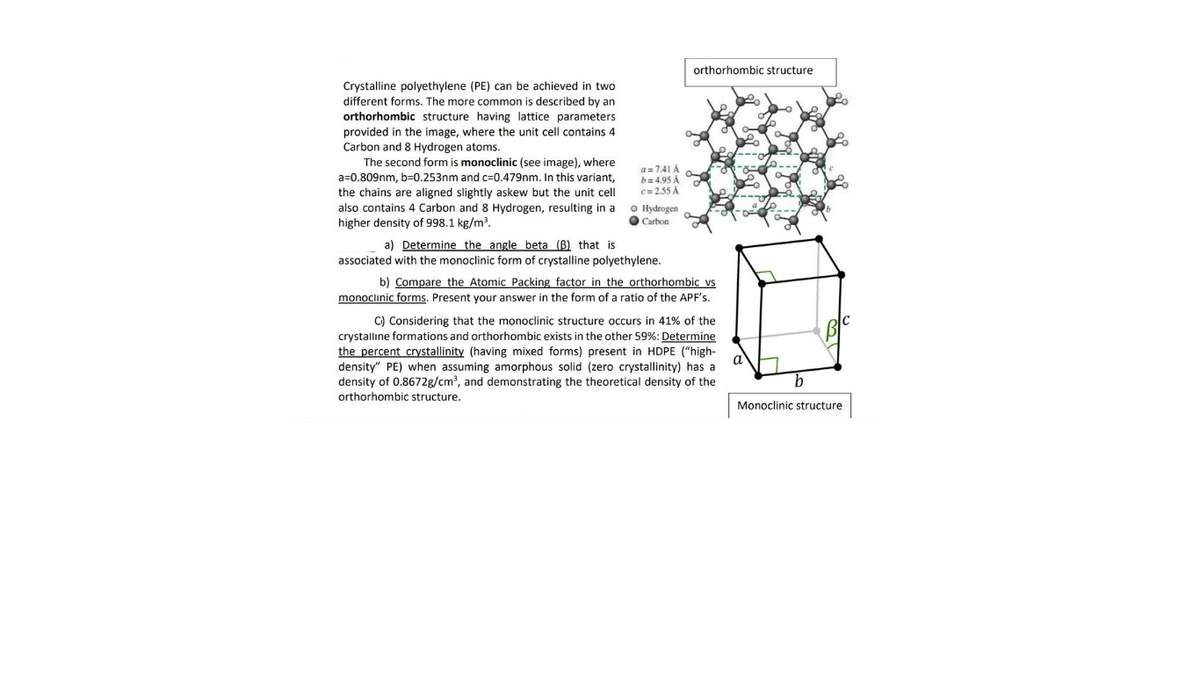
Transcribed Image Text:orthorhombic structure
Crystalline polyethylene (PE) can be achieved in two
different forms. The more common is described by an
orthorhombic structure having lattice parameters
provided in the image, where the unit cell contains 4
Carbon and 8 Hydrogen atoms.
The second form is monoclinic (see image), where
a=0.809nm, b=0.253nm and c=0.479nm. In this variant,
a=7.41 A
b= 4.95 A
c= 2.55 A
the chains are aligned slightly askew but the unit cell
also contains 4 Carbon and 8 Hydrogen, resulting in a
higher density of 998.1 kg/m.
O Hydrogen
O Carbon
a) Determine the angle beta (B) that is
associated with the monoclinic form of crystalline polyethylene.
b) Compare the Atomic Packing factor in the orthorhombic vs
monoclinic forms. Present your answer in the form of a ratio of the APF's.
C) Considering that the monoclinic structure occurs in 41% of the
crystalline formations and orthorhombic exists in the other 59%: Determine
the percent crystallinity (having mixed forms) present in HDPE ("high-
density" PE) when assuming amorphous solid (zero crystallinity) has a
density of 0.8672g/cm?, and demonstrating the theoretical density of the
orthorhombic structure.
Monoclinic structure
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning