Required: Compute the following: a. The net realizable value of Beta-1 for the year ended November 30. b. The joint costs for the year ended November 30 to be allocated. c. The cost of Beta-2 sold for the year ended November 30. (Do not round int d. The value of the ending inventory for Beta-1. (Do not round intermediate c
Required: Compute the following: a. The net realizable value of Beta-1 for the year ended November 30. b. The joint costs for the year ended November 30 to be allocated. c. The cost of Beta-2 sold for the year ended November 30. (Do not round int d. The value of the ending inventory for Beta-1. (Do not round intermediate c
Principles of Cost Accounting
17th Edition
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Chapter6: Process Cost Accounting—additional Procedures; Accounting For Joint Products And By-products
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1MC: Clark Kent Inc. buys crypton for $.80 a gallon. At the end of processing in Dept. 1, crypton splits...
Related questions
Question
Davenport Company buys Alpha-11 for $6 a gallon. At the end of distilling in Department A, Alpha-11 splits off into three products: Beta-1, Beta-2, and Beta-3. Davenport sells Beta-1 at the split-off point, with no further processing; it processes Beta-2 and Beta-3 further before they can be sold. Beta-2 is fused in Department B, and Beta-3 is solidified in Department C. Following is a summary of costs and other related data for the year ended November 30.
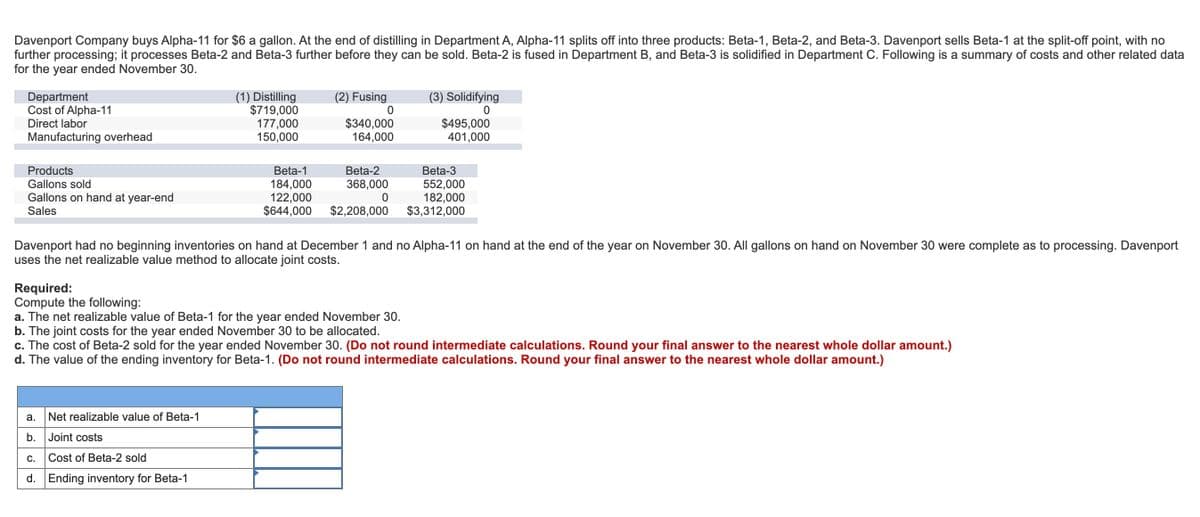
Transcribed Image Text:Davenport Company buys Alpha-11 for $6 a gallon. At the end of distilling in Department A, Alpha-11 splits off into three products: Beta-1, Beta-2, and Beta-3. Davenport sells Beta-1 at the split-off point, with no
further processing; it processes Beta-2 and Beta-3 further before they can be sold. Beta-2 is fused in Department B, and Beta-3 is solidified in Department C. Following is a summary of costs and other related data
for the year ended November 30.
(2) Fusing
Department
Cost of Alpha-11
Direct labor
(1) Distilling
$719,000
177,000
150,000
(3) Solidifying
$340,000
164,000
$495,000
401,000
Manufacturing overhead
Products
Beta-1
Beta-2
Beta-3
184,000
122,000
$644,000
552,000
182,000
$3,312,000
Gallons sold
368,000
Gallons on hand at year-end
Sales
$2,208,000
Davenport had no beginning inventories on hand at December 1 and no Alpha-11 on hand at the end of the year on November 30. All gallons on hand on November 30 were complete as to processing. Davenport
uses the net realizable value method to allocate joint costs.
Required:
Compute the following:
a. The net realizable value of Beta-1 for the year ended November 30.
b. The joint costs for the year ended November 30 to be allocated.
c. The cost of Beta-2 sold for the year ended November 30. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.)
d. The value of the ending inventory for Beta-1. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.)
а.
Net realizable value of Beta-1
b.
Joint costs
С.
Cost of Beta-2 sold
d. Ending inventory for Beta-1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning