What is a Cash Book?
So, before coming to the topic of cash books, I will let you briefly explain about the cash so that you all can be familiar with the word cash. Cash comes under the category of the current asset which is used as a medium of exchange for all the financial transactions in the firm. Cash is something that is universally accepted as a mode of payment. So, now comes to the topic i.e., cash book.
Cash book is one of the types of the subsidiary book, in which only cash related transactions are recorded. Basically, it is used to record all the cash receipts on the debit side and all cash payment is on the credit side by the firm during a particular accounting period. One of the important points to be remembered about the cash book is that the cash book never shows a credit balance. Only a debit balance is shown by the cash book.
Types of Cash Book
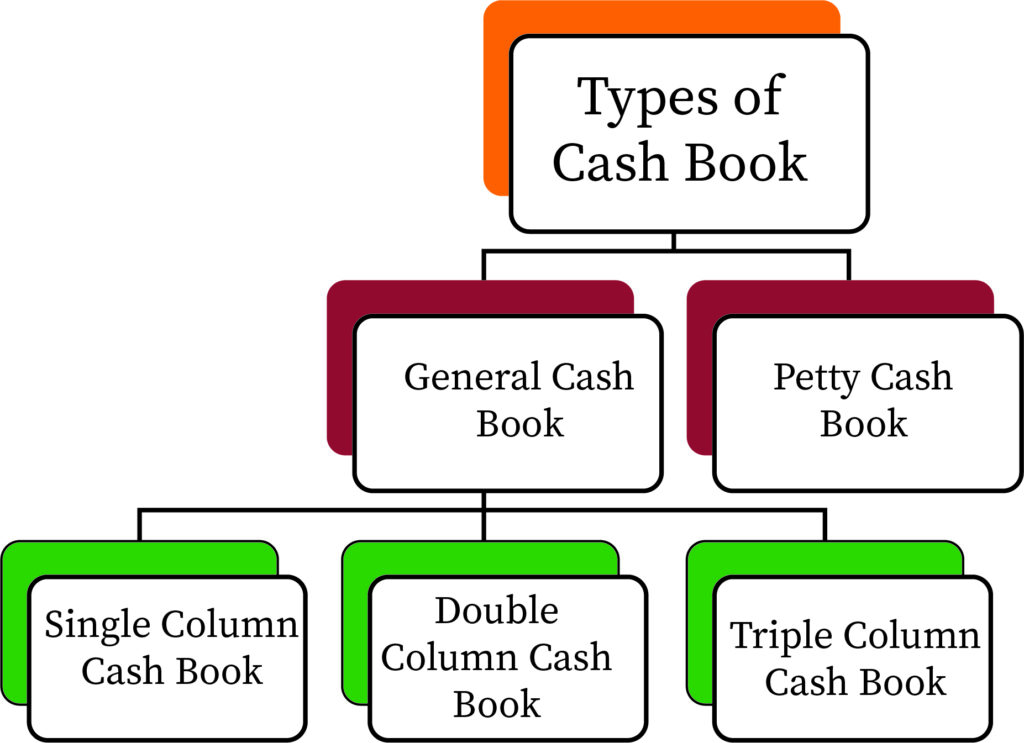
Now, look at the types of cash book that the company usually used to prepare:
Single column cash book: This is also known as simple cash book. This is a single column cash book so it is only used to record cash transactions, no bank transactions or discount given is shown here.
Double column cash book: In double column cash book an additional column is added for bank transactions. So, a double column cash book is used to record both cash and bank related transactions. Now, in this digital world mainly most of the transaction deals in cheques or through any other mode like bills of exchange. So, having a bank column in the cash book makes it simpler to understand which transaction is dealt in cash or which one is with cheques.
Triple column cash book: In triple column cash book, one more column is added in the name of discount. So, a triple column cash book is used to record all transactions related to cash, bank and discount (it may be a sales discount or purchase discount).
Petty cash book: This book is used to record small day to day cash expenditures.
Discount is a nominal account, so if any discount is given then it is considered as a loss for the firm so it recorded on the debit side of the cashbook but if any discount is received by the firm then it is considered as a profit for the firm, so it is recorded on the credit side of the firm.
Contra Entry

In a double column cash book, suppose the firm receives a cheques from their creditor of the due amount, if the firm deposits the cheques into the bank on the same date then the entry is recorded in the debit side of the cash book and the amount is written in the bank column. But, if the firm did not deposit the cheque on the same date he receives but deposited it on a later date this is known as contra entry. Contra entry is a transaction which involves both cash and bank on either side of the cashbook.
Example of such transactions is:
- Cash deposited in to bank
- Cash withdrawn from bank for office use.
For example
- From office cash is deposited into the bank.
- Cash withdrawn from bank for office use.
The journal entry of first transaction is:

Bank a/c
To Cash a/c
In this entry, a bank account is debited because bank balance is increasing so it is recorded in the credit side and cash is credited because cash is decreasing or going out from us. That’s why it is recorded on the debit side of the cash book.
The entry for the second transaction is:
Cash a/c
To bank a/c
Here, the cash account is debited because cash is coming in and the bank account is debited because bank balance is going to decline.
Difference Between Cash Book and Cash Account
- Cash book is such a book which has a function of both journal and ledger on the other hand cash accounts is the account which has a function of journal only.
- Any transaction that happens in the firm is directly recorded in the cash book while in the cash account the transaction is first posted in the journal after that it transfers in the cash account.
- Cash books are of three types – single column cash book, double column cash book, triple column cash book. But the cash account has only one type i.e. cash account itself or we can say that there is no type of cash account.
- In the cash book there is a column of ledger folio but in the cash account there is a column of journal folio.
- Cash book shows cash balances, bank balances, or all the discount balances whether it's allowed or received. But the cash account shows only cash balances
- Cash Book has a narration while there is no need for a cash account.
Advantages of Cash Book
- In a cash book the transaction is recorded on a daily basis and also date wise so it is easy to analyze any transaction at any point of time.
- It helps in identifying any mistake in the Cash balances by matching the balances in the cash book with the actual cash in hand, if in case they do not match then there is some mistake.
- In the cash book the transaction is recorded date wise so it saves so much time and labor and also helps in reducing workload.
Disadvantages of Cash Book
- As a cash book only records only cash transactions as it does not include all types of transaction like credit transaction. so, as a result it can’t be said that business can depend upon this to make business decisions.
- As it does not include credit transactions, so it does not show the liabilities of the business.
Context and Applications
This topic is significant in the professional exams for both undergraduate and graduate courses, especially for
- B.B.A. in Accounts
- M.B.A in Accounts
Want more help with your accounting homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Financial Accounting and Reporting
Intermediate Accounting
Accounting for Cash and cash equivalents
Cash Book Homework Questions from Fellow Students
Browse our recently answered Cash Book homework questions.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.