Why are hydrogen bonds considered a special class of dipole-dipole interactions? Choose one or more: A. These interactions only occur if hydrogen is bonded to nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine. B. They are observed with all molecules that contain a carbon double bonded to an oxygen. C. These interactions are with polar molecules but are stronger than dipole-dipole interactions. D. They are observed with all molecules that contain hydrogen. E. These interactions are between polar molecules but are weaker than normal dipole-dipole interactions. OF. These interactions account for the higher melting and boiling points observed for certain molecules such as water. G. These interactions only occur with organic molecules. 00000
Why are hydrogen bonds considered a special class of dipole-dipole interactions? Choose one or more: A. These interactions only occur if hydrogen is bonded to nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine. B. They are observed with all molecules that contain a carbon double bonded to an oxygen. C. These interactions are with polar molecules but are stronger than dipole-dipole interactions. D. They are observed with all molecules that contain hydrogen. E. These interactions are between polar molecules but are weaker than normal dipole-dipole interactions. OF. These interactions account for the higher melting and boiling points observed for certain molecules such as water. G. These interactions only occur with organic molecules. 00000
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Andrei Straumanis
Chapter4: Polar Bonds, Polar Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13CTQ
Related questions
Question
Answer both

Transcribed Image Text:Why are hydrogen bonds considered a special class of dipole-dipole interactions?
Choose one or more:
A. These interactions only occur if hydrogen is bonded to nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine.
B. They are observed with all molecules that contain a carbon double bonded to an oxygen.
OC. These interactions are with polar molecules but are stronger than dipole-dipole interactions.
OD. They are observed with all molecules that contain hydrogen.
OE These interactions are between polar molecules but are weaker than normal dipole-dipole interactions.
OF. These interactions account for the higher melting and boiling points observed for certain molecules such as
water.
O G. These interactions only occur with organic molecules.
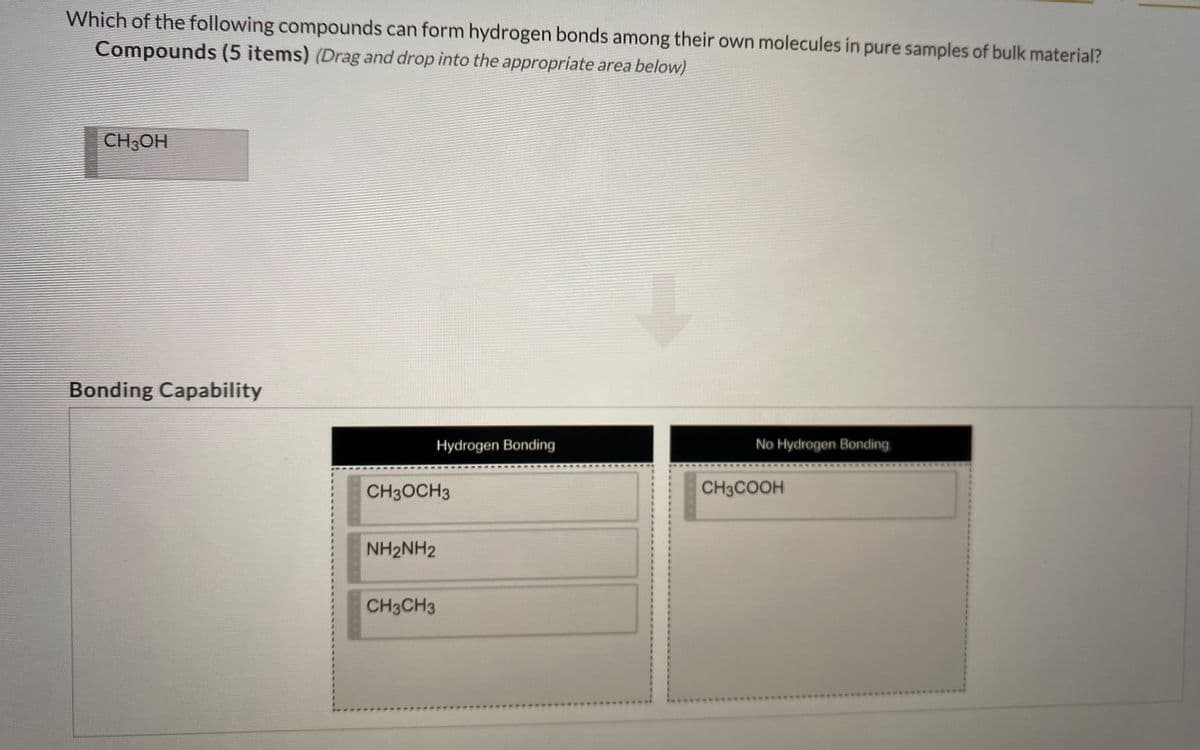
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following compounds can form hydrogen bonds among their own molecules in pure samples of bulk material?
Compounds (5 items) (Drag and drop into the appropriate area below)
CH3OH
Bonding Capability
Hydrogen Bonding
No Hydrogen Bonding
CH3OCH3
CH3COOH
NH2NH2
3.
CH3CH3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
