Reagents Available g. CO, HCI, CUCI/AICI3 h. CH3CH2CH2COCI, AICI3 a. CH2=CHCH,CI, AICI3 b. CH2Br2, OH c. CH3CH,COCI, AICI3 d. H2, Pt e. NBS, CCI4 f. K* tBuO¯ i. BRCH2CH,Br, OH j. CH3CH2CI, AICI3 k. RCO3H CH=CHCH3 I. H3O* Using conditions from the table, show how you would synthesize this compound from catechol (1,2-benzenediol). Select reagents from the table in the order that you wish to use them, i.e. aced; do not include punctuation or spaces. If more than one route exists, choose the shorter one; in no case will a synthesis require more than 5 steps.
Reagents Available g. CO, HCI, CUCI/AICI3 h. CH3CH2CH2COCI, AICI3 a. CH2=CHCH,CI, AICI3 b. CH2Br2, OH c. CH3CH,COCI, AICI3 d. H2, Pt e. NBS, CCI4 f. K* tBuO¯ i. BRCH2CH,Br, OH j. CH3CH2CI, AICI3 k. RCO3H CH=CHCH3 I. H3O* Using conditions from the table, show how you would synthesize this compound from catechol (1,2-benzenediol). Select reagents from the table in the order that you wish to use them, i.e. aced; do not include punctuation or spaces. If more than one route exists, choose the shorter one; in no case will a synthesis require more than 5 steps.
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Andrei Straumanis
Chapter6: Alkanes & Alkenes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21CTQ
Related questions
Question
4

Transcribed Image Text:Reagents Available
a. CH2=CHCH,CI, AICI3
b. CH2Br2, OH
c. CH3CH,COCI, AICI3
d. H2, Pt
e. NBS, CCI4
f. K* tBuO
g. CO, HCI, CUCI/AICI3
h. CH3CH2CH2COCI, AICI3
i. BrCH2CH2Br, OH-
j. CH3CH2CI, AICI3
k. RCO3H
I. H3O*
CH=CHCH3
Using conditions from the table, show how you would synthesize this compound from catechol (1,2-benzenediol).
Select reagents from the table in the order that you wish to use them, i.e. aced; do not include punctuation or spaces.
If more than one route exists, choose the shorter one; in no case will a synthesis require more than 5 steps.
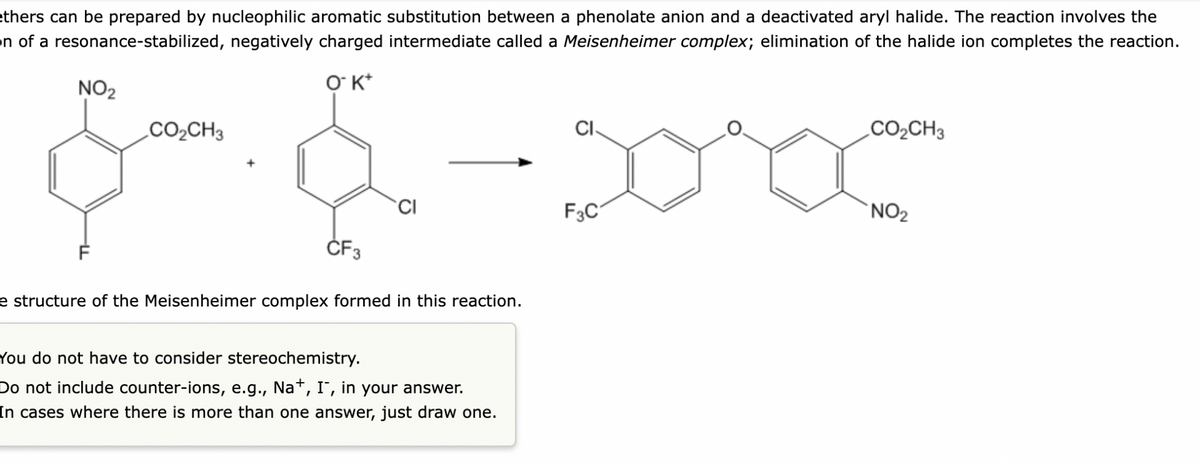
Transcribed Image Text:ethers can be prepared by nucleophilic aromatic substitution between a phenolate anion and a deactivated aryl halide. The reaction involves the
on of a resonance-stabilized, negatively charged intermediate called a Meisenheimer complex; elimination of the halide ion completes the reaction.
NO2
O K*
.CO2CH3
CI.
CO2CH3
CI
F3C
`NO2
ČF3
e structure of the Meisenheimer complex formed in this reaction.
You do not have to consider stereochemistry.
Do not include counter-ions, e.g., Na*, I', in your answer.
In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning