1. Return to our Cournot competition model with two firms. Suppose now that the products aren't quite identical. In fact, both firms face different demand functions, P1 = a- b(q + dq2) P2 = a - b(dqı + 92) where d is some number between 0 and1 that specifies how similar the products are. Everything else about the model remains the same. (a) Calculate the best response functions for each firm. How does the slope of those best responses change with d? What happens when d= 0 or d = 1? (b) Calculate the equilibrium prices and quantities in this market. (Note: the firms are not identical).
1. Return to our Cournot competition model with two firms. Suppose now that the products aren't quite identical. In fact, both firms face different demand functions, P1 = a- b(q + dq2) P2 = a - b(dqı + 92) where d is some number between 0 and1 that specifies how similar the products are. Everything else about the model remains the same. (a) Calculate the best response functions for each firm. How does the slope of those best responses change with d? What happens when d= 0 or d = 1? (b) Calculate the equilibrium prices and quantities in this market. (Note: the firms are not identical).
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter12: Price And Output Determination: Oligopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1E
Related questions
Question
100%
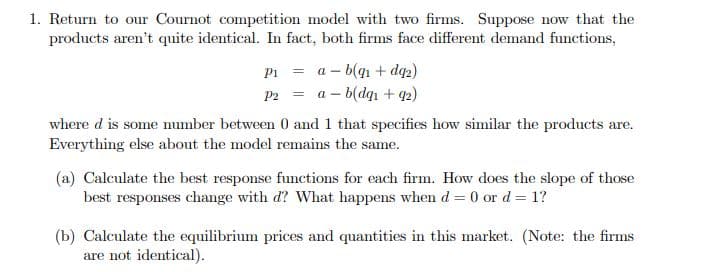
Transcribed Image Text:1. Return to our Cournot competition model with two firms. Suppose now that the
products aren't quite identical. In fact, both firms face different demand functions,
a – b(q1 + dq2)
a – b(dqn + 42)
Pi =
P2 =
where d is some umber between 0 and 1 that specifies how similar the products are.
Everything else about the model remains the same.
(a) Calculate the best response functions for each firm. How does the slope of those
best responses change with d? What happens when d = 0 or d = 1?
(b) Calculate the equilibrium prices and quantities in this market. (Note: the firms
are not identical).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Survey of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305260948
Author:
Irvin B. Tucker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

