Suppose Kevin runs a small business that manufactures teddy bears. Assume that the market for teddy bears is a competitive market, and the market price is $20 per teddy bear. The following graph shows Kevin's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for teddy bears quantities zero through seven (inclusive) that Kevin produces. Calculate Kevin's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven teddy bears he produces, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost at each quantity. Kevin's profit is maximized when he produces ___ teddy bears. When he does this, the marginal cost of the last teddy bear he produces is ___ , which is (greater/less) than the price Kevin receives for each teddy bear he sells. The marginal cost of producing an additional teddy bear (that is, one more teddy bear than would maximize his profit) is ___, which is (greater/less) than the price Kevin receives for each teddy bear he sells. Therefore, Kevin's profit-maximizing quantity corresponds to the intersection of the (Total cost & Marginal Revenue/ Marginal cost & total revenue/ total cost & profit/ total revenue & profit/ marginal cost & marginal revenue/ total cost & total revenue) curves. Because Kevin is a price taker, this last condition can also be written as (Profit=TR-TC / Profit=MR-MC / P=MC / MC=TR / TC=TR ).
Suppose Kevin runs a small business that manufactures teddy bears. Assume that the market for teddy bears is a competitive market, and the market price is $20 per teddy bear. The following graph shows Kevin's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for teddy bears quantities zero through seven (inclusive) that Kevin produces. Calculate Kevin's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven teddy bears he produces, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost at each quantity. Kevin's profit is maximized when he produces ___ teddy bears. When he does this, the marginal cost of the last teddy bear he produces is ___ , which is (greater/less) than the price Kevin receives for each teddy bear he sells. The marginal cost of producing an additional teddy bear (that is, one more teddy bear than would maximize his profit) is ___, which is (greater/less) than the price Kevin receives for each teddy bear he sells. Therefore, Kevin's profit-maximizing quantity corresponds to the intersection of the (Total cost & Marginal Revenue/ Marginal cost & total revenue/ total cost & profit/ total revenue & profit/ marginal cost & marginal revenue/ total cost & total revenue) curves. Because Kevin is a price taker, this last condition can also be written as (Profit=TR-TC / Profit=MR-MC / P=MC / MC=TR / TC=TR ).
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter8: Perfect Competition
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 39P: The AAA Aquarium Co. sells aquariums for 20 each. Fixed costs of production are 20. The total...
Related questions
Question
Suppose Kevin runs a small business that manufactures teddy bears. Assume that the market for teddy bears is a competitive market, and the market price is $20 per teddy bear.
The following graph shows Kevin's total cost curve.
Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for teddy bears quantities zero through seven (inclusive) that Kevin produces.
Calculate Kevin's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven teddy bears he produces, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost at each quantity.
Kevin's profit is maximized when he produces ___ teddy bears. When he does this, the marginal cost of the last teddy bear he produces is ___ , which is (greater/less) than the price Kevin receives for each teddy bear he sells. The marginal cost of producing an additional teddy bear (that is, one more teddy bear than would maximize his profit) is ___, which is (greater/less) than the price Kevin receives for each teddy bear he sells. Therefore, Kevin's profit-maximizing quantity corresponds to the intersection of the (Total cost & Marginal Revenue/ Marginal cost & total revenue/ total cost & profit/ total revenue & profit/ marginal cost & marginal revenue/ total cost & total revenue) curves. Because Kevin is a price taker, this last condition can also be written as (Profit=TR-TC / Profit=MR-MC / P=MC / MC=TR / TC=TR ).
Transcribed Image Text:Calculate Kevin's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven teddy bears he produces, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue
points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost at each quantity.
(?
40
35
Marginal Revenue
30
25
Marginal Cost
20
15
10
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
QUANTITY (Teddy bears)
Kevin's profit is maximized when he produces
|teddy bears. When he does this, the marginal cost of the last teddy bear he produces is
, which is
than the price Kevin receives for each teddy bear he sells. The marginal cost of producing an additional teddy bear
(that is, one more teddy bear than would maximize his profit) is s
sells. Therefore, Kevin's profit-maximizing quantity corresponds to the intersection of the
which is
than the price Kevin receives for each teddy bear he
curves.
Because Kevin is a price taker, this last condition can also be written as
COSTS AND REVENUE (Dollars per teddy bear)
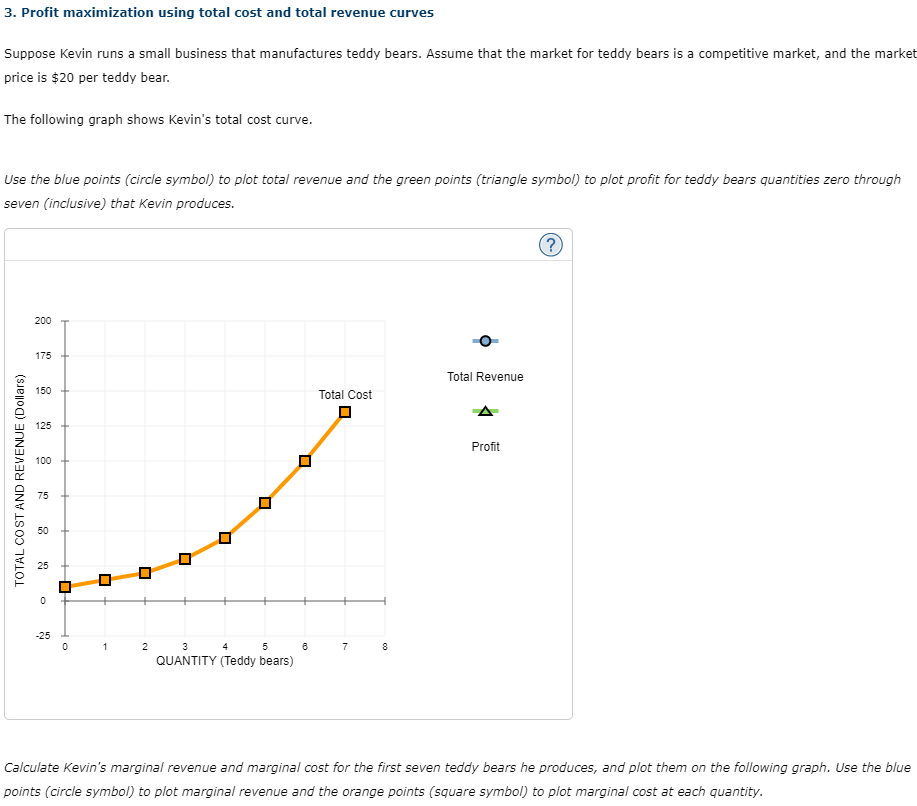
Transcribed Image Text:3. Profit maximization using total cost and total revenue curves
Suppose Kevin runs a small business that manufactures teddy bears. Assume that the market for teddy bears is a competitive market, and the market
price is $20 per teddy bear.
The following graph shows Kevin's total cost curve.
Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for teddy bears quantities zero through
seven (inclusive) that Kevin produces.
(?
200
175
Total Revenue
150
Total Cost
125
Profit
100
75
50
-25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
QUANTITY (Teddy bears)
Calculate Kevin's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven teddy bears he produces, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue
points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost at each quantity.
TOTAL COST AND REVENUE (Dollars)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning