show that the equilibrium constant fc 2 en defined in the earlier problems 1-3 e numerical values at 25° C that hav nine the concentration of Ca2+(aq) ane n solid CaCO3 and water that is expose -ic carbon dioxide, 0.000405 atm. pproximation with the values found fc
show that the equilibrium constant fc 2 en defined in the earlier problems 1-3 e numerical values at 25° C that hav nine the concentration of Ca2+(aq) ane n solid CaCO3 and water that is expose -ic carbon dioxide, 0.000405 atm. pproximation with the values found fc
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter20: Environmental Chemistry-earth's Environment, Energy, And Sustainability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 41PS
Related questions
Question
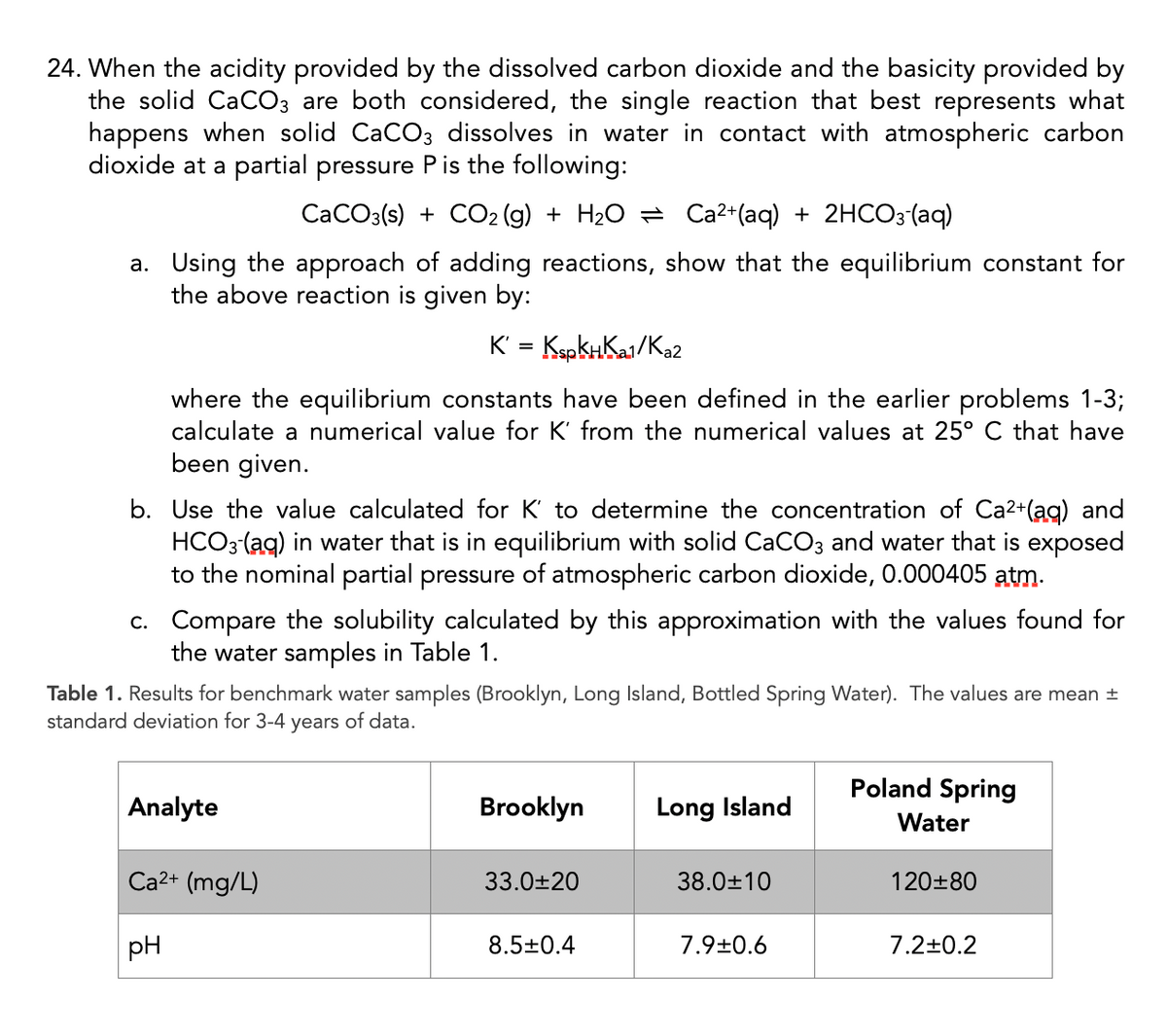
Transcribed Image Text:24. When the acidity provided by the dissolved carbon dioxide and the basicity provided by
the solid CaCO3 are both considered, the single reaction that best represents what
happens when solid CaCO3 dissolves in water in contact with atmospheric carbon
dioxide at a partial pressure Pis the following:
CaCO3(s) + CO2 (g) + H2O = Ca2+(aq) + 2HCO3 (aq)
a. Using the approach of adding reactions, show that the equilibrium constant for
the above reaction is given by:
K' = KspkHKai/Ka2
where the equilibrium constants have been defined in the earlier problems 1-3;
calculate a numerical value for K' from the numerical values at 25° C that have
been given.
b. Use the value calculated for K' to determine the concentration of Ca2+(ag) and
HCO3 (ag) in water that is in equilibrium with solid CaCO3 and water that is exposed
to the nominal partial pressure of atmospheric carbon dioxide, 0.000405 atm.
c. Compare the solubility calculated by this approximation with the values found for
the water samples in Table 1.
Table 1. Results for benchmark water samples (Brooklyn, Long Island, Bottled Spring Water). The values are mean ±
standard deviation for 3-4 years of data.
Poland Spring
Analyte
Brooklyn
Long Island
Water
Ca2+ (mg/L)
33.0±20
38.0±10
120±80
pH
8.5±0.4
7.9+0.6
7.2±0.2
Expert Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
