tatements are TRUE?
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Chapter1: Biochemistry: An Evolving Science
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Multiple answers are accepted for this question
Transcribed Image Text:SAVE ALL
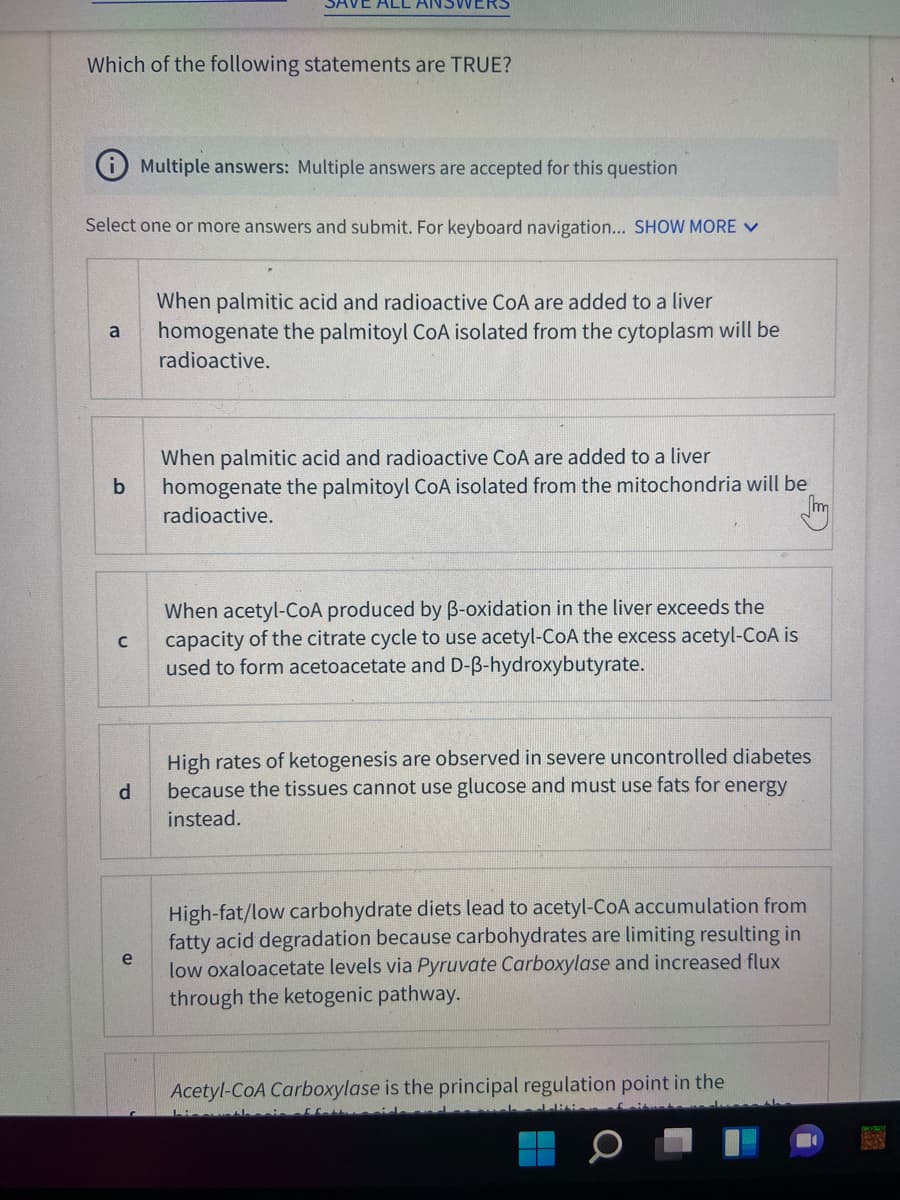
Which of the following statements are TRUE?
Multiple answers: Multiple answers are accepted for this question
Select one or more answers and submit. For keyboard navigation... SHOW MORE V
When palmitic acid and radioactive CoA are added to a liver
homogenate the palmitoyl CoA isolated from the cytoplasm will be
a
radioactive.
When palmitic acid and radioactive CoA are added to a liver
b
homogenate the palmitoyl CoA isolated from the mitochondria will be
radioactive.
When acetyl-COA produced by B-oxidation in the liver exceeds the
capacity of the citrate cycle to use acetyl-CoA the excess acetyl-CoA is
used to form acetoacetate and D-B-hydroxybutyrate.
High rates of ketogenesis are observed in severe uncontrolled diabetes
because the tissues cannot use glucose and must use fats for energy
instead.
High-fat/low carbohydrate diets lead to acetyl-CoA accumulation from
fatty acid degradation because carbohydrates are limiting resulting in
low oxaloacetate levels via Pyruvate Carboxylase and increased flux
through the ketogenic pathway.
e
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase is the principal regulation point in the
Transcribed Image Text:Please save all answers. Questions that you save can still be edited.
