
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
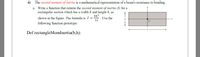
Transcribed Image Text:6) The second moment of inertia is a mathematical representation of a beam's resistance to bending.
a. Write a function that returns the second moment of inertia (1) for a
rectangular section which has a width b and height h, as
bh
shown in the figure. The formula is I = :
following function prototype:
Use the
12
Def rectangleMomlnertia(b,h):
![b. An l-section (i.e. a cross-section in the shape of the letter I) consists of a vertical part called the
web and two horizontal parts called the flanges (see the figure on
the right). The second moment of inertia for an I-section is given
by:
Flange
Web
12
12
12
= [Second moment of inertia of the rectangle, xh] -
[Second moment of inertia of the two rectangles under the
-beam
centroid
flanges, t xh]
I- rectangleMomInertia (b, h) - 2*rectangleMomInertia (0.5 (b-t,),ha)
Now, write a function that returns the second moment of inertia for an I-section. Let your
function use the function rectangleMomInertia () as explained above. Use the following
prototype:
def iSectionMomInertia(b, h, tw, h1);
c. Write a C++ program that inputs the dimensions of the following sections, and then computes
and outputs the second moment of inertia for each.
25 em
-20 em -
40 cm
50 em
2.5 cm
45 ep
ARestangle
An I-Section
7](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/d33b4037-4e90-44df-86f6-9b76f605da9e/5107fe2b-a37f-4532-930b-1386393252ce/0ehg69_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:b. An l-section (i.e. a cross-section in the shape of the letter I) consists of a vertical part called the
web and two horizontal parts called the flanges (see the figure on
the right). The second moment of inertia for an I-section is given
by:
Flange
Web
12
12
12
= [Second moment of inertia of the rectangle, xh] -
[Second moment of inertia of the two rectangles under the
-beam
centroid
flanges, t xh]
I- rectangleMomInertia (b, h) - 2*rectangleMomInertia (0.5 (b-t,),ha)
Now, write a function that returns the second moment of inertia for an I-section. Let your
function use the function rectangleMomInertia () as explained above. Use the following
prototype:
def iSectionMomInertia(b, h, tw, h1);
c. Write a C++ program that inputs the dimensions of the following sections, and then computes
and outputs the second moment of inertia for each.
25 em
-20 em -
40 cm
50 em
2.5 cm
45 ep
ARestangle
An I-Section
7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given a 2n × 2 n checkerboard with one square missing, construct a tiling of this checkerboard using right triominoes. Write a C or C++ program to solve this problem. The input is an integer n ≥ 3 and the position of the missing square. The output is a tiling of the 2n × 2 n checkerboard with one square missing (the position of the missing square is part of the input).arrow_forwardWhen a bouncing ball is droped from the initial height h it bounces back to the height h_1. The ratio b = h_1 / h is called the bounciness ratio. Assuming that the ball bounces freely, and that the bounciness ratio is constant during that process, write a complete C++ program which computes and outputs the distance that the ball travels until it stops bouncing. Note that during one bounce the ball travels the same distance up and down and your program should therefore count that distance twice. Note 1: The distance dist traveled by the ball after the first bounce is dist = h + 2h_1 = h + 2hb Note 2: Your program must accept initial height h and the bounciness ratio b as inputs from the keyboard. Your program must make it impossible to enter b >= 1, b < 0 and h < 0 for obvious reasons. Solution: dist = h(1+b)/(1-b)arrow_forwardThis needs to be done in C Programming. A manufacturing plant has an alarm monitor program that reports any of sixteen possible alarms. A 16-bit variable ALARM is examined, and each 1 bit found corresponds to an active alarm. The alarms are numbered 1 – 16, with the least significant bit (LSB) corresponding to Alarm 1 and the most significant bit (MSB) corresponding to Alarm 16. Prompt for the unsigned short integer ALARM, and then use bitwise logic to determine and display all corresponding active alarms, e.g., output “Alarm 12 Active”.arrow_forward
- For all MATLAB programs you must include MATLAB code and the output from the programarrow_forwardWrite a c program that generates all the numbers 1-10000 with the following conditions it's 4 digits, and the number 5 is used twicearrow_forwardA typical NMR peak after Fourier transform has a Lorentzian absorptive line shape. This line shape is represented by the function below, where x is in Hz 1 f (x) : x2 + 1 Write a program to calculate the integral of this function using Riemann sums on the range from [-10, 10] (inclusive) with dx = 0.01. In other words, estimate the following integral with a Riemann sum. 10 1 x2 + 1 -10arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education