52 D. P(AUB) = P(BNC) 38 52 30 52 = 2 52 = P(BUC) = 0;P(ANB) = 2 52 52
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter5: Inverse, Exponential, And Logarithmic Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 37RE
Related questions
Question
You want to draw cards from a complete poker deck without a joker (52 cards), considering the following events: A={Is a figure}; B={It's red}; C={It's an Ace} The correct probabilities correspond to:
What is the correct?
(IMG 1)
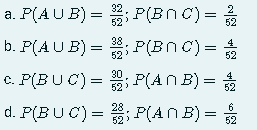
Transcribed Image Text:P(BNC) = 2/1/2
52
a. P(AUB) =
38
b. P(AUB) = 3; P(BNC): =
52
30
c. P(BUC) = 0; P(ANB) =
52
6
d. P(BUC) = P(ANB) = 2
52
52
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Elementary Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9780998625713
Author:
Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Elementary Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9780998625713
Author:
Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell