The following data represent the muzzle velocity (in feet per second) of rounds fired from a 155-mm gun. For each round, two measurements of the velocity were recorded using two different measuring devices, resulting in the following data. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Observation 1 2 3 4 5 6 794.6 792.5 794.2 794.4 790.8 793.8 B 800.1 789.8 794.4 793.5 796.0 793.4 (a) Why are these matched-pairs data? A. Two measurements (A and B) are taken on the same round. O B. All the measurements came from rounds fired from the same gun. O C. The measurements (A and B) are taken by the same instrument. O D. The same round was fired in every trial. (b) Is there a difference in the measurement of the muzzle velocity between device A and device B at the a = 0.01 level of significance? Note: A normal probability plot and boxplot of the data indicate that the differences are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Let d, = A, - B,. ldentify the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: Ha = 0 H: Ha * 0 Determine the test statistic for this hypothesis test. to = -0.83 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Find the P-value. P-value = (Round three decimal places as needed.) %3D
The following data represent the muzzle velocity (in feet per second) of rounds fired from a 155-mm gun. For each round, two measurements of the velocity were recorded using two different measuring devices, resulting in the following data. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Observation 1 2 3 4 5 6 794.6 792.5 794.2 794.4 790.8 793.8 B 800.1 789.8 794.4 793.5 796.0 793.4 (a) Why are these matched-pairs data? A. Two measurements (A and B) are taken on the same round. O B. All the measurements came from rounds fired from the same gun. O C. The measurements (A and B) are taken by the same instrument. O D. The same round was fired in every trial. (b) Is there a difference in the measurement of the muzzle velocity between device A and device B at the a = 0.01 level of significance? Note: A normal probability plot and boxplot of the data indicate that the differences are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Let d, = A, - B,. ldentify the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: Ha = 0 H: Ha * 0 Determine the test statistic for this hypothesis test. to = -0.83 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Find the P-value. P-value = (Round three decimal places as needed.) %3D
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
(REV)00th Edition
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Chapter2: Working With Real Numbers
Section2.3: Rules For Addition
Problem 14P
Related questions
Question
- What is the P Value
- Reject H0?
- Construct a 99% confidence interval about the population mean difference
- Draw a boxplot of the differenced data. Does this visual evidence support the results obtained in part (b)?
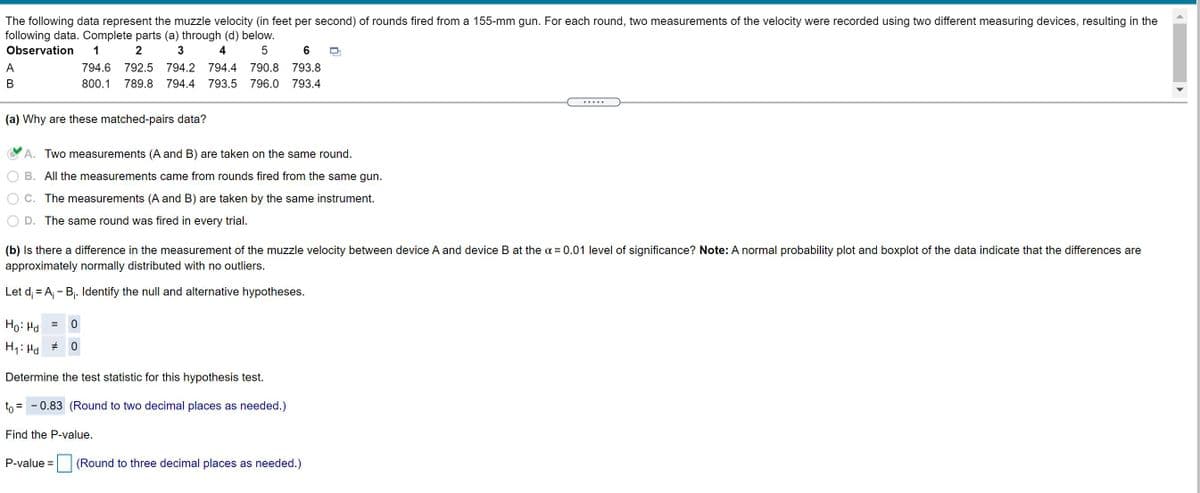
Transcribed Image Text:The following data represent the muzzle velocity (in feet per second) of rounds fired from a 155-mm gun. For each round, two measurements of the velocity were recorded using two different measuring devices, resulting in the
following data. Complete parts (a) through (d) below.
Observation
2
3
4
6
A
794.6
792.5
794.2
794.4
790.8
793.8
В
800.1
789.8
794.4
793.5
796.0
793.4
(a) Why are these matched-pairs data?
A. Two measurements (A and B) are taken on the same round.
B. All the measurements came from rounds fired from the same gun.
C. The measurements (A and B) are taken by the same instrument.
D. The same round was fired in every trial.
(b) Is there a difference in the measurement of the muzzle velocity between device A and device B at the o = 0.01 level of significance? Note: A normal probability plot and boxplot of the data indicate that the differences are
approximately normally distributed with no outliers.
Let d; = A; - Bj. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses.
Ho: Hd
H1: Hd
Determine the test statistic for this hypothesis test.
to = - 0.83 (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Find the P-value.
P-value =
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,