Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter5: Principles Of Chemical Reactivity: Energy And Chemical Reactions
Section5.8: Product- Or Reactant-favored Reactions And Thermodynamics
Problem 1.2ACP
Related questions
Question
The highlighted one is the question :)

Transcribed Image Text:What is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction used to calculate AH; of SrCO3 (s)?
If fractional coefficients are required, enter them as a fraction (i.e. 1/3). Indicate the physical states using the abbreviation (s), (1), or (g) for solid,
liquid, or gas, respectively without indicating allotropes. Use (aq) for aqueous solution.
Express your answer as a chemical equation.
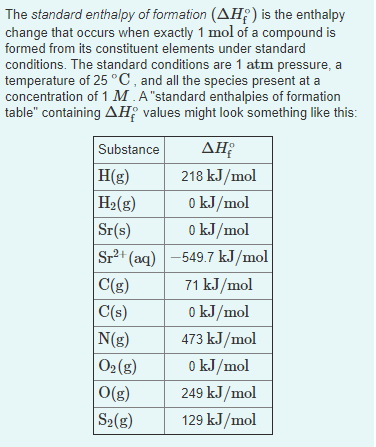
Transcribed Image Text:The standard enthalpy of formation (AH;) is the enthalpy
change that occurs when exactly 1 mol of a compound is
formed from its constituent elements under standard
conditions. The standard conditions are 1 atm pressure, a
temperature of 25 °C , and all the species present at a
concentration of 1 M .A"standard enthalpies of formation
table" containing AH; values might look something like this:
AH
Substance
H(g)
H2(g)
218 kJ/mol
o kJ/mol
0 kJ/mol
Sr+ (aq) -549.7 kJ/mol
Sr(s)
71 kJ/mol
0 kJ/mol
C(g)
C(s)
N(g)
473 kJ/mol
02(g)
0 kJ/mol
O(g)
249 kJ/mol
S2(g)
129 kJ/mol
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning