0.030 moles of a weak acid, HA, was dissolved in 2.0 L of water to form a solution. At equilibrium, the concentration of HA was found to be 0.013 M. Determine the value of Ka for the weak acid. 1 2 NEXT Based on the given values, fill in the ICE table to determine concentrations of all reactants and products. HA(aq) H:O(1) H:O“(aq) A-(aq) + + Initial (M) 0.015 Change (M) -X +x +x Equilibrium (M) 0.015 - x +x +x
0.030 moles of a weak acid, HA, was dissolved in 2.0 L of water to form a solution. At equilibrium, the concentration of HA was found to be 0.013 M. Determine the value of Ka for the weak acid. 1 2 NEXT Based on the given values, fill in the ICE table to determine concentrations of all reactants and products. HA(aq) H:O(1) H:O“(aq) A-(aq) + + Initial (M) 0.015 Change (M) -X +x +x Equilibrium (M) 0.015 - x +x +x
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter16: Solubility And Precipitation Equilibria
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 37P
Related questions
Question
This is the answer I got for this problem, but It's saying I have the change in concentration wrong. I don't understand what the help prompt is saying here.
I also have Ka = 2x/(0.015-x) = 0.0003
Is that correct? It didn't fit on the snip I took, sorry.
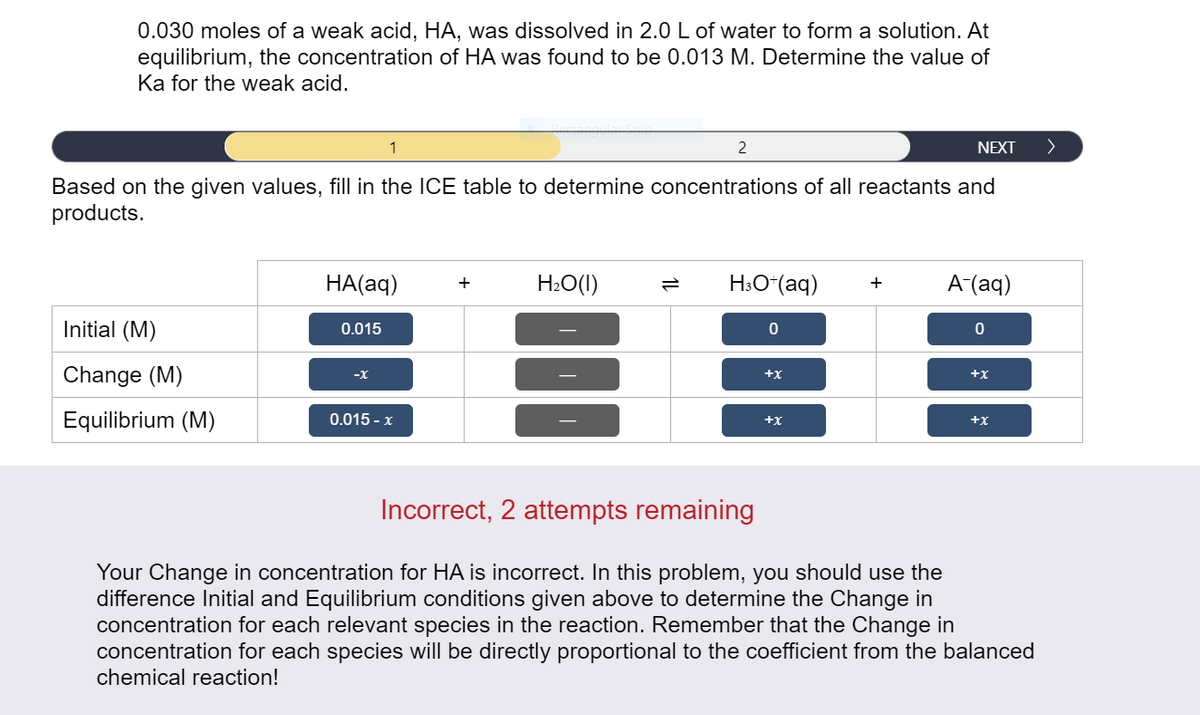
Transcribed Image Text:0.030 moles of a weak acid, HA, was dissolved in 2.0 L of water
equilibrium, the concentration of HA was found to be 0.013 M. Determine the value of
Ka for the weak acid.
form a solution. At
1
2
NEXT
Based on the given values, fill in the ICE table to determine concentrations of all reactants and
products.
HA(aq)
H:O(1)
H:O*(aq)
A (aq)
+
Initial (M)
0.015
Change (M)
-X
+x
+x
Equilibrium (M)
0.015 - x
+x
+x
Incorrect, 2 attempts remaining
Your Change in concentration for HA is incorrect. In this problem, you should use the
difference Initial and Equilibrium conditions given above to determine the Change in
concentration for each relevant species in the reaction. Remember that the Change in
concentration for each species will be directly proportional to the coefficient from the balanced
chemical reaction!
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning