The Favorskii reaction involves treatment of an a-haloketone with base to yield a ring-contracted product. The mechanism involves the following 5 steps: 1. Abstraction of a proton to form enolate anion 1; 2. Formation of a cyclopropanone intermediate 2 with expulsion of chloride ion; 3. Addition of hydroxide ion to form tetrahedral intermediate 3; 4. Collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate and breakage of the three-membered ring to form carbanion intermediate 4; 5. Proton transfer to form the rearranged carboxylic acid. For the following reaction,d kaaction e FrpdtA draw the structure of tetrahedral intermediate 3 in the window, CO2H base
The Favorskii reaction involves treatment of an a-haloketone with base to yield a ring-contracted product. The mechanism involves the following 5 steps: 1. Abstraction of a proton to form enolate anion 1; 2. Formation of a cyclopropanone intermediate 2 with expulsion of chloride ion; 3. Addition of hydroxide ion to form tetrahedral intermediate 3; 4. Collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate and breakage of the three-membered ring to form carbanion intermediate 4; 5. Proton transfer to form the rearranged carboxylic acid. For the following reaction,d kaaction e FrpdtA draw the structure of tetrahedral intermediate 3 in the window, CO2H base
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Andrei Straumanis
Chapter21: Nas: Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7E
Related questions
Question
Please answer the question
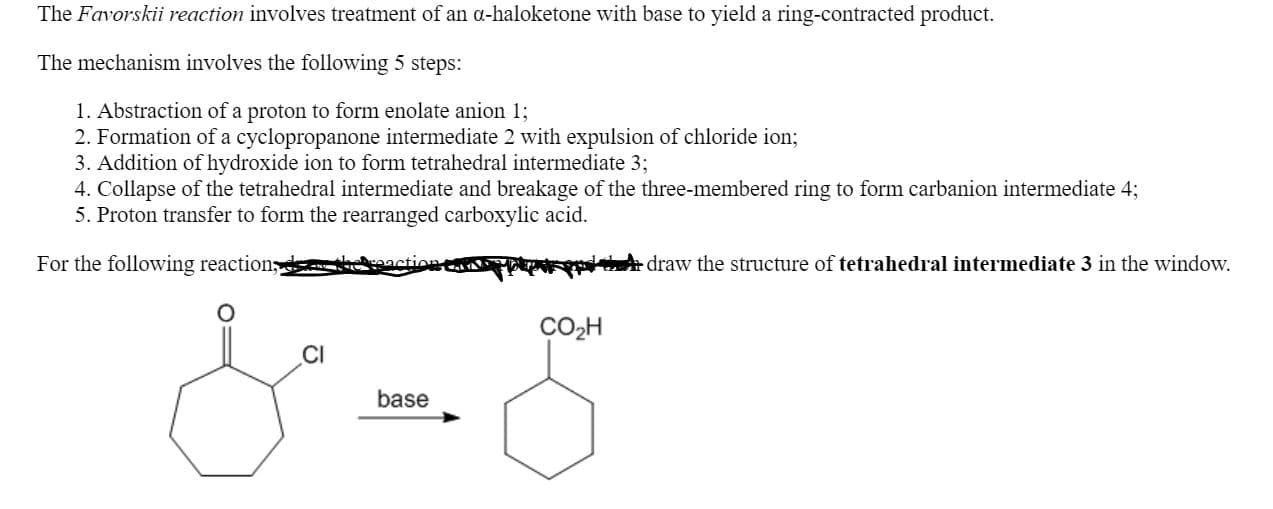
Transcribed Image Text:The Favorskii reaction involves treatment of an a-haloketone with base to yield a ring-contracted product.
The mechanism involves the following 5 steps:
1. Abstraction of a proton to form enolate anion 1;
2. Formation of a cyclopropanone intermediate 2 with expulsion of chloride ion;
3. Addition of hydroxide ion to form tetrahedral intermediate 3;
4. Collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate and breakage of the three-membered ring to form carbanion intermediate 4;
5. Proton transfer to form the rearranged carboxylic acid.
For the following reaction,d kaaction e
FrpdtA draw the structure of tetrahedral intermediate 3 in the window,
CO2H
base
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
