Chapter15: Antibiotic Agents
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18RQ
Related questions
Question
Q4. Why are some plates placed into a candle jar?
Q6. What is the purpose of each kind of medium?

Transcribed Image Text:INCUBATION of plates:
All BHI or blood plates inside of a candle jar, as well as Mitis-salivarius agar plates. The candle jar is lit,
closed and placed in 37 C incubator. Mannitol salt agar and MacConkey's plates are incubated in the
regular 37 C incubator.
Interpretation:
1. Remove all plates from the incubators, and separate them into 2 groups---plaque or toothbrush.
2. Determine the number of bacteria per plaque sample. This will not be per gram since you had
much less than a gram sample of plaque.
3. Determine the number of bacteria per toothbrush head, using counts from blood or BHI.
4. Determine the number of bacteria per toothbrush head for each group of bacteria, based on each
individual media type.
5. Analyze each type of medium for bacteria for BOTH toothbrush and plaque:
• BAP or BHI - for total count of facultatives and aerobes
• Mannitol salt - for salt-resistant Staphylococcus species, Staph aureus turns yellow (see
exercise in lab manual)
MacConkey's - for enteric gram - rods, coliforms turn red and non-coliforms are clearish
Mitis-salivarius agar - small blue colonies (Strep mitis), large blue gumdrop-like colonies
(Strep salivarius) and dark blue/black, shiny colonies (Enterococcus faecalis)
6. Gram stain at least one colony on each type of medium and record the gram reaction,
arrangement, and shape.
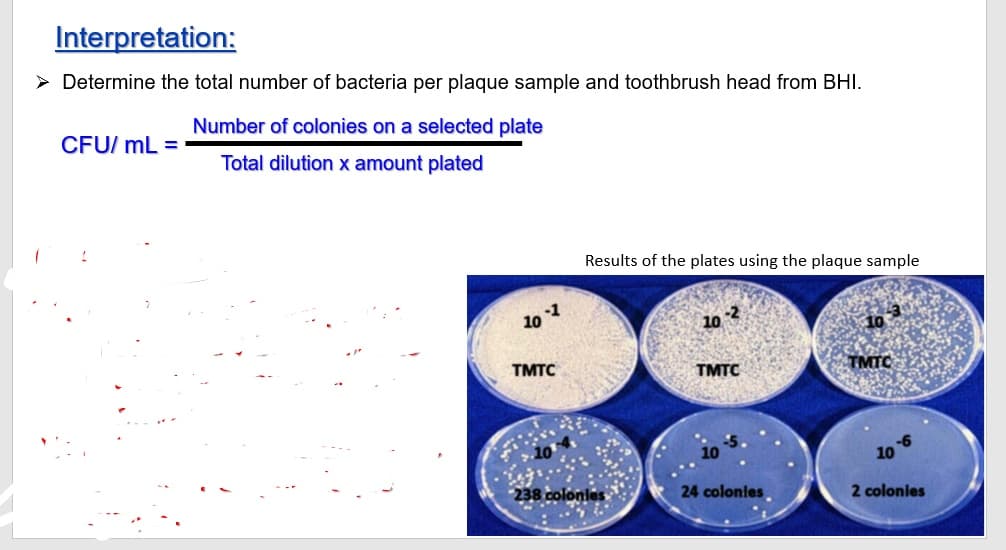
Transcribed Image Text:Interpretation:
> Determine the total number of bacteria per plaque sample and toothbrush head from BHI.
Number of colonies on a selected plate
CFU/ mL =
Total dilution x amount plated
Results of the plates using the plaque sample
101
10 2
TMTC
TMTC
TMTC
10
238 colonies
24 colonles
2 colonies
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



