The management of Brinkley Corporation is interested in using simulation to estimate the profit per unit for a new product. The selling price for the product will be $45 per unit. Probability distributions for the purchase cost, the labor cost, and the transportation cost are estimated as follows: Procurement Cost($) 10 11 12 Probability 0.25 0.45 0.30 Labor Cost ($) 20 22 24 25 Probability 0.10 0.25 0.35 0.30 Transportation Cost ($) 3 ✔/unit ✓ /unit ✓ /unit 5 (a) Compute profit per unit for the base-case, worst-case, and best-case scenarios. Base Case using most likely costs Profit $7 Worst Case Profit $3 Best Case Profit = $12 Probability 0.75 0.25 (b) Construct a simulation model to estimate the mean profit per unit. (Use at least 1,000 trials.) $ 7.50 X (c) Why is the simulation approach to risk analysis preferable to generating a variety of what-if scenarios? Simulation will provide ---Select--- of the profit per unit values which can then be used to find -Select--- (d) Management believes the project may not be sustainable if the profit per unit is less than $5. Use simulation to est less than $5. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
The management of Brinkley Corporation is interested in using simulation to estimate the profit per unit for a new product. The selling price for the product will be $45 per unit. Probability distributions for the purchase cost, the labor cost, and the transportation cost are estimated as follows: Procurement Cost($) 10 11 12 Probability 0.25 0.45 0.30 Labor Cost ($) 20 22 24 25 Probability 0.10 0.25 0.35 0.30 Transportation Cost ($) 3 ✔/unit ✓ /unit ✓ /unit 5 (a) Compute profit per unit for the base-case, worst-case, and best-case scenarios. Base Case using most likely costs Profit $7 Worst Case Profit $3 Best Case Profit = $12 Probability 0.75 0.25 (b) Construct a simulation model to estimate the mean profit per unit. (Use at least 1,000 trials.) $ 7.50 X (c) Why is the simulation approach to risk analysis preferable to generating a variety of what-if scenarios? Simulation will provide ---Select--- of the profit per unit values which can then be used to find -Select--- (d) Management believes the project may not be sustainable if the profit per unit is less than $5. Use simulation to est less than $5. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Solutions for parts b, c, and d please
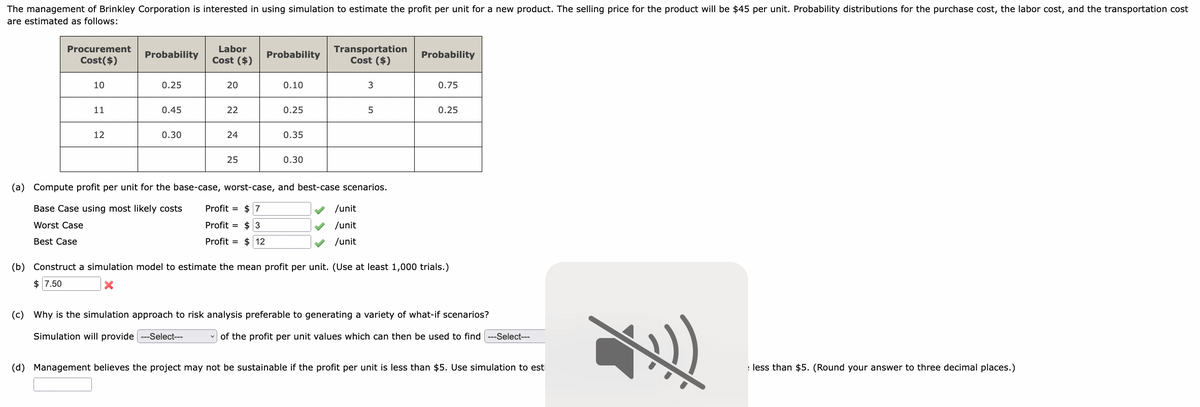
Transcribed Image Text:The management of Brinkley Corporation is interested in using simulation to estimate the profit per unit for a new product. The selling price for the product will be $45 per unit. Probability distributions for the purchase cost, the labor cost, and the transportation cost
are estimated as follows:
Procurement
Cost($)
10
11
12
Probability
0.25
0.45
0.30
Labor
Cost ($)
20
22
24
25
Probability
0.10
0.25
0.35
0.30
Transportation
Cost ($)
3
/unit
/unit
/unit
5
(a) Compute profit per unit for the base-case, worst-case, and best-case scenarios.
Base Case using most likely costs
Profit = $ 7
Worst Case
Profit $ 3
Profit = $ 12
Best Case
Probability
0.75
0.25
(b) Construct a simulation model to estimate the mean profit per unit. (Use at least 1,000 trials.)
$ 7.50
X
(c) Why is the simulation approach to risk analysis preferable to generating a variety of what-if scenarios?
Simulation will provide ---Select---
of the profit per unit values which can then be used to find --Select---
(d) Management believes the project may not be sustainable if the profit per unit is less than $5. Use simulation to est
*)
less than $5. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 7 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman