The floor system of a gymnasium consists of a 130- mm-thick concrete slab resting on four steel beams (A = 9;100 mm") that, in turn, are supported by two steel girders (A = 25;600 mm2), as shown in Fig. P2.7. Determine the dead loads acting on beam BF and girder AD.
The floor system of a gymnasium consists of a 130- mm-thick concrete slab resting on four steel beams (A = 9;100 mm") that, in turn, are supported by two steel girders (A = 25;600 mm2), as shown in Fig. P2.7. Determine the dead loads acting on beam BF and girder AD.
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10P
Related questions
Question
100%
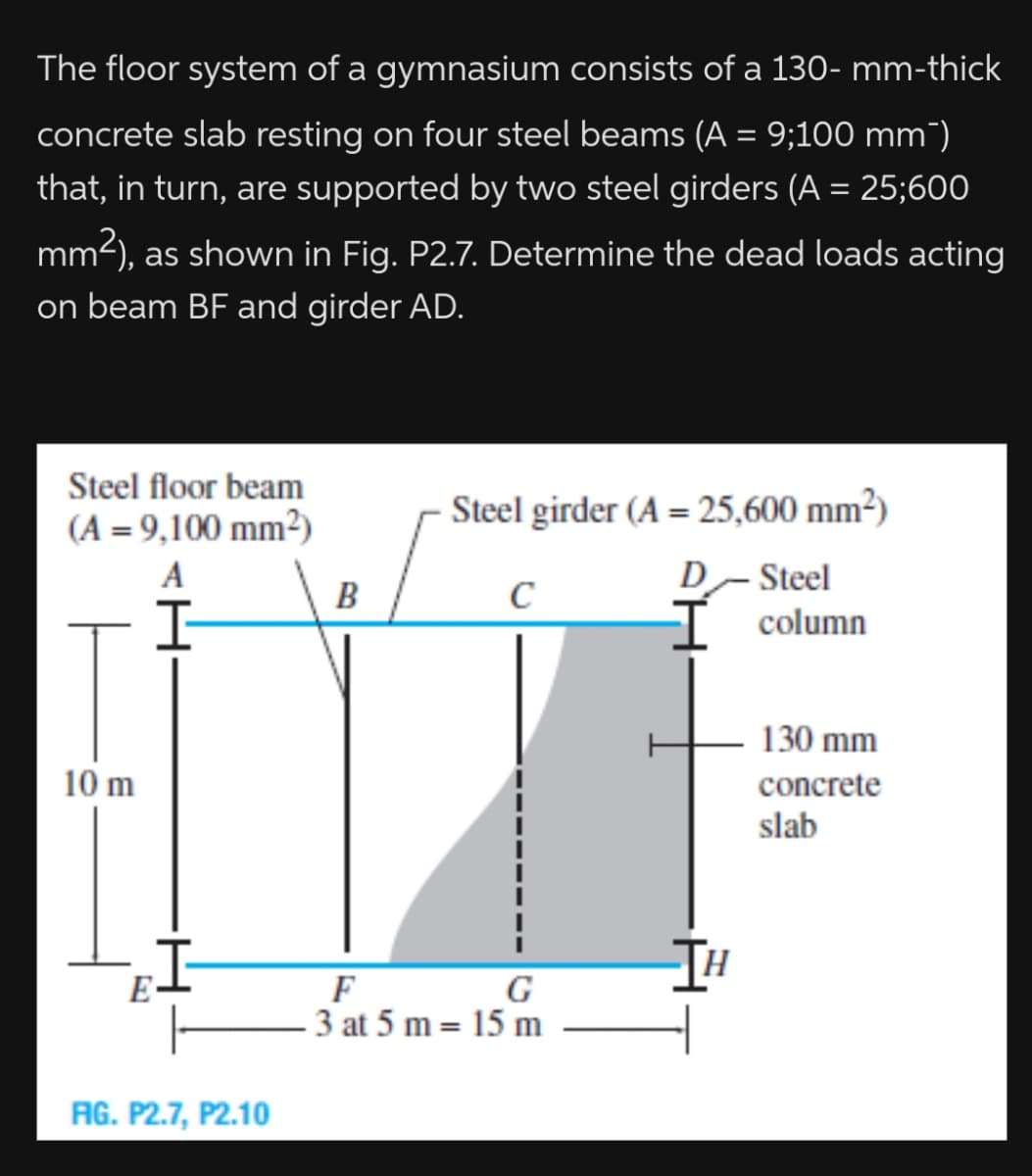
Transcribed Image Text:The floor system of a gymnasium consists of a 130- mm-thick
concrete slab resting on four steel beams (A = 9;100 mm")
that, in turn, are supported by two steel girders (A = 25;600
mm2), as shown in Fig. P2.7. Determine the dead loads acting
on beam BF and girder AD.
Steel floor beam
(A = 9,100 mm²)
Steel girder (A = 25,600 mm²)
D-Steel
T column
A
B
C
I-
130 mm
10 m
concrete
slab
F
3 at 5 m= 15 m
G
AG. P2.7, P2.10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 8 steps with 25 images

Recommended textbooks for you

