
Sub- Part
A
Based on the data, Graphical representation of consumption function, with consumption spending on vertical axis and disposable income on horizontal axis.
Sub- Part
A
Explanation of Solution
(a) − Following graph shows the consumption function in an economy.
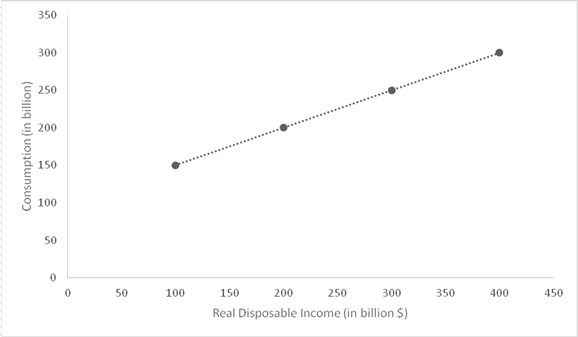
Sub- Part
Introduction: Consumption function represents the functional relationship between total consumption and gross
B
Based on the data, to find:
Slope, if consumption function is a straight line
B
Explanation of Solution
In case of a straight line, slope of the line remains constant or same everywhere along the line. So, if the consumption function is a straight line then its slope will remain same everywhere along it. The difference between two level of income and consumption will be constant. The slope of consumption function can be calculates as follows −
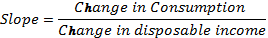
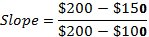
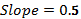
Thus, the slope of given consumption function is 0.5.
Sub- Part
Introduction: Consumption function represents the functional relationship between total consumption and gross national income. Consumer spending depends on three factors: disposable income (Yd), autonomous consumption (a), i.e. when income is zero, and induced income (b), i.e. the percentage of extra income that is spent. The formula for the same is C = a + b*Yd.
C
Based on the data,
Find the Savings at each level of income and the slope when the saving function is a straight line.
C
Explanation of Solution
If the saving function is a straight line then its slope will remain constant. Difference between two level of income and saving will remain constant along the saving function. As saving function is a straight line, change in saving and income would be the same. Thus, the slope of saving function would be:
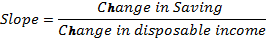
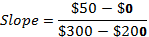
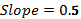
| Real Disposable Income (in billion $) | Consumption Expenditure (in billion $) | Savings (in billion $) |
| 100 | 150 | -50 |
| 200 | 200 | 0 |
| 300 | 250 | 50 |
| 400 | 300 | 100 |
Introduction: Consumption function represents the functional relationship between total consumption and gross national income. Consumer spending depends on three factors: disposable income (Yd), autonomous consumption (a), i.e. when income is zero, and induced income (b), i.e. the percentage of extra income that is spent. The formula for the same is C = a + b*Yd.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Give typing answer with explanation and conclusion what is the US GDP for the first quarter and second quarter of 2021? What is the personal consumption expenditures for the first quarter and second quarter of 2021?arrow_forward13 . Measuring GDP The following table shows data on consumption, investments, exports, imports, and government expenditures for the United States in 2016, as published by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. All figures are in billions of dollars. Fill in the missing cells in the table to calculate GDP using the expenditure approach. Data (Billions of dollars) Consumption (C) 12,757.9 Investment (I) 3,035.7 Exports (X) 2,232.4 Imports (M) 2,733.7 Net Exports of Goods and Services Government Purchases (G) 3,276.7 Gross Domestic Product (GDP)arrow_forward18. What will be the level of consumption spending at an income level of 36? a) 30 b) 24 c) 28 d) 16 e) 8arrow_forward
- The Reliable Aircraft Company manufactures small, pleasure-use aircraft. Based on past experience, sales volume appears to be affected by changes in the price of the planes and by the state of the economy as measured by consumers' disposable personal income. The following data pertaining to Reliable's aircraft sales, selling prices, and consumers' personal income were collected: Year Aircraft Sales Average Price Disposable Constant Income (Dollars) (In constant 2006 dollars, billions) 2006 525 16,800 610 2007 450 8,000 610 2008 400 8,000 580 The arc price elasticity of demand between 2006 and 2007 is: The arc income elasticity of demand between 2007 and 2008 is: Assume that these estimates are expected to remain stable during 2009. Forecast 2009 sales for Reliable assuming that its aircraft prices remain constant at 2007 levels and that disposable personal income will increase by 7%. Also assume that the arc…arrow_forwardGross Domestic Product Explain how net exports affect the US economy. Describe both positive and negative impacts on GDP. Why do national income accountants use net exports to compute GDP, rather than simply adding exports to the other expenditure components of GDP? You have the following information on 3 countries: Soccerland, Handeggland, and Neverland How long will it take until Soccerland’s GDP increases by 75%? How long will it take until Soccerland and Handeggland have the same GDP? Soccerland’s population is not happy that, eventually, Handeggland is going to have higher GDP than their country. They feel that they are a much better country, so they are going to work harder to ensure that Handeggland will never catch up with Soccerland. If Soccerland’s new growth rate is constant every year, what is the minimum growth rate that ensures that Soccerland will always have a higher GDP than Handeggland? Neverland’s ambition is to host the World Cup. At the…arrow_forward1 Which one of these will be deducted from gross output to determine the net output? a. Intermediate consumption b. Factor income from abroad c. Total government spending d. Private incomearrow_forward
- Table 2 shows elements in the national income accounts of an economy. Assume the economy is currently in equilibrium. Elements £ billions Consumption (total) 80 Investment 9 Government Expenditure 6 Imports 15 Exports 8 What is the current equilibrium level of income? What is the level of injections? What is the level of withdrawals? If national income now rises by £22 billion and as a result, the consumption of domestically produced goods rises to £80 billion. Calculate the marginal propensity to consume (MPC)What is the value of the multiplier? What is the value of the multiplier? Comment on the results in part (3) and (4).arrow_forward1(a) In the prescribed research paper “Is Ireland really the most prosperous country in Europe?” Dr. Patrick Honohan states that there are “acute shortcomings” in using GDP in the Irish economy as a measure of economic welfare. Please explain and critically evaluate this viewpoint put forward by Dr. Honohan.arrow_forwardQuestion 2: Fill in the blanks. The three different approaches to measuring the GDP are the expenditure approach, the approach, and the approach. The expenditure approach aggregates the spending by the four sectors of the economy: (a) the household sector, (b) the sector, (c) the sector, and (d) the foreign sector, to yield the total GDP. The largest spending in Canada’s aggregate GDP comes from the sector. When using the income approach, the first step is to calculate the total national income by adding employee compensation, proprietor’s income, , net interest, and rental income. There are six categories of economic exchanges that are omitted from GDP calculations. One such category is government transfer payments (like unemployment insurance payment), because it represents transfers of income without new production. Another category is , because because they are unpaid and not…arrow_forward
- Question 1Explain the expenditure measure of GDP. What is the underlying assumption of this measure? Provide one example where the underlying assumption is violated. Explain the income measure of GDP. What is the underlying assumption of this measure? Provide one example where the underlying assumption is violated. Explain why we need to compute nominal GDP, real GDP, and per capita GDP.arrow_forwardAggregate Variables Value (in billions of dollars) in the base year Consumption spending $900 Investment spending $400 Government spending $200 Transfer payments $60 The marginal propensity to save is equal to 0.4 and there are no exports or imports, (a) Calculate the real GDP in this country, Show your work (b) Calculate the marginal propensity to consume Show your work. (c) Suppose that the government increases spending from $200 billion to $300 billion (i) Calculate the maximum change in real GDP. Show your work (ii) Given the change in real GDP in part (c)(i), calculate the maximum level of the new equilibrium real GDP. Show your work (d) Suppose that taxes decrease by $100 billion. Will the maximum change in real GDP be larger than, smaller than, or equal to the change in part (c)(i)? Explain.arrow_forwardThe rise in consumption is by $590 and the rise in income is by $700 Calculate MPCarrow_forward
