
Biology
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781259188121
Author: Peter Stiling, Robert Brooker, Linda Graham, Eric Widmaier
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 28.1, Problem 1BC
An Introduction to Protists
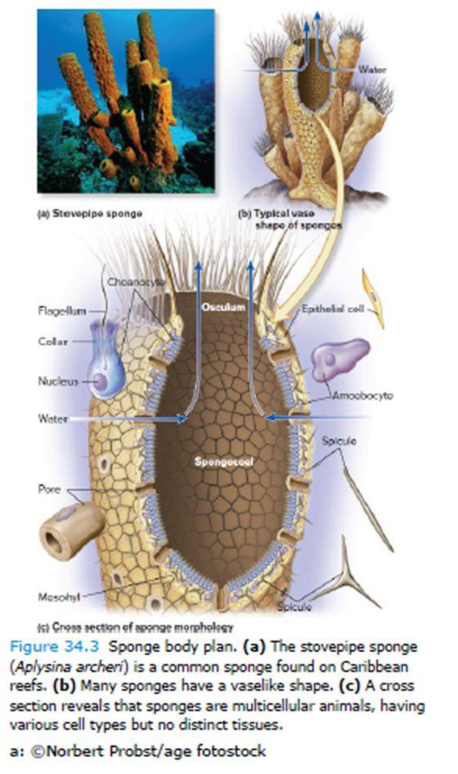
Core Skill: Connections Look ahead to Figure 34.3. What kind of mobile, amoeba-shaped cells carry materials within the bodies of the early-diverging animals known as sponges?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
State and explain the theory of endosymbiosis. Discuss and relate its role in eukaryotic evolution focusing on protists.
Lab 10: Kingdom Animalia Introduction Animals all share some characteristics:
1) Multicellular
2) Heterotrophic
3) Their cells have no cell wall
4) At some time in their life they are motile.
There are many phyla within the animal Kingdom, and in this activity, you will explore these phyla by building a dichotomous key that will allow you to consider almost any animal and determine which phylum it belongs to.
Part 1: Organizing information for the dichotomous key 1) List the 9 animal phyla of macroscopic (visible) animals: Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Nemotoda, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata, and Chordata. 2) Use on-line or library resources of your choice, to gather information about these 9 phyla.
a. Start by finding two example species per phylum to help tie into your previous knowledge about animal types. Write down these examples.
b. Make a list of characteristics that you could use that would help you tell these 9 phyla apart. The final goal is to build a…
Bulleted items are choices for questions
Protists, as a group, represent one of the kingdoms of organisms in the eukaryotic domain. In the other kingdoms, the organisms grouped within a kingdom are very closely related and share many unifying features. The many different organisms grouped as protists are not necessarily closely related, and many different types of traits are represented among them.
Review the following list of statements, and select which statements are correct descriptions of protists. Check all that apply.
Protists represent both heterotrophic and autotrophic nutritional modes.
Some protists are colonial.
No protists are multicellular.
The phylogenetic tree displayed here shows the evolution and relationships between different major protist groups, as scientists currently understand them. It also shows how these different groups of protists are related to animals, fungi, and land plants. The protist groups are highlighted in tan boxes.…
Chapter 28 Solutions
Biology
Ch. 28.1 - An Introduction to Protists Core Skill:...Ch. 28.2 - Prob. 1CCCh. 28.2 - Evolution and Relationships Concept Check: How do...Ch. 28.2 - Evolution and Relationships Concept Check: How do...Ch. 28.2 - Prob. 4CCCh. 28.2 - Prob. 5CCCh. 28.3 - Prob. 1EQCh. 28.3 - Prob. 2EQCh. 28.3 - Prob. 3EQCh. 28.4 - Prob. 1CC
Ch. 28.4 - Prob. 1BCCh. 28.4 - Prob. 2CCCh. 28 - Prob. 1TYCh. 28 - Prob. 2TYCh. 28 - Prob. 3TYCh. 28 - Prob. 4TYCh. 28 - What organisms have tertiary plastids? a. certain...Ch. 28 - What is surprising about mixotrophs? a. They have...Ch. 28 - What advantages do diatoms obtain from sexual...Ch. 28 - What are extrusomes? a. hairs on flagella b....Ch. 28 - Prob. 9TYCh. 28 - Prob. 10TYCh. 28 - Prob. 1CQCh. 28 - Why have molecular biologists sequenced the...Ch. 28 - Core Concept: Science and Society Why are the...Ch. 28 - Prob. 1COQCh. 28 - Prob. 2COQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question. Corals themselves are only a small number of the diverse species that make up a coral-reef ecosystem. What factors might contribute to making reefs so diverse?arrow_forwardWe discussed two theories of the evolution of multicellularity in the animals, the Colonial Theory and the Syncytial Theory. For each of the two theories, give a brief summary of the theory and describe the characteristics you would expect to find in the protist ancestor proposed by each theory.arrow_forwardInstruction: Fill – up the taxonomic account, chemical component of spicule and type of body structure of each poriferan species representatives. Label the visible parts/ observable parts on each species representatives. Taxonomic Account Phylum Class Order Family Scientific Name: Euplectella sp. Common Name: Chemical Component of spicule: Type of Body structure:arrow_forward
- DNA sequence data for a diplomonad, a euglenid, a plant, and an unidentified protist suggest that the unidentified species is most closely related to the diplomonad. Further studies reveal that the unknown species has fully functional mitochondria. Based on these data, at what point on the phylogenetic tree in Figure 1 did the mystery protist’s lineage probably diverge from other eukaryote lineages? Explain.arrow_forwardTest Your Understanding 1. Which of the following is not true of the protists? (a) they are unicellular, colonial, coenocytic, or simple multicellular organisms (b) their cilia and flagella have a 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules (c) they are prokaryotic, as bacteria and archaea are (d) some are free-living, and some are endosymbionts (e) most are aquatic and live in the ocean or in freshwater pondsarrow_forwardDescribe in detail 5 ways to preserve material for the fossil record. List the 3 types of life habits. With regard to life habits, describe/define: solitary vs. colonial, two types of plankton, sessile vs vagrant, and infauna vs epifauna. There are 2 ideas for where life started. Describe both of them in terms of why or why not they are feasible. Within the Protista Kingdom what are the 3 types of plankton, how are they similar or different, and what does that tell scientists of past and present ocean environments. How do the differences in brachiopod structure relate to its life habit?arrow_forward
- Instruction: Fill – up the taxonomic account, chemical component of spicule and type of body structure of each poriferan species representatives. Label the visible parts/ observable parts on each species representatives. Taxonomic Account Phylum Class Order Family Scientific Name: Chalina sp. Common Name: Chemical component of spicule: Type of Body structure:arrow_forwardQ17: what is the correct answer The animals above are members of which taxa? Group of answer choices A. Deutersotomia, Hemichordata B. Deutersotomia, Chordata C. Protostomia, Mollusca D. Deuterostomia, Echinodermataarrow_forwardRedraw the phylogenetic tree for Cnidarians showing only the relationships between Scyphozoa, Rugosa, Tabulata, and Scleractinia. Circle the Anthozoa clade.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Bacterial Endospore Formation -Biology Pundit; Author: Biology Pundit;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6_sinRhE8zA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Taxonomy of Bacteria: Identification and Classification; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8IJRzcPC9wg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY