This DNA molecule has eight copies of a CAG repeat. GYC The two strands separate. GOGICGCGOGICGIGICGE and replicate. GICGTCGICGTC GICGTCGTCGTC CAGCAG CACCAG CAGCAGCAG GICGIC CAGCAG GICGTEGICGTCGCGTA CAG In the course of replication, a hairpin forms on the newly synthesized strand,. র 9 10 11 12 13 3 causing part of the template strand to be repicated twice and increasing the number of repeats on the newly synthesized strand. The two strands of the new DNA molecule separate,. ে AGCAG 12 13 2 and the strand with extra CAG copies serves as a template for replication 9 10 11 12 13 7 8,9 10 11 12 13 B The resulting DNA molecule contairs five additional copies of the CAG repeat TABLE 18.1 Examples of human genetic diseases caused by expanding nucleotide repeats Number of Copies of Repeat Disease Repeated Sequence Normal Disease Range Range Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy Fragile-X syndrome Jacobsen syndrome Spinocerebellar ataxia (several types) Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia Myotonic dystrophy Huntington disease Friedreich ataxia Dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy Myoclonus epilepsy of the Unverricht- CCCCGCCCCGCG 2-3 Lundborg type Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis CAG 11-33 40-62 CGG 6-54 50-1500 CGG 11 100-1000 CAG 4-44 21-130 CAG 7-19 37-220 CTG 5-37 44-3000 CAG 9-37 37-121 GAA 6-29 200-900 CAG 7-25 49-75 12-13 GGGGCC 2-23 700-1600
This DNA molecule has eight copies of a CAG repeat. GYC The two strands separate. GOGICGCGOGICGIGICGE and replicate. GICGTCGICGTC GICGTCGTCGTC CAGCAG CACCAG CAGCAGCAG GICGIC CAGCAG GICGTEGICGTCGCGTA CAG In the course of replication, a hairpin forms on the newly synthesized strand,. র 9 10 11 12 13 3 causing part of the template strand to be repicated twice and increasing the number of repeats on the newly synthesized strand. The two strands of the new DNA molecule separate,. ে AGCAG 12 13 2 and the strand with extra CAG copies serves as a template for replication 9 10 11 12 13 7 8,9 10 11 12 13 B The resulting DNA molecule contairs five additional copies of the CAG repeat TABLE 18.1 Examples of human genetic diseases caused by expanding nucleotide repeats Number of Copies of Repeat Disease Repeated Sequence Normal Disease Range Range Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy Fragile-X syndrome Jacobsen syndrome Spinocerebellar ataxia (several types) Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia Myotonic dystrophy Huntington disease Friedreich ataxia Dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy Myoclonus epilepsy of the Unverricht- CCCCGCCCCGCG 2-3 Lundborg type Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis CAG 11-33 40-62 CGG 6-54 50-1500 CGG 11 100-1000 CAG 4-44 21-130 CAG 7-19 37-220 CTG 5-37 44-3000 CAG 9-37 37-121 GAA 6-29 200-900 CAG 7-25 49-75 12-13 GGGGCC 2-23 700-1600
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter28: Dna Metabolism: Replication, Recombination, And Repair
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 22P
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Draw a hairpin structure like that shown in Figure 18.5 for the repeated sequence found in fragile-X syndrome (see Table 18.1).
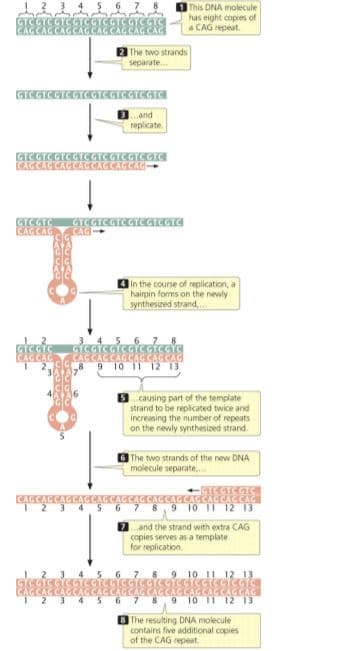
Transcribed Image Text:This DNA molecule
has eight copies of
a CAG repeat.
GYC
The two strands
separate.
GOGICGCGOGICGIGICGE
and
replicate.
GICGTCGICGTC GICGTCGTCGTC
CAGCAG CACCAG CAGCAGCAG
GICGIC
CAGCAG
GICGTEGICGTCGCGTA
CAG
In the course of replication, a
hairpin forms on the newly
synthesized strand,.
র
9 10 11 12 13
3 causing part of the template
strand to be repicated twice and
increasing the number of repeats
on the newly synthesized strand.
The two strands of the new DNA
molecule separate,.
ে
AGCAG
12 13
2 and the strand with extra CAG
copies serves as a template
for replication
9 10 11 12 13
7 8,9 10 11 12 13
B The resulting DNA molecule
contairs five additional copies
of the CAG repeat
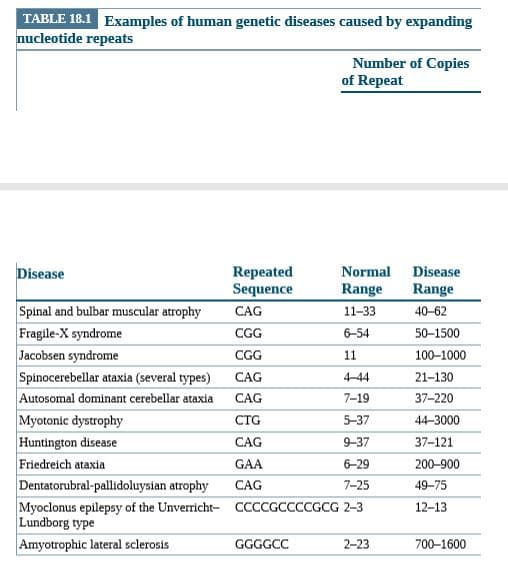
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 18.1 Examples of human genetic diseases caused by expanding
nucleotide repeats
Number of Copies
of Repeat
Disease
Repeated
Sequence
Normal
Disease
Range
Range
Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy
Fragile-X syndrome
Jacobsen syndrome
Spinocerebellar ataxia (several types)
Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia
Myotonic dystrophy
Huntington disease
Friedreich ataxia
Dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy
Myoclonus epilepsy of the Unverricht- CCCCGCCCCGCG 2-3
Lundborg type
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
CAG
11-33
40-62
CGG
6-54
50-1500
CGG
11
100-1000
CAG
4-44
21-130
CAG
7-19
37-220
CTG
5-37
44-3000
CAG
9-37
37-121
GAA
6-29
200-900
CAG
7-25
49-75
12-13
GGGGCC
2-23
700-1600
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