You have 1 UNSAVED ANSWER-
SAVE ALL ANSWERS
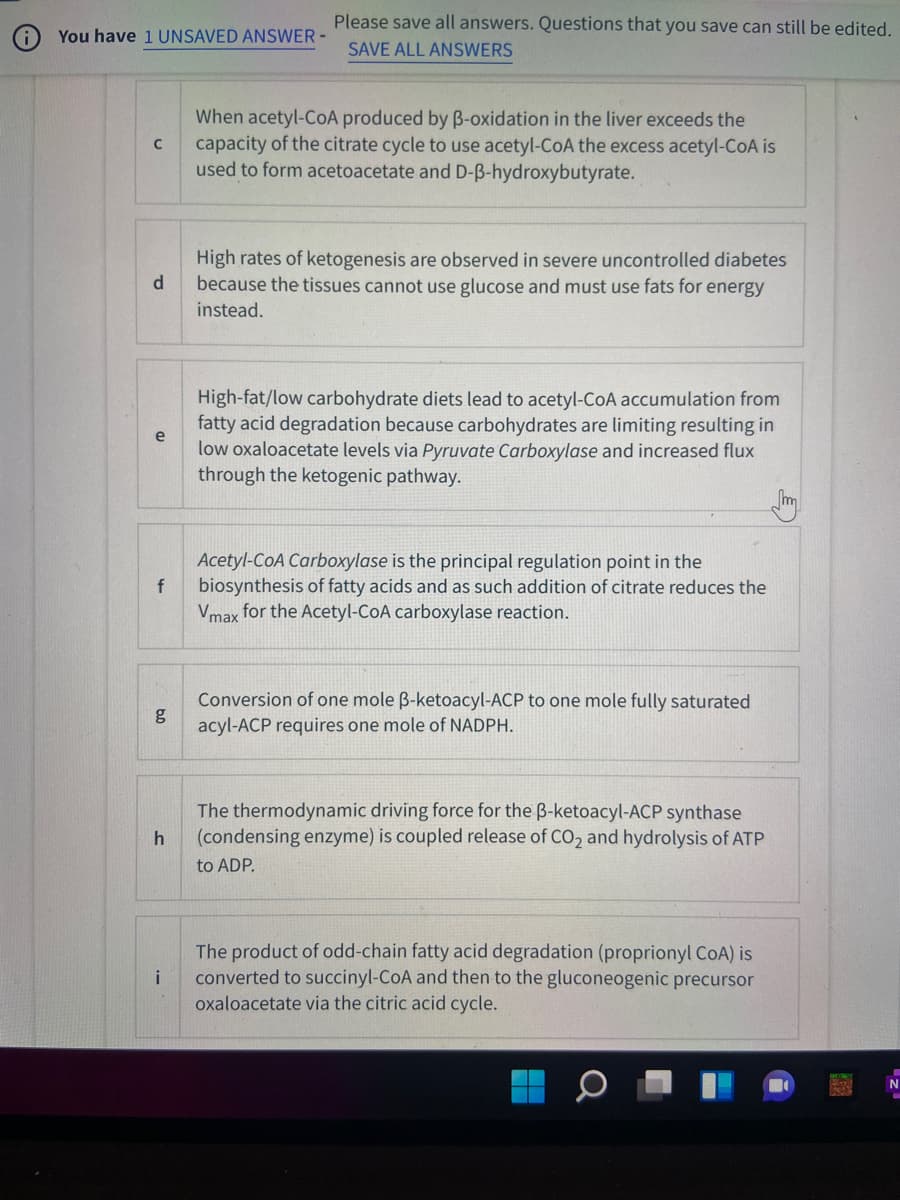
When acetyl-CoA produced by B-oxidation in the liver exceeds the
capacity of the citrate cycle to use acetyl-CoA the excess acetyl-COA is
used to form acetoacetate and D-B-hydroxybutyrate.
High rates of ketogenesis are observed in severe uncontrolled diabetes
because the tissues cannot use glucose and must use fats for energy
d
instead.
High-fat/low carbohydrate diets lead to acetyl-CoA accumulation from
fatty acid degradation because carbohydrates are limiting resulting in
low oxaloacetate levels via Pyruvate Carboxylase and increased flux
through the ketogenic pathway.
m
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase is the principal regulation point in the
biosynthesis of fatty acids and as such addition of citrate reduces the
Vmax for the Acetyl-CoA carboxylase reaction.
Conversion of one mole B-ketoacyl-ACP to one mole fully saturated
g
acyl-ACP requires one mole of NADPH.
The thermodynamic driving force for the B-ketoacyl-ACP synthase
(condensing enzyme) is coupled release of CO, and hydrolysis of ATP
h
to ADP.
The product of odd-chain fatty acid degradation (proprionyl CoA) is
converted to succinyl-CoA and then to the gluconeogenic precursor
i
oxaloacetate via the citric acid cycle.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological …
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9780134015187
Author:
John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:
PEARSON