
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Program Input
The input file consists of blocks of lines, each of which is a test case. Each block except the last
describes one train and possibly more requirements for its reorganization. In the first line of the block
there is the integer , which is the number of coaches in the train. In each of the next lines of the block
there is a permutation of 1, 2, ..., N . For example, if N is 5, and the permutation could be 5, 3, 2, 1, 4.
Your program will take this permutation as input and determine whether you can marshal the coaches
from track A an incoming order 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 to track B with an outgoing order 5, 3, 2, 1, 4 using the
station, which can be treated as a stack.
The last line of the block contains just 0.
If a block starts with a zero, the program will terminate.
The input file consists of blocks of lines, each of which is a test case. Each block except the last
describes one train and possibly more requirements for its reorganization. In the first line of the block
there is the integer , which is the number of coaches in the train. In each of the next lines of the block
there is a permutation of 1, 2, ..., N . For example, if N is 5, and the permutation could be 5, 3, 2, 1, 4.
Your program will take this permutation as input and determine whether you can marshal the coaches
from track A an incoming order 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 to track B with an outgoing order 5, 3, 2, 1, 4 using the
station, which can be treated as a stack.
The last line of the block contains just 0.
If a block starts with a zero, the program will terminate.
You should use the input file named lab1in.txt (download from Canvas) to test your program; an
output file named lab1out.txt (with correct output) is also provided for you to verify your program.
Input Sample
5 // start of first block
1 2 3 4 5
5 4 1 2 3
0 // end of first block
6 // start of second block
6 5 4 3 2 1
0 // end of second block
0 // end of input
Program Output
The output file contains the lines corresponding to the lines with permutations in the input file. A line of the
output file contains "Yes" if it is possible to marshal the coaches in the order required on the corresponding
line of the input file. Otherwise it contains "No". In addition, there is one empty line after the lines
corresponding to one block of the input file. There is no line in the output file corresponding to the last
"null'' block of the input file.
Output Sample
This is an output sample of the previous input sample
Hint
Key points to understand/solve the problem:
The train station can be regarded as a stack.
One can push a coach from track A into the stack; when the coach is popped out of the stack, it gets
into track B, and a coach in the station can never go back to track A.
Taking a train with 5 coaches as an example.
Coaches in track A is always in strictly increasing order, i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
The train chief tries to marshal the coaches into track B via a sequence of push and pop operations.
Each test case in the input file is asking a question: is it possible to marshal the the coaches into track B
such that the coach order matches the test case?
For instance, if the test case is "1, 2, 3, 4, 5", then we can perform the following sequence of
operations
Input Sample
5 // start of first block
1 2 3 4 5
5 4 1 2 3
0 // end of first block
6 // start of second block
6 5 4 3 2 1
0 // end of second block
0 // end of input
Program Output
The output file contains the lines corresponding to the lines with permutations in the input file. A line of the
output file contains "Yes" if it is possible to marshal the coaches in the order required on the corresponding
line of the input file. Otherwise it contains "No". In addition, there is one empty line after the lines
corresponding to one block of the input file. There is no line in the output file corresponding to the last
"null'' block of the input file.
Output Sample
This is an output sample of the previous input sample
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
Hint
Key points to understand/solve the problem:
The train station can be regarded as a stack.
One can push a coach from track A into the stack; when the coach is popped out of the stack, it gets
into track B, and a coach in the station can never go back to track A.
Taking a train with 5 coaches as an example.
Coaches in track A is always in strictly increasing order, i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
The train chief tries to marshal the coaches into track B via a sequence of push and pop operations.
Each test case in the input file is asking a question: is it possible to marshal the the coaches into track B
such that the coach order matches the test case?
For instance, if the test case is "1, 2, 3, 4, 5", then we can perform the following sequence of
operations

Transcribed Image Text:Page
Background
There is a famous railway station in PopPush City. Country there is incredibly hilly. The station was built in
last century. Unfortunately, funds were extremely limited that time. It was possible to establish only a
surface track. Moreover, it turned out that the station could be only a dead-end one (see picture) and due to
lack of available space it could have only one track.
5, 4, 3, 2, 1
1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B
A
Station
The local tradition is that every train arriving from the direction A continues in the direction B with coaches
reorganized in some way.
• Assume that the train arriving from the direction A has N≤ 1000 coaches numbered in increasing order
1, 2, ..., N.
• The chief for train reorganizations must know whether it is possible to marshal coaches continuing in
the direction B so that their order will be a, a,....ay. Help him and write a program that decides
whether it is possible to get the required order of coaches.
• You can assume that single coaches can be disconnected from the train before they enter the station
and that they can move themselves until they are on the track in the direction B.
• You can also suppose that at any time there can be located as many coaches as necessary in the
station. But once a coach has entered the station it cannot return to the track in the direction A and
also once it has left the station in the direction B it cannot return back to the station.
Program Input
• The input file consists of blocks of lines, each of which is a test case. Each block except the last
describes one train and possibly more requirements for its reorganization. In the first line of the block
there is the integer N, which is the number of coaches in the train. In each of the next lines of the block
there is a permutation of 1, 2, ..., N. For example, if N is 5, and the permutation could be 5, 3, 2, 1, 4.
Your program will take this permutation as input and determine whether you can marshal the coaches
from track A an incoming order 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 to track B with an outgoing order 5, 3, 2, 1, 4 using the
station, which can be treated as a stack.
• The last line of the block contains just 0.
•
If a block starts with a zero, the program will terminate.
1>.
Transcribed Image Text:ANNI
2
3
News
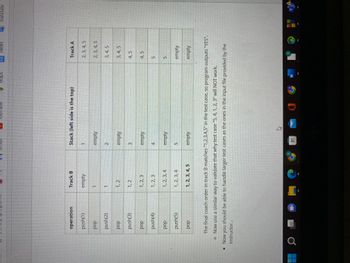
operation
Stack (left side is the top)
Track A
push(1)
1
2,3,4,5
pop
empty
2,3,4,5
push(2)
1
2
3,4,5
pop
1,2
empty
3,4,5
push(3)
1,2
3
4,5
pop
1,2,3
empty
4,5
push(4)
1,2,3
4
5
1, 2, 3, 4
empty
5
pop
push(5)
1, 2, 3, 4
5
empty
pop
1, 2, 3, 4, 5
empty
empty
The final coach order in track B matches "1,2,3,4,5" in the test case, so program outputs "YES".
o Now use a similar way to validate that why test case "5, 4, 1, 2, 3" will NOT work.
• Now you should be able to handle larger test cases as the ones in the input file provided by the
instructor.
0
0
W
Track B
empty
1
Maps
Translate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Write a function to determine the resultant force vector R of the two forces F₁ and F₂ applied to the bracket, where 0₁ (positive, unit in degree) and ₂ (negative, unit in degree). Write R in terms of unit vector along the and y axis. R must be a vector, for example R = [R₂, R₂]. Note that is expressed in degrees. The coordinate system is shown in the figure below: F2 021 return R # import numpy as np. import math from math import * # Import all the math functions from the math library from numpy import array # Complete the function given the variables F1, F2, thetal (positive, degree), theta2 (negative, degree) and return the value as array #Hints: Use numpy.array to form the force vector and then add the force vectors # Remember to convert the degree to radian in the calculations and be careful of the sign def force_vec (F1, F2, thetal, theta2): R=np.array([0,0]) # Resultant force vector, Initiation of the value # YOUR CODE HERE # Check your answer F1=300 F2=200 0₁ Theta1=60…arrow_forwardDescription Xiao Zhang is often distressed because there are too many things to arrange. Now he has n tasks at hand, and each task has a starting times, and an ending time e;. To complete a task, he must do it from the starting time to the ending time, and Xiao Zhang can only perform one task at the same time. Xiao Zhang wants to know how many tasks he can accomplish at most. Input The first line is an integer n (1sns300000), indicating the number of tasks Xiao Zhang has at hand. In the next n lines, each line contains two integers s₁, e¡ (1≤s;arrow_forwardcode in matlabarrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education