What is Motor Startup and Troubleshooting Basics?
The electric motor startup serves the purpose to switch the electricity to a electric motor automatically or manually while also protecting the motor from overload or failures. Troubleshooting is a problem-solving technique that is widely used to repair malfunctioning of motor system components or processes. It's the meticulous, methodical search for the source of an issue in order to fix it and get the process back on track. After diagnosing the symptoms, troubleshooting is required.
Motor startup
A electric motor starter's main job is to start and stop the motor it is attached to. These are electro-mechanical switches, comparable to relays, that have been particularly designed. A starter has overload protection for the electric motor, which is the fundamental distinction between a relay and a starter.
Electric motor starters come in a variety of ratings and sizes. These starters provide the electric motor with the necessary power while also preventing the electric motor from drawing excessive current. In order to protect against starting current, the electric motor starter also protects against overload, single phasing, and low voltage.
Self-starting is a feature of a three-phase induction electric motor. A revolving magnetic field is created when the supply is linked to the stator of a three-phase induction electric motor, causing the rotor to rotate and the induction electric motor to start. The electric motor slip is unity at startup, and the beginning current is extremely high.
The electric motor can be started by connecting the three-phase induction electric motor directly to the full voltage of the power source. The electric motor can also be started by reducing the voltage connected to it. An induction motor's torque is determined by the square of the applied voltage. When an electric motor is started on full voltage, it produces more torque than when it is started on decreased voltage. And also an electric motor draws high starting current and it has high starting torque, so to limit high starting current and torque, starter is used.
Purpose of Starter
- To minimize the heavy initial current and torque.
- To prevent against overload and under voltage.
Types of Starting Method
- Direct On-line Starter
- Star-Delta Starter
- Auto-transformer Starter
- Stator Resistance Starter
Factors to be considered while installing an electric Motor
During the installation of new electric motors (single-phase motors and three phase electric motors) and controllers, they should be tested for functioning under load for at least one hour. During this time, the electrician might listen for unusual noises or look for hot areas (motor failure). The operating current must be compared to the ampere rating on the nameplate.
If the electric motor was not installed in a clean, well-ventilated area, clean the area. Cleanliness, as well as direct accident and fire prevention techniques, must be emphasized at all times.
Electric Motor Mounts
Motor mounts must be examined to ensure that they are secure and stable. Grout the mounts if needed. Ball-bearing motors can be installed vertically or horizontally on sidewalls or in the ceiling.
Rotate the end shields to put grease fittings, plugs, or any other apertures in the best, or most accessible, spot possible. If the bearings need to be lubricated, do that.
Nameplate
Compare the values on the power supply to the values on the name plate; they should match. Most motors will run satisfactorily if the line voltage is within 10% (plus or minus) of the name plate value, or if the frequency is within 5% of the name plate value (hertz). Most 220-volt motors can be utilized on 208-volt network systems, however performance will be significantly reduced. The 230-volt motors should generally not be utilized on 208-volt systems.
Follow the directions on the connection diagram on the nameplate to reconnect a dual-voltage motor to a specified voltage. Motor starting overload relay heaters of the right size must be installed. The engine will not start without them. The control enclosure lid contains sizing information. Similarly, the starting fuses should be tested. The correct fuse size must be chosen in compliance with the NEC (national electrical code) or local criteria.
Collector Ring and Commutators
Collector rings on wound rotor motors are occasionally film-coated at the factory to preserve them while in stock and during shipment. Brushes can be secured in an elevated position. The collector ring surface must be cleansed of the protective coating before the motor may be used. The brushes must then be placed on the collector ring or commutator.
Keep the rings clean and their polished surfaces in good condition while the motor is in service.
For commutators, chocolate brown is a good operating color. Normally, the rings will only need to be wiped down every now and again with a piece of canvas or a non-linting cloth. Allow no dust, dirt, moisture, or oil to collect between the collector rings.
Brushes
Brushes should be able to freely move about in their holders. They must also maintain firm, even touch with the collecting rings and commutators at the same time.
Fit fresh brushes to collector rings with care when installing them. Make that the pigtail conductors are securely attached to the brush holders and are in excellent contact with them. To suit the contour of the commutator or slip rings, it may be required to "sand in" brushes.
Loads
Electrical Load
A careful examination of the operating line voltages, both at the incoming line and near the motor terminals, may uncover imbalances that can be addressed. A three-phase electrical system that is out of balance might generate issues. In a three-phase distribution panel, avoid unbalanced single-phase loads. For solid-state devices, check if surge suppressors are needed.
Mechanical Load
To check rotation and free running action, run the motor without any load. The driving load's needed rotational direction is determined by the desired rotational direction. Some gearboxes, machinery, and equipment can be severely damaged if the rotation direction is incorrect. Interchanging any two line leads will reverse the rotation of a three-phase motor. Follow the wiring diagram to reverse the spin of a single-phase motors. To reduce vibration, the associated loads must be properly balanced. A machine that runs smoothly is more efficient and will cause less problems in the future.
What is Troubleshooting ?
Troubleshooting is a method of identifying and resolving problems in complicated equipment, electronics, computers, and software systems. A systematic technique to resolving a problem is known as troubleshooting. The purpose of troubleshooting is to figure out why something isn't working as it should and how to fix it.
Process of Troubleshooting
Step 1: Determine the issue.
Step 2: Create a reasonable cause theory.
Step 3: Determine the cause by putting the theory to the test.
Step 4: Create a plan of action for resolving the issue and putting the solution into action.
Step 5: Verify the entire system's functionality and, if necessary, take preventative steps.
Step 6: Keep a record of one's discoveries, actions, and outcomes.
Troubleshooting for Motor
1. After initial installation, motor does not start.
a) The motor is wrongly wired.
-Verify that the motor is properly wired using the wiring diagram.
b) The motor has been damaged, and the rotor is impacting the stator.
-Feel for rubbing as the rotation of the motor shaft occur.
c) Problems with the power supply or the line
-Check the power supply, overload, fuses, and controls, among other things.
2. After the motor has been running for a while, it fails to start.
a) The circuit breaker or fuse has tripped.
-Reset the breaker or replace the fuse.
b) The stator has been shorted or has gone to ground
-Examine the coils for any leakage. The motor must be changed if leaks are discovered.
c) Overloaded or jammed motor
-Check to see if the load is empty. Compare the motor's amp draw to the nameplate rating.
3. The motor turns on, but then stops.
a) Drop in voltage
- If the voltage is less than 90% of the motor's rated voltage, call one's utility company or double-check that another piece of equipment isn't stealing power from the motor.
b)The load has been raised.
-Check to see whether the load has changed or if the equipment has tightened. If you're using a fan, be sure the air flow hasn't altered.
4. The acceleration of the motor takes too long
a) Capacitor failure
- As per the prior instructions, test the capacitor and check capacitor.
b) Faulty bearings
- The motor supplier should replace any bearings that are noisy or feel rough.
c) Too low a voltage
- Ensure that the voltage is within 10% of the motor's rated voltage. If not, check with power company or see if something else is using power from the motor.
5. Overheating of the motor
a) Overload
-Compare the measured amps to the nameplate rating. Find the source of excessive friction in the motor or load and eliminate it. Reduce the load or replace the motor with a more powerful one.
b) Phasing with only one phase (three phase only)
- At all times, keep an eye on the current. It should be close to the name plate.
c) Inadequate ventilation
- Make sure that the external cooling fan is working correctly and that air is circulating via the cooling channels. Clean the motor if there is a lot of dirt on it.
6. Motor rotates in reverse direction
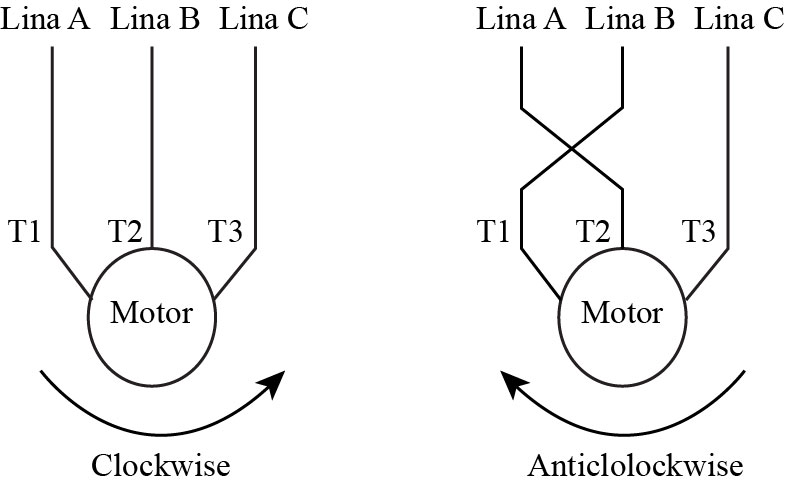
- Check line sequence of supply.
-If motor rotates in anticlockwise direction then change the sequence of supply line.
7. Motor winding damaged.
- Motor winding more heated.
-High current flowing through motor winding due to increasing load.
Advantages
- It enables the user to swiftly identify and correct the immediate common causes of motor failure.
- It will bring the user to the source of the problem as well as a long-term remedy.
Context and Applications
- In Industrial Motors
- Single-phase motors (Capacitor start capacitor run motor, Capacitor start motor, Permanent split capacitor motor)
- Various Machines
- Bachelor of Technology in Electrical Engineering
- Master of Technology in Electrical Engineering
Related Concepts
- Troubleshooting for Motor failure
- Troubleshooting for Transformer
- Troubleshooting for Induction Motors
- Troubleshooting for Generators
- Troubleshooting for single-phase motors(Capacitor start capacitor run motor, Capacitor start motor, Permanent split capacitor motor )
- Troubleshooting for Motor Winding
- Common causes for Motor failure
Common Mistake
- Overload
- Contamination
- Low resistance
- Over heating
- Vibration
Practice problems
Q1. What are types of Starting method?
A. DOL Starter
B. Star-Delta Starter
C. Autotransformer Starter
D. All of the above.
Answer: D
Explanation: The starting method of three phase induction motor are Direct On-line Starter, Star-Delta Starter, Auto-transformer Starter, Stator Resistance Starter.
Q2. Why starter is required?
A. To limit the starting current and torque.
B. To increase the starting current and torque.
C. To stabilize the torque
D. None
Answer: A
Explanation: When motor is directly connect to the supply then it draws heavy current so to minimize this current starter is used.
Q3. When motor does not start or motor failure? What do to?
A. Check the power supply, overload, fuses, and controls, among other things.
B. Verify that the motor is properly wired using the wiring diagram.
C. Both A and B
D. None
Answer: C
Explanation: Check the power supply, overload, fuses, and controls, among other things and Verify that the motor is properly wired using the wiring diagram taking these two actions when motor does not start.
Q4. A systematic technique to resolving a problem is known as...............
A. Troubleshooting
B. software
C. Maintenance
D. None
Answer: A
Explanation: A systematic technique to resolving a problem is known as troubleshooting.
Q5. What is the purpose of Troubleshooting?
A. To limit the starting current and torque.
B. To increase the starting current and torque.
C. To figure out why motor isn't working as it should and how to fix it.
D. None
Answer: C
Explanation: The purpose of troubleshooting is to figure out why motor isn't working as it should and how to fix it.
Want more help with your electrical engineering homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Electrical Machines
Electric motor control
Motor startup and troubleshooting basics
Motor Startup and Troubleshooting basics Homework Questions from Fellow Students
Browse our recently answered Motor Startup and Troubleshooting basics homework questions.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.