What are adjustable frequency drives?
Adjustable frequency drives are solid-state devices popularly known as variable frequency drives. In some cases, they are also known as variable speed drives, microdrives, inverter drives, or motor speed controllers. The variable frequency drives are the motor drives specially used in the electromechanical system for controlling motor speeds. These variable frequency drives control the motor speed by regulating the input frequency and voltage of the alternating current (AC). An inductor can also be used in place of variable frequency drive to control the motor speeds, but it leads to huge losses in the form of heat energy. Hence, the variable frequency drives account for safe and efficient control of motor speeds. Besides speed control, a variable frequency drive can also be used to control the sudden torque experienced by a motor during its start-up and stopping, it also reduces torque fluctuations. Thus, a motor can run at constant torque at the required speeds.
There are other motor controllers such as the soft starters and across-the-line contractors, but they are less reliable and possess less efficiency than the variable frequency drives. Some of the applications of using variable frequency drives are:
- Variable frequency drives are used in large industries for controlling large induction motors, compressors, motor-driven pumps, and so on.
- Variable frequency drives are largely used in railway traction systems using large electro-mechanical systems.
- Variable frequency drives find their extensive uses in modern escalators, pumps, and lifts.
- Variable frequency drives are largely used in modern refrigerators and air-conditioning systems.
- With the variable frequency drives, a motor can run at a fixed speed without fluctuations.
In this article, a brief introduction has been provided regarding the variable frequency drives and their wide advantages over other motor control systems.

Working stages of variable frequency drives (VFD)
The VFDs are usually incorporated to control the speed of single-phase and three-phase induction motors. Their work is generally based on three stages, they are discussed below:
Rectifier stage
In the VFD rectifier stage, a diode acting as a full-wave rectifier is used. It converts a standard 50 Hz, 220 V, or 440 V AC voltage into a DC voltage. A suitable transformer is sometimes used to handle high voltages.
Inverter stage
The VFD houses an inbuilt inverter that produces a pure sine wave for controlling most of the single-phase and three-phase motors. The inverter consists of different power electronic switches such as insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT), gate turn-off thyristor (GTO), and silicon controlled rectifier (SCR). These switches perform on and off operations to switch the DC voltage at a required new frequency. The VFD inverters primarily use the pulse-width modulation (PWM) methodology. These switching operations by these power switches are at high speeds, which produce a short-width pulse of constant amplitude. The gain of the inverter adjusts the output voltage while the output frequency is varied by changing the number of pulses per half cycle.
Control system
The primary job of the control system of a VFD is to maintain a constant voltage to frequency ratio and to control the voltage that is being fed to the motor from the inverter. The control system also has an attached feedback system that continuously provides feedback from the motor to the control system regarding motor speed. Any mismatch in the motor speed is quickly regulated by the control system. The control system mainly uses sine wave PWM and space vector modulated PWM.
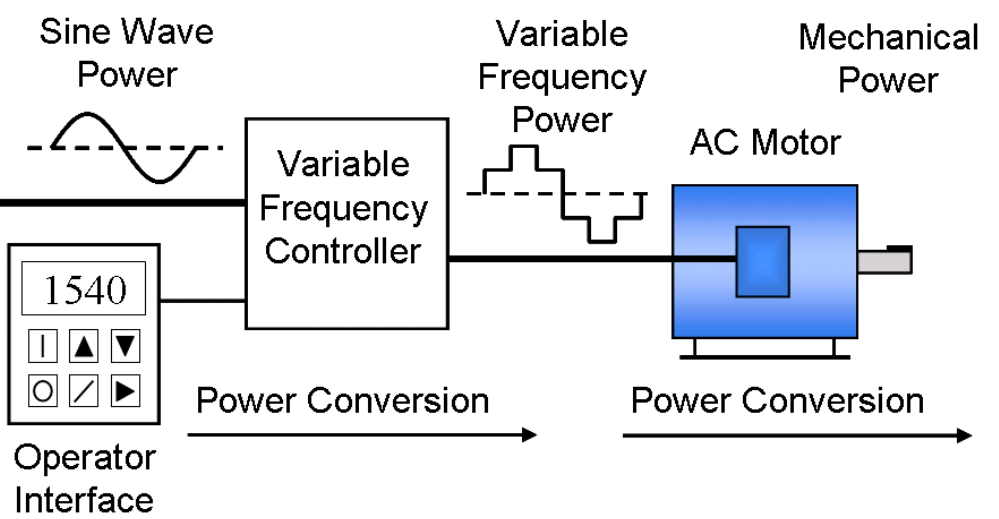
VFD system
A VFD system consists of different equipment, a complete VFD system architecture is discussed below.
AC motor
Three-phase induction motors are majorly used in a VFD system, while some of the synchronous single-phase induction motors are also used in a VFD system, which can result in certain advantages. Motors, specially designed for full-speed operations are generally controlled by the VFDs.
These AC motors are in turn used to operate a wide number of devices such as pumps and compressors in a power plant.
VFD controller
This is a solid-state power electronics system mainly coupled with a rectifier bridge controller, DC link, and inverter. The rectifier bridge mainly uses an AC-AC drive where they convert AC line input to AC line output. However, some applications use DC-AC drives. The DC-link converter houses a capacitor that reduces the voltage ripples and smoothens the out voltage that goes into the inverter. The inverter of the VFD controller converts the input voltage from the DC link to a quasi-sinusoidal AC voltage, by making power switches.
Operator interface
The operator interface of a VFD is a module through which a user can control the motor speed and can perform start/stop operations. The operator interface of the VFD is an alphanumeric type of display including lights and meters. These components allow the user to view the status of the motor during its operation. The interface also includes a keypad through which the user can input data regarding motor control. Some VFDs are also controlled by programmable logic controllers (PLCs).
Speed control
The speed controls can be achieved by using two ways, namely network and hardware. The network mode involves control by using transfer of speed data through communication protocols such as modbus, ethernet, keypad, and so on, whereas, the hardware mode includes pure communication cables for speed data transmissions.
Advantages of VFD
There are multiple advantages of using a VFD, some of them are outlined below:
- VFDs account for great energy savings and less energy loss in the form of heat.
- VFDs reduce the power when not required.
- VFDs account for dynamic torque control of motors.
- The motor speed and torque can be fully adjusted using a VFD.
- These devices reduce the peak energy demand.
- VFDs can control the starting current of a motor.
- Adjustable torque limit and controlled acceleration.
- VFDs provide smooth motor reversing.
- VFDs reduce mechanical drive systems for motor speed reductions such as gearboxes.
Context and Applications
The topic is widely used in many undergraduate and postgraduate degree courses of:
- Bachelors in Technology (Electrical Engineering)
- Bachelors in Technology (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)
- Masters in Technology (Electrical Engineering)
- Masters in Technology (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)
- Masters in Technology (Industrial Automation)
Practice Problems
1. Which of the following is the characteristic of a VFD?
- It is sensorless.
- It is a solid-state device.
- Both a and b.
- None of these
Answer: Option b
Explanation: VFDs are solid-state devices that are mostly used to control a variety of motor-driven equipment like pumps and compressors.
2. What is the function of soft starters?
- To control motor speed
- To make a motor run at full speed
- To reduce heating in motors
- For signal switching purposes
Answer: Option a
Explanation: Soft starters are conventional devices that are used to control motor speeds. But these devices are less reliable and are inefficient.
3. What is the abbreviation for PWM?
- Pulse-width modulation
- Pure width modulation
- Pulse width magnification
- None of these
Answer: Option a
Explanation: The correct abbreviation for PWM is pulse-width modulation.
4. Which of the following component of a VFD acts as a rectifier?
- Capacitor
- Diode
- GTO
- IGBT
Answer: Option b
Explanation: The diode acts as a rectifier in a VFD.
5. What is the other name of VFD?
- Variable speed drives
- Variable torque drives
- Variable voltage devices
- Both b and c
Answer: Option a
Explanation: The other name of VFD is variable speed drives.
Want more help with your electrical engineering homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Electrical Machines
Electric motor control
Adjustable frequency drive
Adjustable Frequency Drives Homework Questions from Fellow Students
Browse our recently answered Adjustable Frequency Drives homework questions.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.