
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
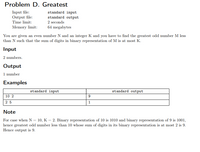
Transcribed Image Text:Problem D. Greatest
Input file:
Output file:
standard input
standard output
Time limit:
2 seconds
Memory limit:
64 megabytes
You are given an even number N and an integer K and you have to find the greatest odd number M less
than N such that the sum of digits in binary representation of M is at most K.
Input
2 numbers.
Output
1 number
Examples
standard input
standard output
10 2
25
Note
For case when N = 10, K = 2. Binary representation of 10 is 1010 and binary representation of 9 is 1001,
hence greatest odd number less than 10 whose sum of digits in its binary representation is at most 2 is 9.
Hence output is 9.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 4. The largest number with two-byte word length is: Ans: 5. How many lines needed in parallel representation to transimmit decimal integer values up to 17 in binary. Ans: is (2), -Q₁. 6. The base of the following is Ans:arrow_forwardSuppose A = +54 and B = -3 (both in base 10).Q1: What is the lowest number of rounds theoretically to complete the integer division using the optimized division algorithm?Q2: What is the resulting number in binary representation if we use 8 bits to represent it?Q3: What is the resulting number in FP decimal representation if we use the IEEE 754 standard for single precision? (form of this result should be in sign, true exponent in binary, IEEE-754 Exponent in binary and IEEE-754 exponent in decimal (base 10 number) )arrow_forwardWrite a program that swaps 5th~11th bits in data_a with 25th~31th bits in data_bYour program must work for any data given, not just the example belowIn this question, we assume that the positions of bits count from right to left.That is, the first bit is the least significant bit.data_a DCD 0x77FFD1D1data_b DCD 0x12345678arrow_forward
- C++ Problem!! Sort A List Of Integers Given a file of 100,000 unsorted integers, write a program that first prompt user to enter file name and reads those integers into an array and sorts the integers in the array. The program should then prompt the user for an index, and then display the integer at that index. For example, if the array contains ten integers and the contents are 79 4 42 51 12 22 33 17 91 10 after sorting, the integer at index 6 is 42 Download the "List of 100,000 Unsorted Integers" from below link and sort that list, then enter the value at index 10000 (ten thousand) for a screenshot. https://1drv.ms/t/s!AuFS4mkcuYyBjHZ_SIudb93bq2uy?e=CsyvZjarrow_forwardWrite pseudocode to solve the following problem. Must use iterative dynamic programming (tabulation) and run in O(n) time. Input: positive integer n Output: two non-negative integer x and y where n = x185 + y120 Example: if n=1230 then x=6 and y=1 (1314 = 6(185) + 1(120))arrow_forwardAssume we are running code on a 7-bit machine using two's complement arithmetic for signed integers. A "short" integer is encoded using 3 bits. Fill in the empty boxes in the table below. The following definitions are used in the table: short sy = -3; int y = sy; int x = -12; unsigned ux = x; Note: You need not fill in entries marked with "-". Expression Decimal Binary Zero -8 10 0110 ux y x >> 2 ux & y TMax TMax + TMinarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY