The following joint distribution that has been constructed using data from the 1995 National Health Survey conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics. This is a large, nationally represented survey of Australians. The data in the Table refer to whether an individual has used any medications in the last 2 weeks prior to interview and their self-assessed health status (SAHS). For SAHS individuals are asked to rate their current health on a five-level scale ranging from poor to excellent. Table : Joint frequency distribution of self assessed health and use of medications for Australians in 1995 Self-assessed health Excellent Very good Good Fair Poor Totals Use medication 10.7 20.7 20.0 9.7 3.5 64.6 No medication 9.4 13.7 9.7 2.2 0.4 35.4 Totals 20.1 34.4 29.7 11.9 3.9 100.0 Using the distribution as an estimate of the population distribution, which of the following is not correct? Select one: O a. The probability that a randomly selected Australian used medication in the last two weeks is 0.646 O b. The probability that a randomly selected Australian is in very good health and took no medication in the last two weeks is 0.137 O c. Conditional on being in poor health, the probability that a randomly selected Australian used medications in the last two weeks is 0.035. O d. The majority of Australians are either in excellent or very good health.
The following joint distribution that has been constructed using data from the 1995 National Health Survey conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics. This is a large, nationally represented survey of Australians. The data in the Table refer to whether an individual has used any medications in the last 2 weeks prior to interview and their self-assessed health status (SAHS). For SAHS individuals are asked to rate their current health on a five-level scale ranging from poor to excellent. Table : Joint frequency distribution of self assessed health and use of medications for Australians in 1995 Self-assessed health Excellent Very good Good Fair Poor Totals Use medication 10.7 20.7 20.0 9.7 3.5 64.6 No medication 9.4 13.7 9.7 2.2 0.4 35.4 Totals 20.1 34.4 29.7 11.9 3.9 100.0 Using the distribution as an estimate of the population distribution, which of the following is not correct? Select one: O a. The probability that a randomly selected Australian used medication in the last two weeks is 0.646 O b. The probability that a randomly selected Australian is in very good health and took no medication in the last two weeks is 0.137 O c. Conditional on being in poor health, the probability that a randomly selected Australian used medications in the last two weeks is 0.035. O d. The majority of Australians are either in excellent or very good health.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
Hello, I'm struggling with these 2 questions.
Any detailed help would be greatly appreciated!
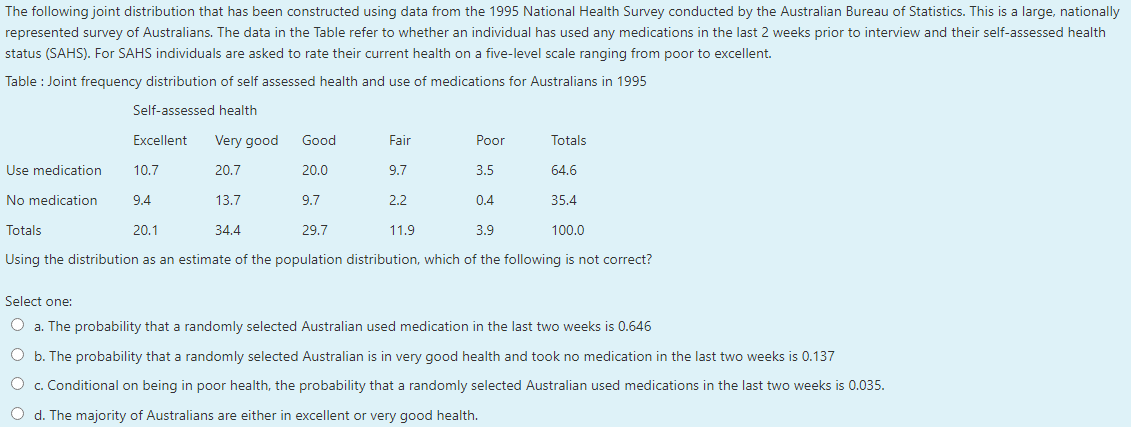
Transcribed Image Text:The following joint distribution that has been constructed using data from the 1995 National Health Survey conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics. This is a large, nationally
represented survey of Australians. The data in the Table refer to whether an individual has used any medications in the last 2 weeks prior to interview and their self-assessed health
status (SAHS). For SAHS individuals are asked to rate their current health on a five-level scale ranging from poor to excellent.
Table : Joint frequency distribution of self assessed health and use of medications for Australians in 1995
Self-assessed health
Excellent
Very good
Good
Fair
Poor
Totals
Use medication
10.7
20.7
20.0
9.7
3.5
64.6
No medication
9.4
13.7
9.7
2.2
0.4
35.4
Totals
20.1
34.4
29.7
11.9
3.9
100.0
Using the distribution as an estimate of the population distribution, which of the following is not correct?
Select one:
O a. The probability that a randomly selected Australian used medication in the last two weeks is 0.646
O b. The probability that a randomly selected Australian is in very good health and took no medication in the last two weeks is 0.137
O c. Conditional on being in poor health, the probability that a randomly selected Australian used medications in the last two weeks is 0.035.
O d. The majority of Australians are either in excellent or very good health.

Transcribed Image Text:The unemployment rate of persons with a disability is typically higher than for those with no disability. Recent statistics report that the unemployment rate amongst those with a
disability is 14.5%. An advocacy group in Sydney selects a random sample of 250 people with a disability. What is the probability that no more than 30 people in this sample are
unemployed? Use the sampling distribution of the sample proportion.
Select one:
O a. 0.0018
O b. 0.1314
O c.0.9500
O d. 0.8686
e. 0.6573
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill