You may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question. Three different methods for assembling a product were proposed by an industrial engineer. To investigate the number of units assembled correctly with each method, 36 employees were randomly selected and randomly assigned to the three proposed methods in such a way that each method was used by 12 workers. The number of units assembled correctly was recorded, and the analysis of variance procedure was applied to the resulting data set. The following results were obtained: SST = 12,620; SSTR = 4,520. (a) Set up the ANOVA table for this problem. (Round your values for MSE and F to two decimal places, and your p-value to four decimal places.) Source Sum Degrees Mean p-value of Variation of Squares of Freedom Square Treatments Error Total (b) Use a = 0.05 to test for any significant difference in the means for the three assembly methods. State the null and alternative hypotheses. OH₂H₂H₂ Hy ⒸHg! H₂H₂H₂ H: Not all the population means are equal. O Hg! H₂H₂H₂ OH,: Not all the population means are equal. H₂H₂H₂H₂ OH: At least two of the population means are equal. H: At least two of the population means are different. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) p-value= State your conclusion. O Reject H. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal. O Do not reject H. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal. O Do not reject H. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal. Reject H. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal.
You may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question. Three different methods for assembling a product were proposed by an industrial engineer. To investigate the number of units assembled correctly with each method, 36 employees were randomly selected and randomly assigned to the three proposed methods in such a way that each method was used by 12 workers. The number of units assembled correctly was recorded, and the analysis of variance procedure was applied to the resulting data set. The following results were obtained: SST = 12,620; SSTR = 4,520. (a) Set up the ANOVA table for this problem. (Round your values for MSE and F to two decimal places, and your p-value to four decimal places.) Source Sum Degrees Mean p-value of Variation of Squares of Freedom Square Treatments Error Total (b) Use a = 0.05 to test for any significant difference in the means for the three assembly methods. State the null and alternative hypotheses. OH₂H₂H₂ Hy ⒸHg! H₂H₂H₂ H: Not all the population means are equal. O Hg! H₂H₂H₂ OH,: Not all the population means are equal. H₂H₂H₂H₂ OH: At least two of the population means are equal. H: At least two of the population means are different. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) p-value= State your conclusion. O Reject H. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal. O Do not reject H. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal. O Do not reject H. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal. Reject H. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.5: Comparing Sets Of Data
Problem 14PPS
Related questions
Question
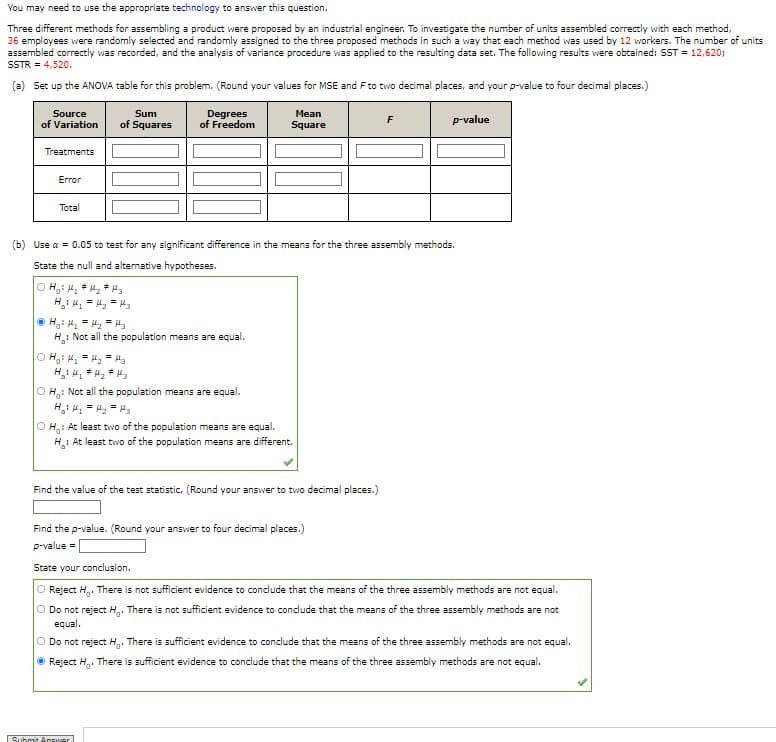
Transcribed Image Text:You may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question.
Three different methods for assembling a product were proposed by an industrial engineer. To investigate the number of units assembled correctly with each method,
36 employees were randomly selected and randomly assigned to the three proposed methods in such a way that each method was used by 12 workers. The number of units
assembled correctly was recorded, and the analysis of variance procedure was applied to the resulting data set. The following results were obtained: SST = 12,620;
SSTR = 4,520.
(a) Set up the ANOVA table for this problem. (Round your values for MSE and F to two decimal places, and your p-value to four decimal places.)
Sum
Source
of Variation
Degrees
Mean
Square
F
of Squares of Freedom
p-value
Treatments
Error
Total
(b) Use a = 0.05 to test for any significant difference in the means for the three assembly methods.
State the null and alternative hypotheses.
O Hg ² H₂ # H₂ # Hz
H₂H₂ = H₂ = H₂
ⒸH₁ H₂=H₂ = 3
H: Not all the population means are equal.
O H₂² H₂ = H₂ = H₂
OH: Not all the population means are equal.
H₁₂ : H₁ = H₂ = H₂
OH: At least two of the population means are equal.
H₂: At least two of the population means are different.
Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
p-value =
State your conclusion.
O Reject H. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal.
O Do not reject H. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not
equal.
O Do not reject H. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal.
Ⓒ Reject H. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the three assembly methods are not equal.
Submit Answer I
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill