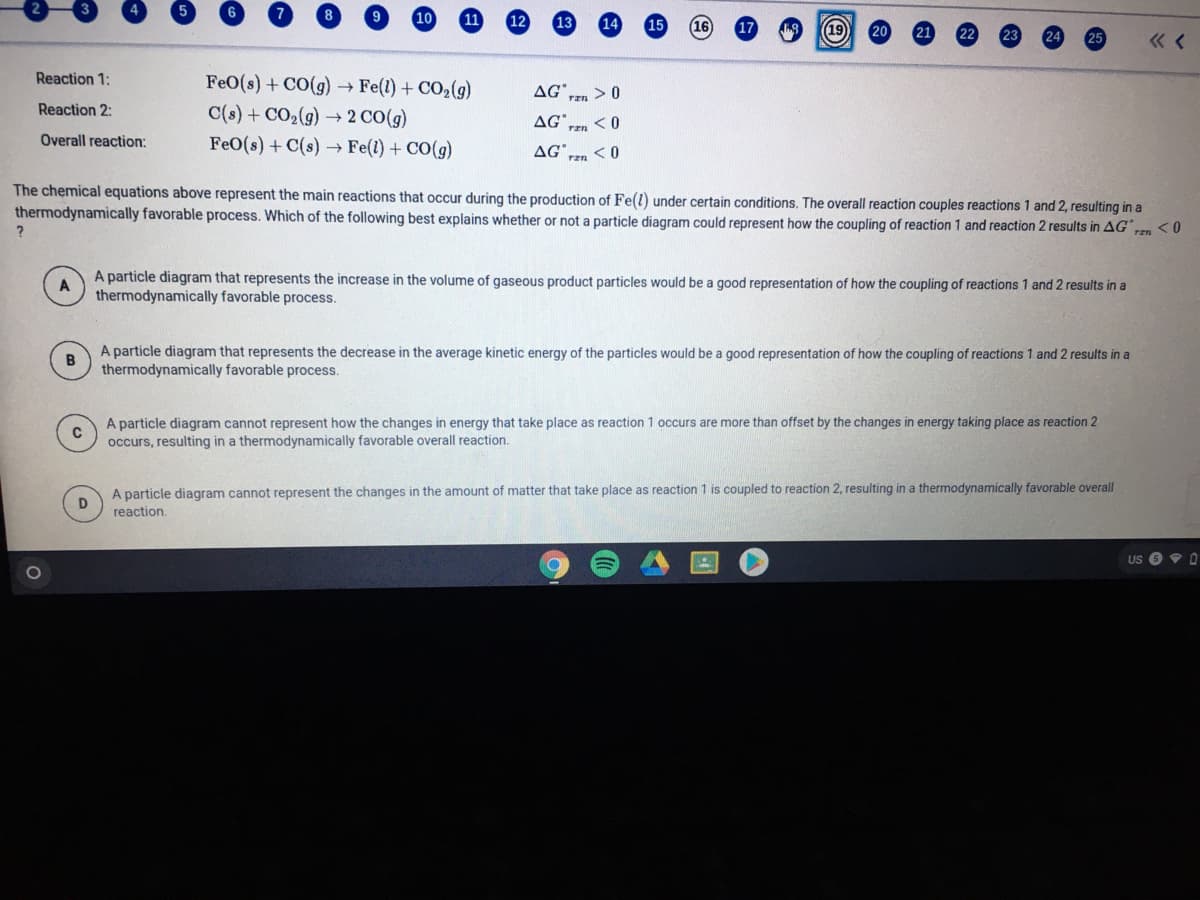
Reaction 1: FeO(s) + CO(g) → Fe(1) + CO2(g) AG" rzn > 0 Reaction 2: C(s) + CO2(g) → 2 CO(g) AG* rzn Overall reaction: FeO(s) + C(s) → Fe(1) + CO(g) AG* The chemical equations above represent the main reactions that occur during the production of Fe(l) under certain conditions. The overall reaction couples reactions 1 and 2, resulting in a thermodynamically favorable process. Which of the following best explains whether or not a particle diagram could represent how the coupling of reaction 1 and reaction 2 results in AG <0 A particle diagram that represents the increase in the volume of gaseous product particles would be a good representation of how the coupling of reactions 1 and 2 results in a thermodynamically favorable process. A particle diagram that represents the decrease in the average kinetic energy of the particles would be a good representation of how the coupling of reactions 1 and 2 results in a thermodynamically favorable process. A particle diagram cannot represent how the changes in energy that take place as reaction 1 occurs are more than offset by the changes in energy taking place as reaction 2 occurs, resulting in a thermodynamically favorable overall reaction. A particle diagram cannot represent the changes in the amount of matter that take place as reaction 1 is coupled to reaction 2, resulting in a thermodynamically favorable overall reaction.
Reaction 1: FeO(s) + CO(g) → Fe(1) + CO2(g) AG" rzn > 0 Reaction 2: C(s) + CO2(g) → 2 CO(g) AG* rzn Overall reaction: FeO(s) + C(s) → Fe(1) + CO(g) AG* The chemical equations above represent the main reactions that occur during the production of Fe(l) under certain conditions. The overall reaction couples reactions 1 and 2, resulting in a thermodynamically favorable process. Which of the following best explains whether or not a particle diagram could represent how the coupling of reaction 1 and reaction 2 results in AG <0 A particle diagram that represents the increase in the volume of gaseous product particles would be a good representation of how the coupling of reactions 1 and 2 results in a thermodynamically favorable process. A particle diagram that represents the decrease in the average kinetic energy of the particles would be a good representation of how the coupling of reactions 1 and 2 results in a thermodynamically favorable process. A particle diagram cannot represent how the changes in energy that take place as reaction 1 occurs are more than offset by the changes in energy taking place as reaction 2 occurs, resulting in a thermodynamically favorable overall reaction. A particle diagram cannot represent the changes in the amount of matter that take place as reaction 1 is coupled to reaction 2, resulting in a thermodynamically favorable overall reaction.
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter18: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9RQ: What characterizes an electrolytic cell? What is an ampere? When the current applied to an...
Related questions
Question
100%
19
Transcribed Image Text:10
11
13
15
19
20
« <
Reaction 1:
FeO(s) + CO(g) → Fe(l) + CO2(g)
C(s) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g)
AG° > 0
Reaction 2:
AG.
rzn
Overall reaction:
FeO(s) + C(s) → Fe(1) + CO(g)
AG
ren <0
The chemical equations above represent the main reactions that occur during the production of Fe(l) under certain conditions. The overall reaction couples reactions 1 and 2, resulting in a
thermodynamically favorable process. Which of the following best explains whether or not a particle diagram could represent how the coupling of reaction 1 and reaction 2 results in AG"
<0
ran
A particle diagram that represents the increase in the volume of gaseous product particles would be a good representation of how the coupling of reactions 1 and 2 results in a
thermodynamically favorable process.
A particle diagram that represents the decrease in the average kinetic energy of the particles would be a good representation of how the coupling of reactions 1 and 2 results in a
thermodynamically favorable process.
A particle diagram cannot represent how the changes in energy that take place as reaction 1 occurs are more than offset by the changes in energy taking place as reaction 2
occurs, resulting in a thermodynamically favorable overall reaction.
A particle diagram cannot represent the changes in the amount of matter that take place as reaction 1 is coupled to reaction 2, resulting in a thermodynamically favorable overall
reaction.
US 6 9 O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning