1. What is the color of the doubly ionized Eriochrome Black T indicator in slightly basic solution? 2. Is it possible to use the sodium salt of EDTA as a primary standard?
1. What is the color of the doubly ionized Eriochrome Black T indicator in slightly basic solution? 2. Is it possible to use the sodium salt of EDTA as a primary standard?
Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305264434
Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Chapter27: Relative Stabilities Of Complex Ions And Precipitates Prepared From Solutions Of Copper(ii)
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1ASA
Related questions
Question
Hi answer these 2 questions. The two photos are just guide
1. What is the color of the doubly ionized Eriochrome Black T indicator in slightly basic solution?
2. Is it possible to use the sodium salt of EDTA as a primary standard?

Transcribed Image Text:..ll.l 0.02KB/s
10:45
59%
Experiment N...
Objective: At the end of the experiment, the student should be able to determine the total
hardness caused by dissolved calcium and magnesium ions by complexation
titration.
Materials and Reagents
Erlenmeyer flasks
Beaker
Pipet
Stirring rod
Na,H,Y.2H,O
calmagite indicator
NH,CI/NH,buffer, 3.2 g NH.CI + 28.5 ml conc. NH, diluted to 500 ml
volumetric flask
buret
dropper
watch glass
NaOH
Procedure
A. Preparation of EDTA solution
1. Weigh approximately 0.94 g of the dihydrate Na:H;Y.2H;O in a 100-ml beaker and dry
for one hour at 80°C.
2. Cool and add about 50.00 ml distilled water into the beaker and stir to dissolve the
EDTA.
3. Transfer the solution into a 250-ml volumetric flask through a funnel.
4. Add another 50.00 ml distilled water in the beaker to completely remove the EDTA
remained in the beaker
5. Transfer the washings into the flask and add water up to the mark.
6. Correct the mass of the EDTA by subtracting the 0.30% moisture it usually contains.
Using this mass and the formula weight of the sodium salt dihydrate, calculate the
molarity of the EDTA solution prepared. The solution prepared should be approximately
0.0100M
B. Preparation of pH 10 buffer solution
1. Weigh approximately 3.500g of ammonium chloride in 100 ml beaker
2. Add 30.00 ml of concentrated aqueous ammonia with sufficient distilled water to yield
50.00 ml of solution.
C. Analysis of the unknown
1. Pipet a 100.00 ml water sample assigned to your group into a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask
and swirl the solution.
2. Add 3-4 ml of the ammonia-ammonium chloride buffer to the flask and add sufficient
calmagite indicator so that the solution turns a deep red.
3. Heat the solution to between 60-80°C, place a magnetic stir bar in the flask
4. Titrate with the EDTA solution until the last tint of red disappears.
Transcribed Image Text:..l.l 0.23KB/s?
10:45
59%
Experiment N...
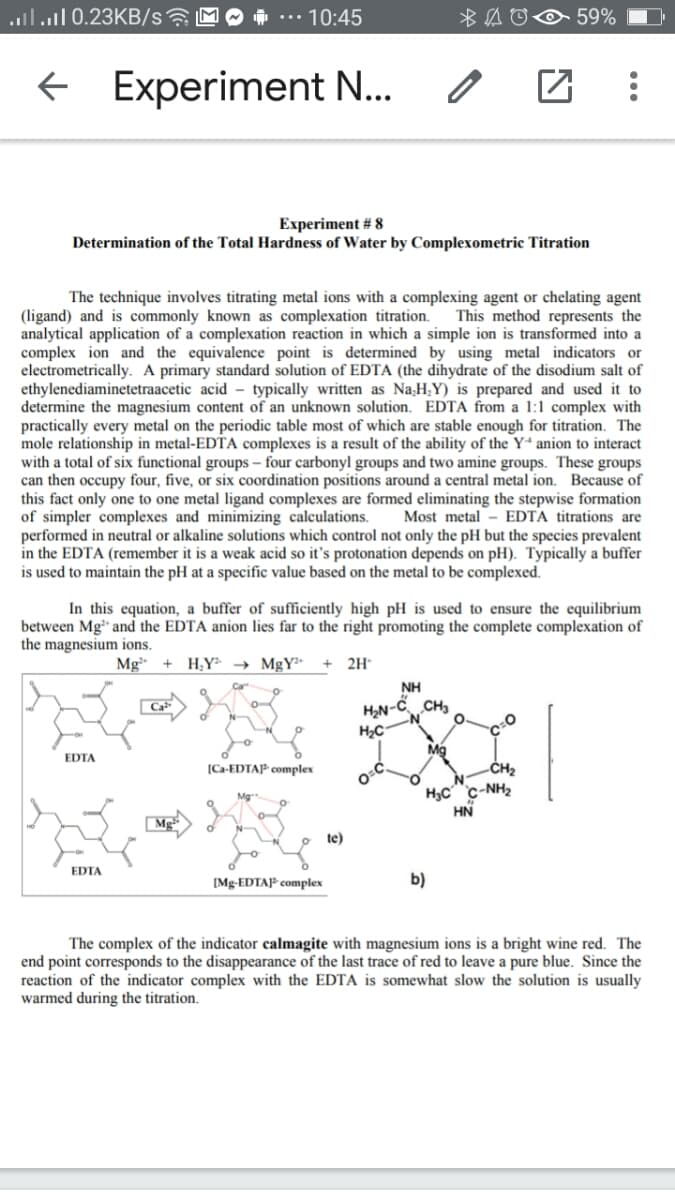
Experiment # 8
Determination of the Total Hardness of Water by Complexometric Titration
The technique involves titrating metal ions with a complexing agent or chelating agent
This method represents the
(ligand) and is commonly known as complexation titration.
analytical application of a complexation reaction in which a simple ion is transformed into a
complex ion and the equivalence point is determined by using metal indicators or
electrometrically. A primary standard solution of EDTA (the dihydrate of the disodium salt of
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid - typically written as NaH,Y) is prepared and used it to
determine the magnesium content of an unknown solution. EDTA from a 1:1 complex with
practically every metal on the periodic table most of which are stable enough for titration. The
mole relationship in metal-EDTA complexes is a result of the ability of the Y“ anion to interact
with a
can then occupy four, five, or six coordination positions around a central metal ion. Because of
this fact only one to one metal ligand complexes are formed eliminating the stepwise formation
of simpler complexes and minimizing calculations.
performed in neutral or alkaline solutions which control not only the pH but the species prevalent
in the EDTA (remember it is a weak acid so it's protonation depends on pH). Typically a buffer
is used to maintain the pH at a specific value based on the metal to be complexed.
of six functional groups – four
rbonyl groups a
e groups. Th
e groups
Most metal - EDTA titrations are
In this equation, a buffer of sufficiently high pH is used to ensure the equilibrium
between Mg" and the EDTA anion lies far to the right promoting the complete complexation of
the magnesium ions.
Mg
H;Y → MgY²*
2H
NH
H2N-
-č CH3
Mg
EDTA
[Ca-EDTAP complex
-CH2
H3C c-NH2
HN
te)
EDTA
[Mg-EDTAP complex
b)
The complex of the indicator calmagite with magnesium ions is a bright wine red. The
end point corresponds to the disappearance of the last trace of red to leave a pure blue. Since the
reaction of the indicator complex with the EDTA is somewhat slow the solution is usually
warmed during the titration.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305264434
Author:
Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305264434
Author:
Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
