Using the mass of sodium bicarbonate used for runs 1 and 2, calculate the theoretical yield of solid products 2) from each of the possible decomposition reactions, then calculate the percent yield by dividing your actual yield by the theoretical yield you calculate for each reaction. DATA Record all masses to the maximum number of Run 1 Run 2 sig figs 200°C 400°C 1. Mass of beaker 27.986 32.267 81.061 2. Mass of beaker + NaHCO3 85.457 3. Initial mass of NaHCO3 4.476 4.292 Mass of beaker plus products after heating. 4. 84.380 30.743 5. Mass of product (actual yield)
Using the mass of sodium bicarbonate used for runs 1 and 2, calculate the theoretical yield of solid products 2) from each of the possible decomposition reactions, then calculate the percent yield by dividing your actual yield by the theoretical yield you calculate for each reaction. DATA Record all masses to the maximum number of Run 1 Run 2 sig figs 200°C 400°C 1. Mass of beaker 27.986 32.267 81.061 2. Mass of beaker + NaHCO3 85.457 3. Initial mass of NaHCO3 4.476 4.292 Mass of beaker plus products after heating. 4. 84.380 30.743 5. Mass of product (actual yield)
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter9: Chemical Quantities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 100CP: he production capacity for acrylonitrile (C3H3N)in the United States is over 2 billion pounds per...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Reaction C
_NaHCO3(s)
->
NazCO3(s) +
CO2(g) +
_H20(g)
Run 1: Initial grams of NaHCO3
Theoretical yield (grams) of NażCO3:.
Percent yield (Run 1) =
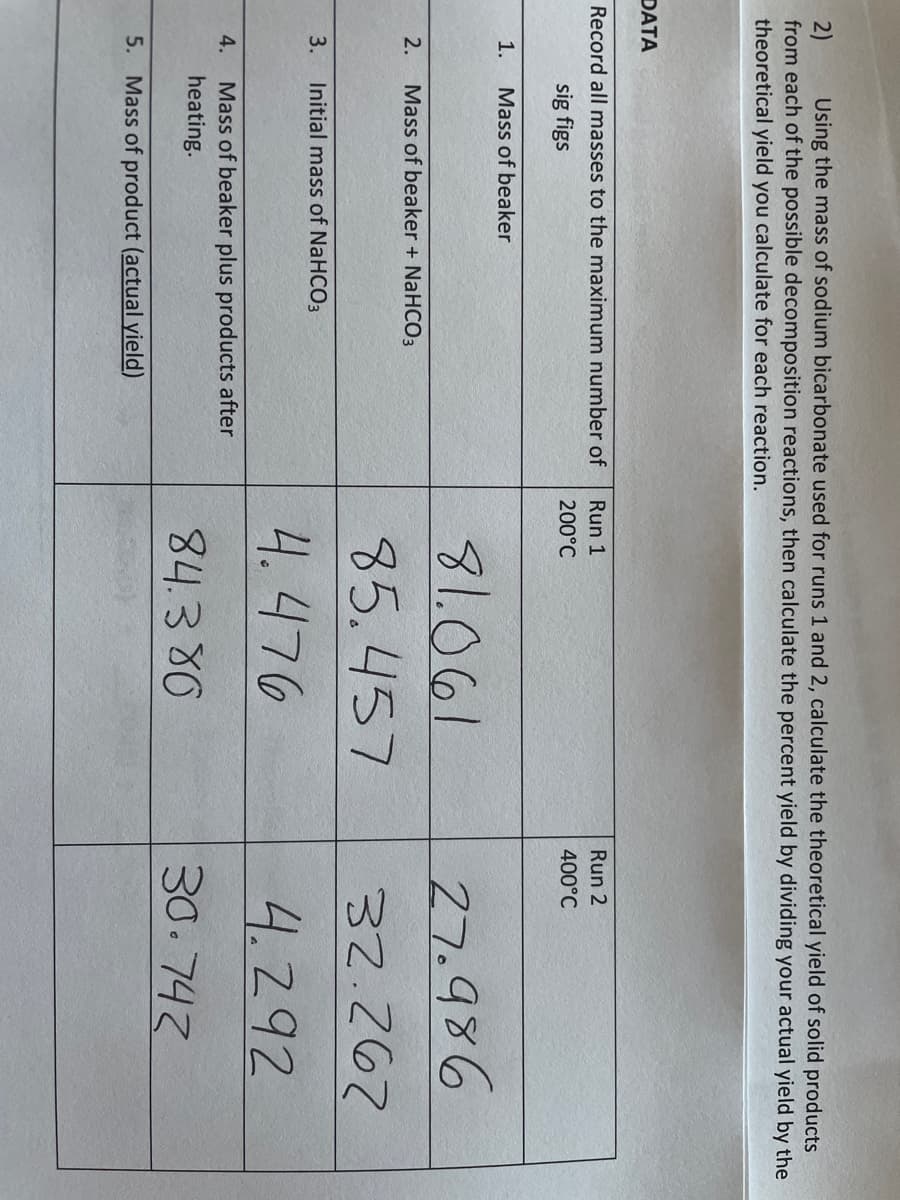
Transcribed Image Text:Using the mass of sodium bicarbonate used for runs 1 and 2, calculate the theoretical yield of solid products
2)
from each of the possible decomposition reactions, then calculate the percent yield by dividing your actual yield by the
theoretical yield you calculate for each reaction.
DATA
Record all masses to the maximum number of
Run 1
Run 2
sig figs
200°C
400°C
1.
Mass of beaker
27.986
32.267
81.061
2.
Mass of beaker + NaHCO3
85.457
3.
Initial mass of NaHCO3
4.476
4.292
Mass of beaker plus products after
heating.
4.
84.380
30.743
5. Mass of product (actual yield)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618562763
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin College Div

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning