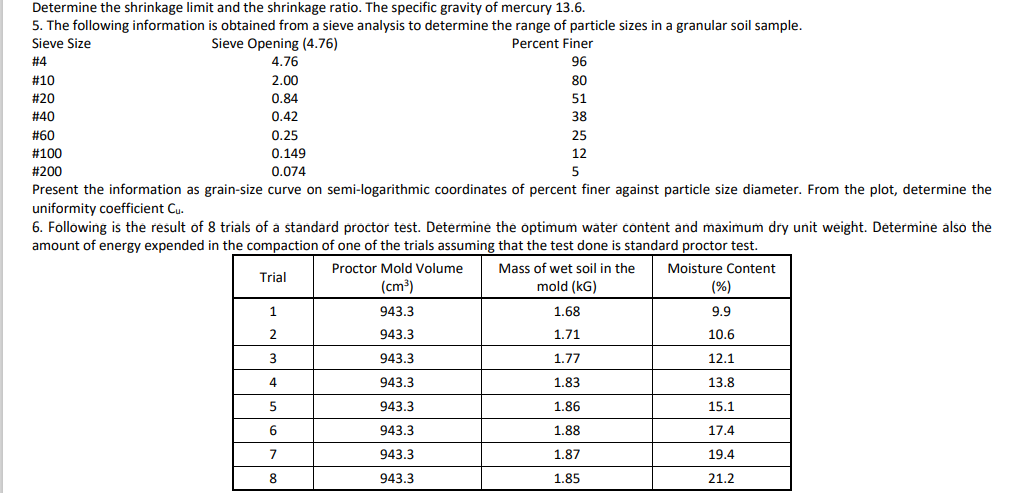
5. The following information is obtained from a sieve analysis to determine the range of particle sizes in a granular soil sample. Sieve Size Sieve Opening (4.76) Percent Finer # 4 4.76 96 #10 2.00 80 #20 0.84 51 #40 0.42 38 #60 0.25 25 #100 0.149 12 #200 0.074 Present the information as grain-size curve on semi-logarithmic coordinates of percent finer against particle size diameter. From the plot, determine the uniformity coefficient Cu.
5. The following information is obtained from a sieve analysis to determine the range of particle sizes in a granular soil sample. Sieve Size Sieve Opening (4.76) Percent Finer # 4 4.76 96 #10 2.00 80 #20 0.84 51 #40 0.42 38 #60 0.25 25 #100 0.149 12 #200 0.074 Present the information as grain-size curve on semi-logarithmic coordinates of percent finer against particle size diameter. From the plot, determine the uniformity coefficient Cu.
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
5th Edition
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Chapter2: Soil Deposits-origin, Grain-size, And Shape
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.14P
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the shrinkage limit and the shrinkage ratio. The specific gravity of mercury 13.6.
5. The following information is obtained from a sieve analysis to determine the range of particle sizes in a granular soil sample.
Sieve Size
Sieve Opening (4.76)
4.76
Percent Finer
#4
96
#10
2.00
80
#20
0.84
51
#40
0.42
38
#60
0.25
25
#100
0.149
12
#200
0.074
5
Present the information as grain-size curve on semi-logarithmic coordinates of percent finer against particle size diameter. From the plot, determine the
uniformity coefficient Cu.
6. Following is the result of 8 trials of a standard proctor tést. Determine the optimum water content and maximum dry unit weight. Determine also the
amount of energy expended in the compaction of one of the trials assuming that the test done is standard proctor test.
Proctor Mold Volume
Mass of wet soil in the
Moisture Content
Trial
(cm³)
mold (kG)
(%)
1
943.3
1.68
9.9
943.3
1.71
10.6
3
943.3
1.77
12.1
4
943.3
1.83
13.8
943.3
1.86
15.1
6.
943.3
1.88
17.4
7
943.3
1.87
19.4
943.3
1.85
21.2
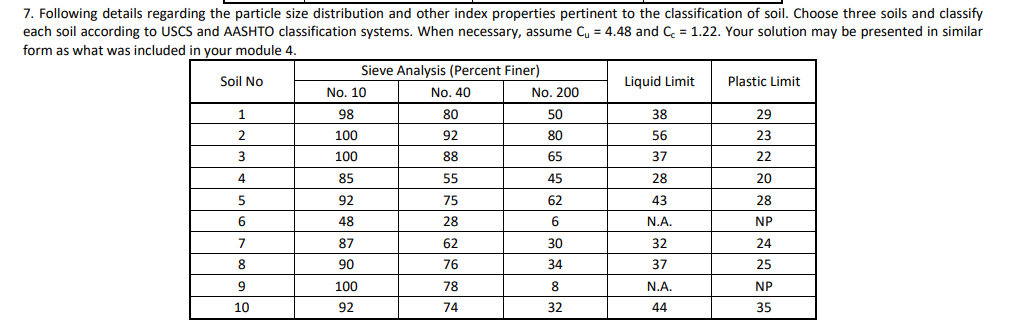
Transcribed Image Text:7. Following details regarding the particle size distribution and other index properties pertinent to the classification of soil. Choose three soils and classify
each soil according to USCS and AASHTO classification systems. When necessary, assume Cu = 4.48 and C = 1.22. Your solution may be presented in similar
form as what was included in your module 4.
Sieve Analysis (Percent Finer)
Soil No
Liquid Limit
Plastic Limit
No. 10
No. 40
No. 200
1
98
80
50
38
29
2
100
92
80
56
23
3
100
88
65
37
22
4
85
55
45
28
20
5
92
75
62
43
28
6
48
28
6
N.A.
NP
7
87
62
30
32
24
8
90
76
34
37
25
9
100
78
8
N.A.
NP
10
92
74
32
44
35
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305635180
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305970939
Author:
Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305635180
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305970939
Author:
Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning