What is a strain gauge?
All the components used in civil engineering and mechanical engineering applications undergo deformations due to induced internal stresses under the application of external loads. Under repeated application of loads, there is a high possibility of failure of the components. Hence, periodic monitoring of the components and determination of stresses are very important.
Under practical scenarios and when the component is under functionality, estimation of stress is not possible. Hence, the stresses of the strain associated with the component are estimated with the use of sensors. The data from these sensors are interpreted with the stress-strain relationship to determine the stresses. These sensors are known as strain gauges. The strain gauges remain attached with the components or test specimen whose stresses are to be determined. The strain gauge is connected to a computer that shows the required values of stresses and deformations in the component under the 'view all' option of the software. A strain gauge can measure tensile strain, compressive strain, and shear strain. For instance, components with different cross-sectional areas can be examined for strains by using strain gauges.
Working principle of a strain gauge
The strain gauge can also be referred to as a strain sensor, whenever any external influence, such as force, is applied to it, there is a change in electrical resistance in the strain gauge. Measuring the amount of changed electrical resistance, the given value of forces is measured. These measured force values are used to estimate the stresses and strains in the component. The strain gauges can be compared with a transducer. A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy into another. In the case of a strain gauge, the mechanical energy due to applied forces is converted to electrical energy. There are various ways for the measurement of these electrical signals.
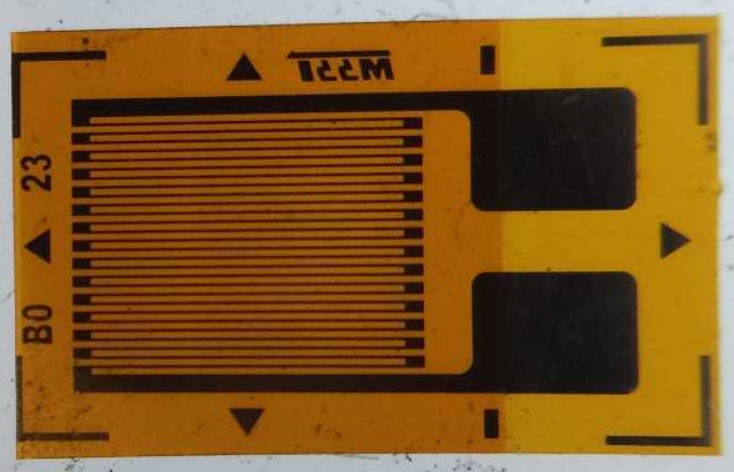
Types of strain gauge
General-purpose strain gauges
General-purpose strain gauges are foil-type strain gauges used for strain measurement in most civil engineering and mechanical engineering applications. This kind of foil-based strain gauges are used for experimental stress analysis and strain measurements; and for live monitoring purposes, when the components are in their functional conditions. The opposite sides of the foils in these types of strain gauges are made up of metals.
Transducer quality strain gauges
These kinds of strain gauges are extensively used for large experimental stress analysis and strain measurements. They are primarily meant for people who build transducer devices. The strain gauges are implemented inside the device for energy conversions.
Karma strain gauges
The karma strain gauges are used where measurements related to the long stability of values are required. These kinds of strain gauges can retain their values for longer periods of time. Karma strain gauges can also sustain high-temperature applications. Karma is an alloy of nickel and chromium.
Bonded metallic foil gauges
This kind of strain gauge has a diaphragm of a grid of resistors with certain resistance values. The gauge is directly bonded with the surface whose strain value needs to be measured by an epoxy resin. When there is a deformation in the component, there is a proportional deformation in the grid that is transferred by the resin. A change in resistance is observed that is converted to equivalent strain values.
Piezoresistors
Piezoresistors are a kind of strain gauge sensor that uses piezoelectric materials. Piezoelectric materials release small electric signals under deformations. These kinds of sensors are ideal for measuring small miniature strain values.
Strain gauge load cells
Load cells are a kind of force sensor that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Load cells have inbuilt strain gauges inside for measuring strains and deformations. These kinds of sensors are also known as pressure sensors.
Strain gauge circuits
Full bridge circuit
A full bridge circuit makes use of four strain gauges for measuring the strain. These strain gauges are connected in the form of a circuit. The strain can be measured by measuring the resistance that leads to a voltage change across terminals.
Quarter bridge circuit
A quarter bridge has a single strain gauge at the circuit arrangement. Due to applied force, there is an imbalance in the resistance of the circuit arrangement that is indicated as a voltage change by the voltmeter.
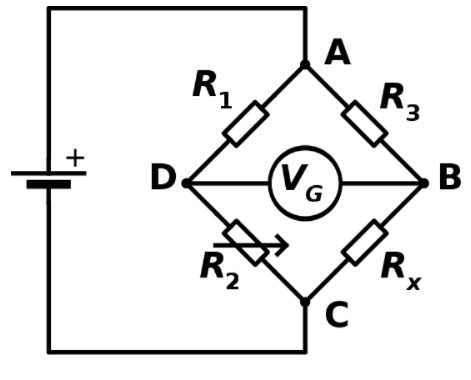
Wheatstone bridge circuit
Wheatstone bridge is a circuit arrangement that is used to determine an unknown resistance by comparing this unknown resistance with known resistances. It has four arms containing resistances, with one of the resistance being unknown whose value is to be measured. The bridge generally remains balanced with the voltmeter indicating zero.
Context and Applications
The topic is extensively used in civil engineering and mechanical engineering applications to measure strains associated with buildings and mechanical components. This topic is taught in undergraduate and post-graduate courses of bachelor of science and master of science degrees.
- Bachelors in Technology (Civil)
- Bachelors in Technology (Mechanical)
- Masters in Technology (Mechanical)
- Masters in Technology (Civil)
Practice Problems
1. Which of the following is a strain gauge?
- Karma strain gauge
- Gauge factor
- Foil strain gauge
- Both a and c
Correct option- d
Explanation: Karma strain gauge and foil strains gauges are all different types of strain gauges used for different applications.
2. Which of the following circuit implements only one strain gauge?
- Half bridge circuit
- Full bridge circuit
- Quarter bridge circuit
- None of these
Correct option- c
Explanation: A quarter bridge circuit implements a single strain gauge along with three resistances in the circuit.
3. Which of the following is true for transducers?
- It converts one form of strain to another.
- It converts one value of resistance to another.
- It converts one form of energy to another.
- It converts force values into pressure.
Correct option- c
Explanation: A transducer is a device that is used to convert one form of energy into another form of energy. As a transducer converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in strain gauges.
4. Which of the following represents the correct number of resistances present in a Wheatstone bridge?
- Two
- Three
- Four
- Five
Correct option- c
Explanation: A Wheatstone bridge implements four resistance in the circuit. Three are known resistance while the fourth one is an unknown resistance.
5. Which of the following is true for strain gauge?
- It measures strain values
- It measures force values
- It measures pressure values
- All of these
Correct option- d
Explanation: A strain gauge is used to measure strain values, force, and pressure.
Related Concepts
- Gauge factor
- Experimental stress analysis
Want more help with your mechanical engineering homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.