Venture capital (VC) firms are pools of private capital that typically invest in small, fast-growing companies that can't raise funds through other means. In exchange for this financing, VCs receive a share of a company's equity, and the founders of the firm typically stay on and continue to manage the company. The incentive conflict is between the managers, who are the and venture capitalists, who are the vc investments have two typical components: (1) managers maintain some ownership in the company and often eam additional equity if the company performs well: (2) vcs demand seats on the company's board. Management ownership serves to the alignment of the incentives of managers with the incentives of owners
Venture capital (VC) firms are pools of private capital that typically invest in small, fast-growing companies that can't raise funds through other means. In exchange for this financing, VCs receive a share of a company's equity, and the founders of the firm typically stay on and continue to manage the company. The incentive conflict is between the managers, who are the and venture capitalists, who are the vc investments have two typical components: (1) managers maintain some ownership in the company and often eam additional equity if the company performs well: (2) vcs demand seats on the company's board. Management ownership serves to the alignment of the incentives of managers with the incentives of owners
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter17: Making Decisions With Uncertainty
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17.3IP
Related questions
Question
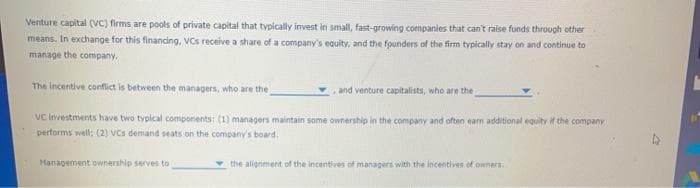
Transcribed Image Text:Venture capital (vC) firms are pools of private capital that typically invest in small, fast-growing companies that can't raise funds through other
means. In exchange for this financing, VCs receive a share of a company's equity, and the founders of the firm typically stay on and continue to
manage the company,
The Incentive conflict is between the managers, who are the
, and venture capitalists, who are the
vc investments have two typical components: (1) managers maintain some ownership in the company and often earn additional equity if the company
performs well: (2) vCs demand seats on the company's board.
Management ownership serves to
the alignment of the incentives of managers with the incentives of owners
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
