Step 4: Decarboxylation In the final step to synthesize dimedone, the carboxylic acid is heated in aqueous HCl to promote decarboxylation (Ch. 21.5, Klein). Draw the arrow pushing mechanism using the following prompts: e. First, protonate the carboxylate anion. f. Redraw the structure of the keto acid so that the OH group of the carboxylic acid is positioned near the ketone carbonyl. The hydrogen of the OH group will hydrogen bond to the carbonyl oxygen of the ketone. g. Push arrows in such a way that CO2 is lost from the molecule, and the enol form of dimedone is generated. This enol form tautomerizes to form the 1,3-diketone. Decarboxylation OH HCI (aq)
Step 4: Decarboxylation In the final step to synthesize dimedone, the carboxylic acid is heated in aqueous HCl to promote decarboxylation (Ch. 21.5, Klein). Draw the arrow pushing mechanism using the following prompts: e. First, protonate the carboxylate anion. f. Redraw the structure of the keto acid so that the OH group of the carboxylic acid is positioned near the ketone carbonyl. The hydrogen of the OH group will hydrogen bond to the carbonyl oxygen of the ketone. g. Push arrows in such a way that CO2 is lost from the molecule, and the enol form of dimedone is generated. This enol form tautomerizes to form the 1,3-diketone. Decarboxylation OH HCI (aq)
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Chapter24: Catalytic Carbon-carbon Bond Formation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 24.38P
Related questions
Question
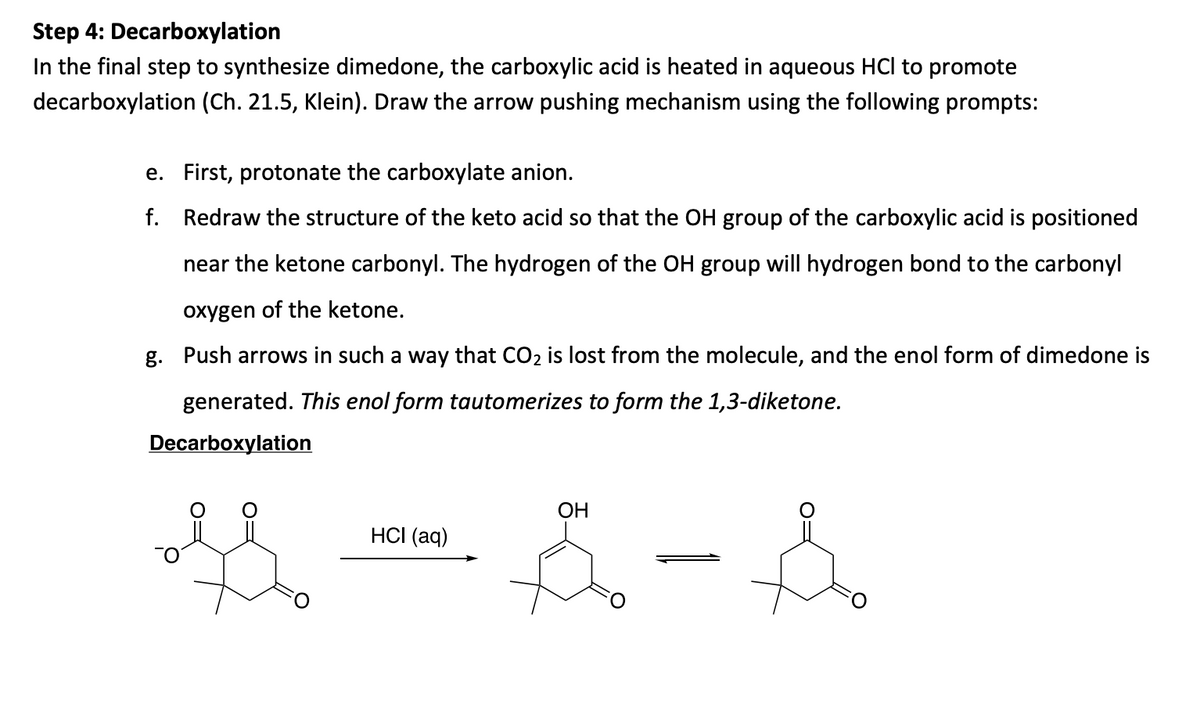
Transcribed Image Text:Step 4: Decarboxylation
In the final step to synthesize dimedone, the carboxylic acid is heated in aqueous HCl to promote
decarboxylation (Ch. 21.5, Klein). Draw the arrow pushing mechanism using the following prompts:
e. First, protonate the carboxylate anion.
f. Redraw the structure of the keto acid so that the OH group of the carboxylic acid is positioned
near the ketone carbonyl. The hydrogen of the OH group will hydrogen bond to the carbonyl
oxygen of the ketone.
g. Push arrows in such a way that CO2 is lost from the molecule, and the enol form of dimedone is
generated. This enol form tautomerizes to form the 1,3-diketone.
Decarboxylation
ОН
HСI (aq)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning