What is Hazard?
Hazard is the intrinsic property of a material or process which harms the people, buildings, or environment. Health, safety, hazard, risk assessment, loss prevention, and environmental consideration play an important role while designing a chemical processing plant. Hazard is often confused with risk. Risk measures the magnitude of loss and injury of likelihood incidents or the consequence and frequency of incidents.
Types of hazards and control
The individuals working in an industry are exposed to various health hazards. They are broadly classified into hazards caused by materials used, hazards by fire, and hazards by an explosion.
Hazard by materials used in industry
One of the health hazards caused is because of the material used in the industry. The intensity of the hazard is a function of inherent toxicity and period of exposure to the material. The threshold limit value (TLV) is the upper permissible concentration limit of material safe for humans when inhaled for a long duration of time. The main source of workplace exposure to chemicals is inhalation. It can be controlled by source control, transmission barriers, and using personal protection equipment.
Hazard by fire
Fire and explosion are the other hazards likely to happen in a chemical plant. Fire can be controlled by keeping all the flammable substances under close control. A fire protection system can be active or passive type. In an active system, we use water sprays, foam, and dry chemicals to prevent fire. In a passive system, smoke detectors are installed during the construction of the plant. This can also be exemplified by an insulating material or fireproofing applied to the steel structures and equipment supports.
Hazard by an explosion
An explosion happens when a huge amount of energy is released causing a pressure wave. Fire is not compulsory to cause an explosion. Explosions can happen by the failure of a boiler due to overpressure. Explosions can also happen due to uncontrolled physical, chemical, or nuclear reactions. Two main types of explosions can happen mainly in industry.
- The boiling-liquid expanding-vapor explosion (BLEVE): This happens due to heat leakage into a container filled with a boiling liquid which causes excessive vaporization. This leads to steady pressure build-up that ruptures the tank followed by an explosion.
- The unconfined vapor cloud explosion (UVCE): A large cloud of gas or vapor forms following the release of flammable material. If ignition occurs, the cloud may burn with a higher burning speed and may reach detonation velocities. This causes an explosion.
Loss prevention
Loss prevention means the prevention of financial loss associated with an accident. Loss prevention has the following steps:
- Identification and assessment of hazards
- Control of hazards by containment, substitution, and maintenance
- Control of process
- Restrict the loss when the accident occurs.
Hazard analysis
Hazard can be identified by asking “what if” questions during design review. It can also be identified using the checklist provided with the equipment or processes which outlines the general hazards associated with them. In both of these methods, the designing team may overlook some items in the checklist or may forget to ask some questions which may lead to process hazards.
The formal method of hazard assessment techniques is Hazard and operability study (HAZOP), Fault-tree analysis (FTA), Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA), Safety indexes, and Safety Audit.
Hazard and operability study (HAZOP)
HAZOP study helps in identifying plant and equipment hazards and operability problems. In this study, each process, equipment, pipeline, and so on are carefully checked by applying guide words, and deviations from normal operating conditions are identified. Guide words can be no or not, more, less, part of, reverse, other than, and so on. First, we apply these guide words to flow, temperature, composition, pressure, and any other variable affecting the process. Then the impact of these deviations on the process is assessed and correction methods are established.
In daily life, if we see while adding water to the cooker, we always try to ask ourselves whether water is more or less. If the quantity of water is not optimum the texture of the material cooked may not be as desired and our dish may not taste good. HAZOP is a vital tool in loss prevention throughout the life of the facility. The assessment should be done throughout the conceptual design phase, final design stage, and the pre-start-up period as well as when the plant is in full operation. In the conceptual design phase, the hazards can be identified and correction can be done with minimum cost. The major hazards are toxicity, fire, explosions thermal radiation, noise, and asphyxiation. When the plant starts the normal working phase, the operating variables and conditions may vary. Hence, it is advised to do periodic HAZOP analysis of the plant throughout its life.
Fault-tree analysis (FTA)
FTA helps to estimate the likelihood of an accident by breaking down the event into a smaller sequence of events with individual existence. “AND” and “OR” logic gates are used to synthesize a failure model of a plant. “AND” gate combines all input events which must occur simultaneously for an output. “OR” gate also combines inputs but any one input is enough to cause the output. The top event frequency or probability is generated from failure data of simpler events. FTA is done after hazards are analyzed by HAZOP or any other technique. Finally, the consequences of various loss events are combined by listing injuries, fatalities, property damage, and so on. This data is compared with data for other risks to the public in similar conditions or areas to judge whether the risk is within an acceptable limit or not.
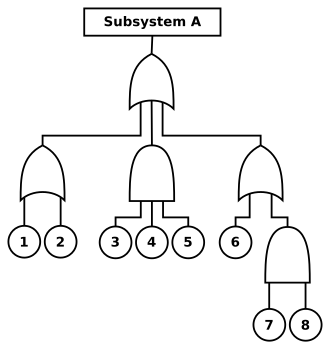
Failure mode and effect analysis (FEMA)
In FEMA analysis we evaluate the consequences and frequency of component failure on the process and surroundings. It is applied to a particular piece of equipment or process. It focuses on component failure and it does not consider the error in operating procedures.
Safety indexes
Safety Indexes are developed by Dow Chemical Company. It is a safety and loss prevention guide in which a numerical fire and explosion index is calculated, based on the properties of the material used and the nature of the process. In the preliminary design stage, this index will help select an alternative less hazardous process. In the final design stage, it helps to select and design preventive and protective equipment for safe plant operation.
Safety audits
Safety Audit verifies the adequacy of safety equipment for fire protection, personnel protection, and on-site emergency responses. It reviews general safety rules, gives explicit safety rules for new process areas, and generates a new set of rules for emergency response procedures. Detailed checklists covering the aspect of health, safety, loss prevention, and so on are prepared. Checklists help to identify the major hazards in plants and assist in recommending preventive actions. Nowadays, safety audits have become a significant activity for all chemical process companies. Detailed checklists have been developed that cover every aspect of health, safety, and loss prevention.
Context and Applications
Hazard analysis when applied to a process design or an operating plant helps to identify the potential hazards that may occur due to the deviations from the intended design conditions or disturbances. After completing graduation, students can undergo special value-added courses on Hazard and Risk analysis which make them industry-ready. This topic is useful in the following graduate and post-graduate courses such as Bachelor in Engineering (Chemical, Mechanical, Industrial Management & Petroleum), Master in Engineering (Chemical, Mechanical, Industrial Management & Petroleum).
Practice Problems
1. What is the full form of HAZOP?
- Hazard and operability study
- Hazard minimization
- Hazard operating system
- None of the above
Answer: Option a
Explanation: The full form of HAZOP is a hazard and operability study. It helps to identify the plant and equipment hazards and operability problems.
2. Who developed safety indexes?
- BASF
- DOW chemicals
- SGL carbon
- Dupont
Answer: Option b
Explanation: DOW chemicals developed Safety Indexes. Based on the properties of the material and nature of the process a numerical fire and explosion index will be calculated.
3. Logic gate analysis is a form of which hazard analysis?
- Hazard and operability Study
- Fault-tree Analysis
- Safety Indexes
- Safety Audits.
Answer: Option b
Explanation: Fault-tree analysis (FTA) uses AND” and “OR” logic gates to develop a failure model of a plant which helps to do hazard assesment.
4. When does an explosion happen?
- When a reaction occurs.
- When fuel and oxidant get mixed.
- When there is fire.
- When a huge amount of energy is released causing a pressure wave.
Answer: Option d
Explanation: When a huge amount of energy is released causing a pressure wave, an explosion occurs.
5. What is UVCE?
- Unidentified vapor explosion
- Unconfined vapor cloud explosion
- Unconfined velocity explosion
- None of the above
Answer: Option b
Explanation: Unconfined vapor cloud explosion (UVCE) occurs when the ignition of a large cloud of flammable material happens and the cloud burns at high speed causing an explosion.
Related Concepts
- Risk assessment
- Safety regulation
- Environment protection
- Safety devices
Want more help with your chemical engineering homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Process Design and Economics
Design considerations
Hazard analysis and design
Hazard Analysis and Design in Chemical Engineering Homework Questions from Fellow Students
Browse our recently answered Hazard Analysis and Design in Chemical Engineering homework questions.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.