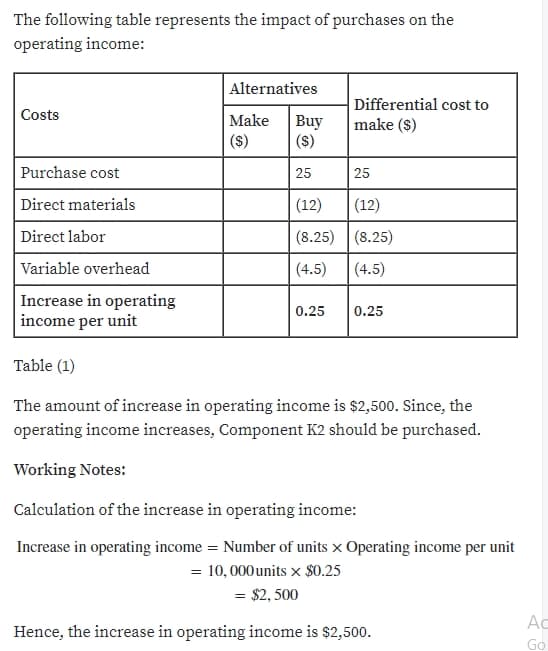
The following table represents the impact of purchases on the operating income: Alternatives Differential cost to make (S) Costs Make Buy (S) (S) Purchase cost 25 25 Direct materials (12) (12) Direct labor (8.25) (8.25) Variable overhead (4.5) |(4.5) Increase in operating income per unit 0.25 0.25 Table (1) The amount of increase in operating income is $2,500. Since, the operating income increases, Component K2 should be purchased. Working Notes: Calculation of the increase in operating income: Increase in operating income = Number of units x Operating income per unit = 10,000 units x $0.25 = $2, 500 A Hence, the increase in operating income is $2,500. Go
Process Costing
Process costing is a sort of operation costing which is employed to determine the value of a product at each process or stage of producing process, applicable where goods produced from a series of continuous operations or procedure.
Job Costing
Job costing is adhesive costs of each and every job involved in the production processes. It is an accounting measure. It is a method which determines the cost of specific jobs, which are performed according to the consumer’s specifications. Job costing is possible only in businesses where the production is done as per the customer’s requirement. For example, some customers order to manufacture furniture as per their needs.
ABC Costing
Cost Accounting is a form of managerial accounting that helps the company in assessing the total variable cost so as to compute the cost of production. Cost accounting is generally used by the management so as to ensure better decision-making. In comparison to financial accounting, cost accounting has to follow a set standard ad can be used flexibly by the management as per their needs. The types of Cost Accounting include – Lean Accounting, Standard Costing, Marginal Costing and Activity Based Costing.
in exercise 8-39 number 1 the fixed overhead not included, why?

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









