
Concept explainers
DRAW IT Diagram each of the following flagellar arrangements:
a. lophotrichous
b. monotrichous
c. peritrichous
d. polar
e. amphitrichous
To review:
The bacteria flagella arrangements.
Introduction:
Flagella are present both in prokaryotes and eukaryotes and they facilitate cell motility. It is a whip-like, hollow, cylindrical structure that contains the protein called flagellin. The arrangement of flagella is different in different species. It consists of three different parts, namely filament, hook, and basal body. Flagella eukaryotes derive energy from ATP, whereas flagella in prokaryotes derive energy from proton motive force.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
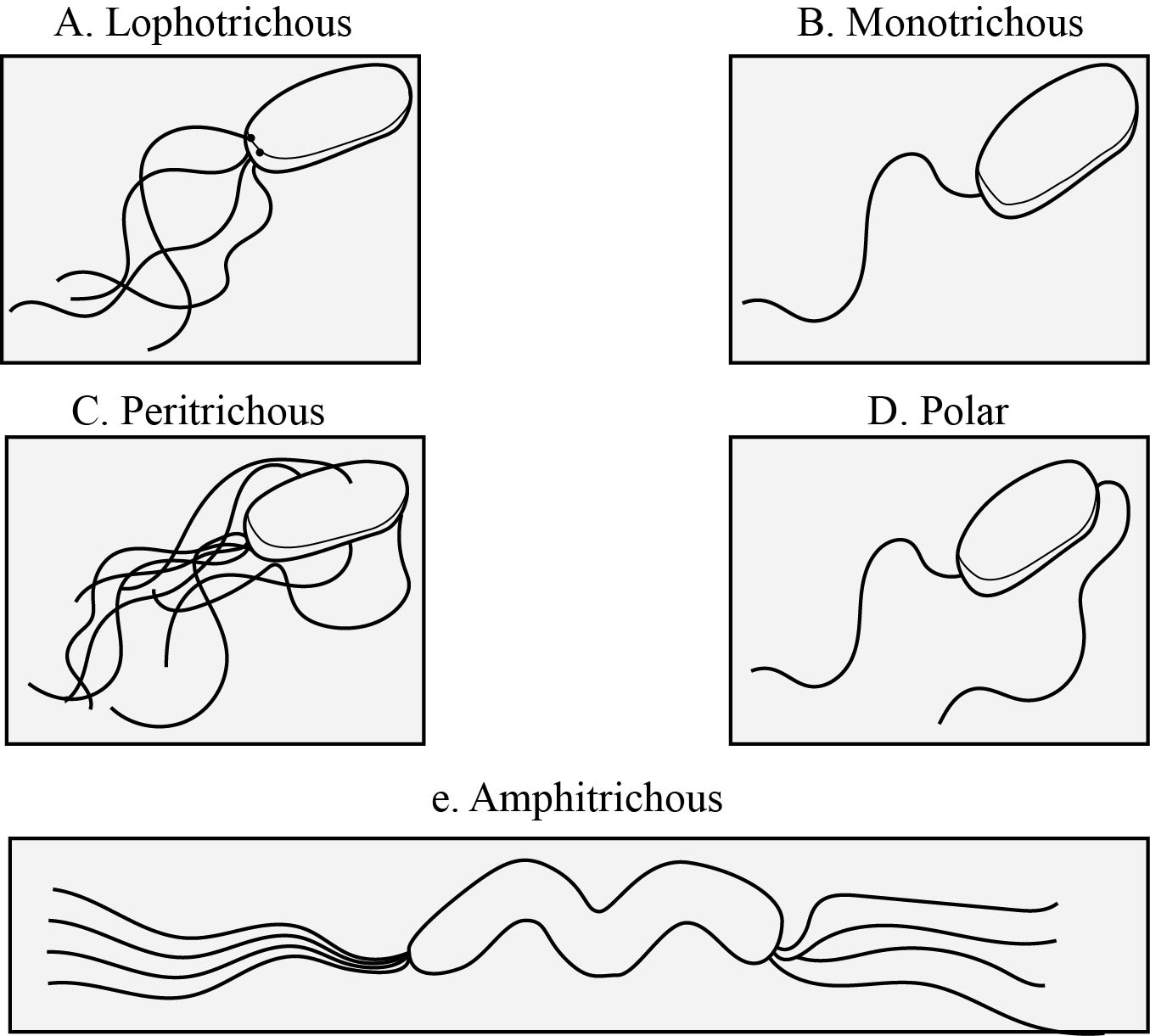
Based on the flagella arrangements, the organisms are classified into different types.
- Lophotrichous: Two or more flagella at one end of the cell.
- Monotrichous: Single flagellum present at one end of the cell.
- Peritrichous: More number of flagella present on the entire surface of the cell.
- Polar: Flagella are present at each pole of the bacterial cell.
- Amphitrichous: A bunch of flagella present at both ends of the bacterial cell.
The flagella present on the cells are useful for locomotion and attachment. It contains filamentous protein which helps to propel a cell through liquid. The flagella also act as sensory organelle and aid in detecting changes in the temperature and pH.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
- Define the following terms: a. carotenoid b. stroma c. β-carotene d. lutein e. thylakoid membranearrow_forwardDescribe the function of each cell modification 1. Flagella 2. Cilia 3. Microvilli 4. Pseudopodiaarrow_forwardIdentify Three subtypes of polar arrangement where the flagella are attached at one or both ends of the cell.arrow_forward
- Which of the following is a CORRECT similarity between Archaeal and Bacterial flagella? • A. Flagella from both domains have the same function; they act to move the cell B. The filaments both domains are made of two or more different versions of the protein flagellin • C. Flagella from both domains are hollow O D. The filaments from both domain exhibit the same level of thinness O E. Flagella from both domains grow from the tiparrow_forwardMatch the letters on the diagram below to the terms. ________ stroma ________ thylakoid ________thylakoid space ________ outer membranearrow_forwardwhich of these are important in creating biofilms? (select all that apply) choose the correct answer. A) GLYCOCALYX B) FLAGELLA C) ARCHAELLA D) AXIAL FILAMENTS E) FIMBRIAEarrow_forward
- Draw simple sketches of a Euglena and a Paramecium. Choose the appropriate structures for each organism from the following list and label them in your drawings: flagellum, cilia, chloroplast, mitochondrion, nucleus, macronucleus, micronucleus, contractile vacuole, pellicle, food vacuole.arrow_forwardCompare and contrast flagellar swimming motility, swarming, spirochete flagellar motility, and twitching and gliding motilityarrow_forwardWhich of the following does not possess cilia or flagella? a.)Amoeba b.)Paramecium c.)Trypanosoma d.)Mastigamoebaarrow_forward
- 1. As a cilium moves, it is fairly well established that: a) the microtubules slide relative to each other along the length of the cilium b) it is an action of the microfilaments expanding and contracting c) The basal body is actually actinf as the ‘motor’ d) The microtubules slide relative to each other along the length of the cilium e.) This action is very different than that of eukaryotic flagellaarrow_forwardThe Prokaryotes are associated with the following structures EXCEPT: A) ribosomes, B) Lysosomes and liposomes, C) a nucleoid area, D) mesosomes, E) chlorophyll.arrow_forwardGive the different arrangement of flagella and provide an example of each flagellar arrangement. (Illustrate each flagellar arrangementarrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
