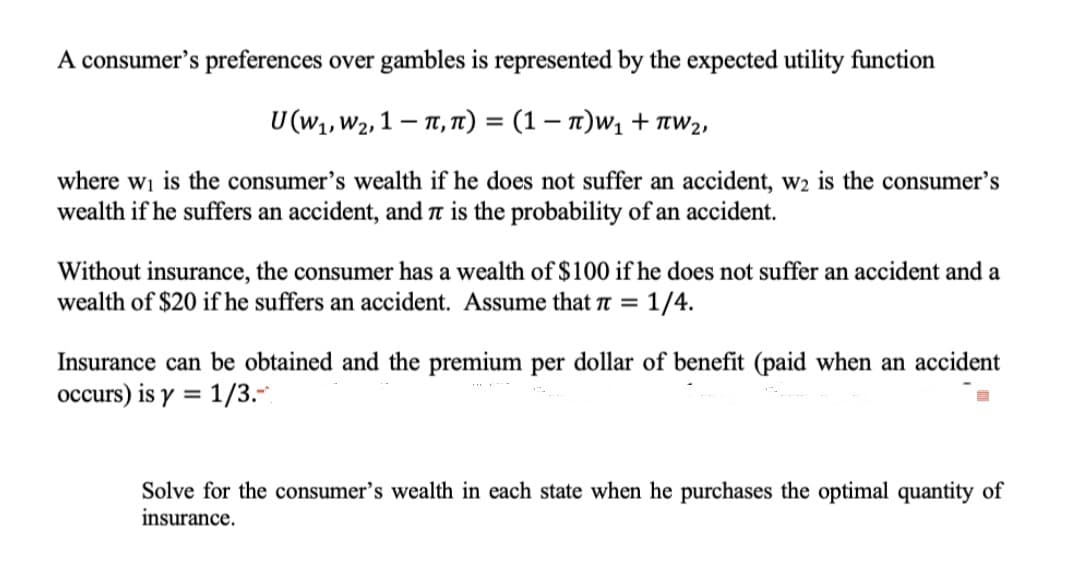
A consumer's preferences over gambles is represented by the expected utility function U (W,, W2, 1 – 1T, T1) = (1 – n)w1 + aw2, %3D where wi is the consumer's wealth if he does not suffer an accident, w2 is the consumer's wealth if he suffers an accident, and is the probability of an accident. Without insurance, the consumer has a wealth of $100 if he does not suffer an accident and a wealth of $20 if he suffers an accident. Assume that r = 1/4. Insurance can be obtained and the premium per dollar of benefit (paid when an accident occurs) is y = 1/3. %3D
Q: 37. A nominal rate of 15% compounded monthly is equal to what effective rate of interest. 18.95% 15....
A: Answer- "Thank you for submitting the questions.But, we are authorized to solve one question at a ti...
Q: Determine the accumulated amounts after 5 years of P1,000.00 invested at the rate of 10% compounded ...
A: Since you have posted multiple questions, as per guidelines we can solve only the first question per...
Q: A company manufactures two products A and B. Each unit of A requires 4 labour hours of processing an...
A: Answer is given below
Q: O Consi der Hhe following » The inverse femand function is given by p= 30-@ where Q= Eit $ Cournet m...
A: First, we look at the answers form previous parts. Firm 1 reaction function: 2q1+q2=24Firm 2 reactio...
Q: A firm's marginal cost can always be thought of as the change in total cost if O the firm moves to t...
A: The marginal cost definition is the cost of producing a service or product unit that is not intended...
Q: What is the Marginal Cost if TC =10+5q What is the marginal cost if TC= 100+5q Explain
A: TC=10+5qNow,MC=∂TC∂qMC=∂(10+5q)∂qMC=10
Q: 2. Zhoran has a budget of $36 for fruit. Strawberries cost $4 per pound and grapes cost $3 per pound...
A: Consumer will maximise utility at a point where slope of an indifference curve is equal to the slope...
Q: A person with utility function Ux, y) = 5+ y+ 2x has nonconvex preferences. True False
A: Answer:- TRUE
Q: TABLE 2.2 Present-Worth Analysis (cost/ft) Based on 80-yr Life and 10% Simple Interest Assumed Initi...
A: Given:
Q: 4. Under imperfect competition with with and horizontaly differentiated products, the firm units fro...
A: "Since you have asked multiple questions, we will solve first question for you .. If you want any sp...
Q: You want to buy an apartment at the price of 4 million Hong Kong dollars. You will do this with a mo...
A: Given, Amount- 4 million Rate of Interest- 8% Time- 30 years
Q: Asian Monetary Fund is existing today. The International Monetary Fund is an example that illustrat...
A: Here, two information about international agreement among the nations, especially by the Asian natio...
Q: 4) Suppose each stock in a portfolio has returns (over the upcoming year) of R = BRm + e, i=1,2,.n W...
A: In order to proceed onto the given case study, we first need to analyze the meaning of basic terms u...
Q: Prepare a flow chart for a typical family of 4 (3 drivers), taking a two-week (Monday is 1st-14th is...
A: The given case is tied in with making a flowchart for a family get-away outing for four individuals ...
Q: person receives SR10,000 today and wants to invest it at 8% per year to be able to withdraw SR2000 e...
A: Investment is the act of keeping money in bank or any other organization for earning profit.
Q: The table shows the price and quantity demanded for floor mats. Using the Midpoint Method, what is t...
A: Point Price Quantity B P1=43 Q1=480 C P2=46 Q2=460 Mid point method of price elasticity of ...
Q: Calculate GDP, what is included...what is not? Criteria USD in Billions Personal Consumption Expendi...
A: Y = C+I+G+NX Y= GDP = Gross domestic product = National income C= Consumption expenditure I= Investm...
Q: The economy of Ashenvale is currently in a long-run equilibrium, depicted by point E, on the graph. ...
A: The given question is related to the aggregate demand-aggregate supply macroeconomics model.
Q: 21.Consider the following game, which depicts US and Soviet confrontation during the Cuban Missile C...
A: In economics, the game theory is a tool for the strategic interaction of two rational decision-maker...
Q: 69. Quantity of a certain commodity that is bought at a certain price at a given place and time. lux...
A: Dear student as you have posted multiple questions on the portal, but according to policies and guid...
Q: 4. )At Alan's landscaping firm, labor is fixed in the short run. Increasing his use of capital alway...
A: The first stage is increasing returns, the second stage is diminishing returns and the third stage i...
Q: In 1938, major powers met in Munich to discuss Germany’s demands to annex part of Czechoslovakia. Le...
A: Given information 2 countries Allies and Germany Allies has 2 strategy compromise and fight Germany ...
Q: Explain the two types of demand.
A: Demand: It is one of the two forces of the economy which drives the economy and the market. It is cl...
Q: Consider the following Cobb-Douglas production function. Q=10 K1/2L1/2 a. Find the first, second, an...
A: The Cobb-Douglas production function shows the technological relationship between the amount of two ...
Q: Figure 8 shows a price-taker firm with demand curve, D, a short run cost curve, AC, and marginal cos...
A: A perfectly competitive firm is a price taker. It means the price is determined by the market forces...
Q: Consider the following Cobb-Douglas production function. Q = 25K0.4L0.3 a. Find the first, second, a...
A: The Cobb-Douglas production functions show the technical relationship between two or more inputs and...
Q: A magician recorded his magic show and broadcast it freely in internet. How would you classify the ...
A: Excludable – Some people can be prevented by the producers from consuming the good/service based on ...
Q: Suppose that the demand in a particular industry is given by Qd = 100 - 2P. When the market price in...
A: Introduction: Demand is defined as the number of customers that are willing and able to purchase thi...
Q: 1. The demand for good X is given by Qdx 1,200-P+P,-8P, +M. Research shows that the prices of relate...
A: Cross price elasticity = Percentage change in quantity for good X / Percentage change in the price o...
Q: All of the following statements about government-supported research are true, except: Select the cor...
A: Government-supported research refers to the funding of the government to conduct research. This is d...
Q: Match the following: a) Diamond water paradox b) Value and capital c) Principles of economics d) Lan...
A: Diamond Water Paradox was pondered by Adam Smith. Value and Capital is a book by J.R. Hicks. Princip...
Q: 1. A passenger train was bought at Php 36000000 and will incur 1500000 of annual operation and maint...
A: We are going to use PW approach to calculate Capitalized Cost of this project.
Q: B. Suppose fast food workers currently earn $8 per hour and the aggregate price level is $2. A numbe...
A: Real wage=Nominal wagePrice
Q: The following table shows the composition of GDP in 2015 for a hypothetical country. Complete the ta...
A: GDP =? Consumption = 11486 Investment = 2431 Non Residential = 1889 Residential = ? Government Spend...
Q: The following table shows the composition of GDP in 2015 for a hypothetical country. Complete the ta...
A: Gross domestic product measures the value of goods and services at current year market prices.
Q: Consider an economy with 2 workers. If the value of the marginal product of labor (VMPL) is $50 and ...
A: The marginal revenue product (MRP) is the additional revenue generated by a single additional unit o...
Q: a) Graph her consumer choice model (with chicken onthe x axis. Nowlet price of chicl fall, causing L...
A: Two goods are considered in the market chicken and rice with price of chicken and rice denoted as Pc...
Q: Which of the following legislative constraints applies to the issue of minimum wage? a. human rights...
A: The answer is - b. trade union legislation
Q: A 10,000 Par Disney bond has a 4% coupon and will mature in 10 years. If its yielding (YTM) 5% w...
A: Yield to Maturity: The yield to maturity (YTM) is the expected annual rate of return for a bond assu...
Q: The price p (in dollars) and the quantity q sold of a certain product obey the demand equation q = 8...
A: The demand equation is given below: q = 800 - 20p or, 20p = 800 - q p = 800 - q20 Total Revenue (TR)...
Q: Distinguish between (Any Three): a) Short-run and Long-run Production function b) Gains from exchang...
A: a) short run production function long run production function 1 short run is ...
Q: Four hundred driver's license applicants were randomly selected and asked whether they passed their ...
A:
Q: Compute price index number by simple average of price relatives method using arithmetic mean and geo...
A: The formula used to calculate Price Index is : Price Index = Cost of Market Basket in current yearCo...
Q: 41. An equipment costs P100,000.00 and the salvage value is 15% of the original cost after 25 years....
A: We will answer the first question since the exact one was not specified. Please submit a new questio...
Q: What changes has the supply and demand of micro chip seen recently and expected for the future? How ...
A: The demand curve shows the association between the amounts of commodity demanded by the consumer at ...
Q: What is economic integration
A: Government resorts to fiscal policy to increase employment by increasing aggregate demand. Now there...
Q: The following table shows how three voters ranked Policy A, Policy B, and Policy C. Which policy is ...
A: Majority Decision is the one where more than 50% of the votes are in favor of one policy.
Q: Every year in September, the NFL (National Football League) announces official prices of their next ...
A: Give information:1. Price range for tickets is from $6800 to $81800. 2. Three fourth tickets are dis...
Q: 1.Consider the Economy of Rwanda. The consumption function is given by ?=200+0.75[?−?] while the inv...
A: Note:- Since we can only answer up to three subparts, we'll answer first three. Please repost the qu...
Q: Consider the following version of the short run monetary model: (UK) MD/P = exp(-0.50*i)*Y MS = M i=...
A:
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

- A woman with current wealth X has the opportunity to bet an amount on the occurrence of an event that she knows will occur with probability P. If she wagers W, she will received 2W, if the event occur and if it does not. Assume that the Bernoulli utility function takes the form u(x) = with r > 0. How much should she wager? Does her utility function exhibit CARA, DARA, IARA? Alex plays football for a local club in Kumasi. If he does not suffer any injury by the end of the season, he will get a professional contract with Kotoko, which is worth $10,000. If he is injured though, he will get a contract as a fitness coach worth $100. The probability of the injury is 10%. Describe the lottery What is the expected value of this lottery? What is the expected utility of this lottery if u(x) = Assume he could buy insurance at price P that could pay $9,900 in case of injury. What is the highest value of P that makes it worthwhile for Alex to purchase insurance? What is the certainty…Dr. Gambles has a utility function given as U(w)=In(w). Due to the pandemic affecting his consulting business, Dr Gambles faces the prospect of having his wealth reduced to £2 or £75,000 or £100,000 with probabilities of 0.15, 0.25, and 0.60, respectively. Suppose insurance is available that will protect his wealth from this risk. How much would he be willing to pay for such insurance?Leora has a monthly income of $20,736. Unfortunately, there is a chance that she will have an accident that will result in costs of $10,736. Thus leaving her an income of only $10,000. The probability of an accident is 0.5. Finally assume that her preferences over income can be represented by the utility function u(x) = 2ln(x).a) What is the expected income? What is Leora’s expected utility (you may leave in log form)? b) What is the certainty equivalent to her situation? What is the risk premium associated with her situation?c) What is the maximum that Leora would be willing to pay for a full insurance policy?d) Illustrate her expected utility, expected wealth, certainty equivalent, the risk premium and her willingness to pay for a full insurance policy in a diagram.
- Y5 Alfred is a risk-averse person with $100 in monetary wealth and owns a house worth $300, for total wealth of $400. The probability that his house is destroyed by fire (equivalent to a loss of $300) is pne = 0.5. If he exerts an effort level e = 0.3 to keep his house safe, the probability falls to pe = 0.2. His utility function is: U = w0.5 – e where e is effort level exerted (zero in the case of no effort and 0.3 in the case of effort).a. In the absence of insurance, does Alfred exert effort to lower the probability of fire?HINT: Calculate and compare the expected utility i) with effort, and ii) without effort. If effort is exerted, then the effort cost is paid regardless of whether or not a fire occurs.b. Alfred is considering buying fire insurance. The insurance agent explains that a home owner’s insurance policy would require paying a premium α and would repay the value of the house in the event of fire, minus a deductible “D”. [A deductible is an amount of money that the…Suppose that consumers have utility function U(C) = log(C) where C is the consumption level and log is the natural logarithm. Consumers have initial consumptionlevels of 100 and are exposed to the following risk of loss: lose 10 with probability0.4 and lose 5 with probability 0.6. They are considering buying insurance to coverthese losses. What is the fair price for the insurance?Let U(x)= x^(beta/2) denote an agent's utility function, where Beta > 0 is a parameter that defines the agent's attitude towards risk. Consider a gamble that pays a prize X = 10 with probability 0.2, a price X = 50 with probability 0.4 and a price X = 100 with probability 0.4. Compute the agentís expected utility for such gamble and find the value of Beta such that the agentis risk neutral? Suppose B= 1, what is the certainty equivalent of the gamble described above? What is the Arrow-Pratt measure of absolute risk aversion?
- Assume that your utility has a natural log function U(W)=ln(W), which is a concave function. Your car is worth $10,000 and your total wealth is $20,000 including the car. There is a 5% chance that a major accident occurs and you have a total loss of $10,000; a 10% chance that a minor accident occurs and you have a loss of $500; 85% chance you will not have any accident. Given these assumptions, how much are you willing to pay for an insurance that provides full coverage against car accidents? Thank you. Regards, Jim CarrollGary likes to gamble. Donna offers to bet him $31 on the outcome of a boat race. If Gary’s boat wins, Donna would give him $31. If Gary’s boat does not win, Gary would give her $31. Gary’s utility function is p1x^21+p2x^22, where p1 and p2 are the probabilities of events 1 and 2 and where x1 and x2 are his wealth if events 1 and 2 occur respectively. Gary’s total wealth is currently only $80 and he believes that the probability that he will win the race is 0.3. Which of the following is correct? (please submit the number corresponding to the correct answer). Taking the bet would reduce his expected utility. Taking the bet would leave his expected utility unchanged. Taking the bet would increase his expected utility. There is not enough information to determine whether taking the bet would increase or decrease his expected utility. The information given in the problem is self-contradictory.The von-Neumann Morgenstern utility function is of the form u(e) - In(e). There is a lottery over consumption outcomes: with probability 0.3, the consumption will be 1 and with probability 0.7 the consumption will be 3; Compute the risk premium (round to 2 decimals).
- By using the expected utility theory approach with u(x)=x2, choose the optimal decision for three different possible outcomes with probabilities p(ω1)=1/2, p(ω2)=p(ω3)=1/4, rewards R(d1,ω1)=£49,R(d1,ω2)=R(d1,ω3)=£25, R(d2,ω1)=£36,R(d2,ω2)=£100,R(d2,ω3)=£0, R(d3,ω1)=£81,R(d3,ω2)=R(d3,ω3)=£0John is a farmer with $225 of wealth. He can either plant corn or beans. If he plants corn, John earns an income of $675 if the weather is GOOD and $0 if the weather is BAD. If he plants beans, John earns an income of $451 under both GOOD and BAD weather. The probability of GOOD weather is 0.7. The probability of BAD weather is 0.3. John’s utility function is U(c) = 5√c , where c is the value of consumption. Mae owns an insurance company in a nearby town and has decided to offer conventional crop insurance to corn farmers in the area. Assume that Mae has perfect information and can write and enforce an insurance contract that requires the farmer to plant corn. Here’s how the insurance contract works. At the beginning of the year, the corn farmer pays an insurance premium of $202.5. If the weather is GOOD, Mae makes no payment to the farmer. If the weather is BAD, Mae makes an indemnity payment of $675 to the farmer. a. If a farmer buys this insurance contract,what is Mae’s expected…Tess and Lex earn $40,000 per year and all earnings are spent on consumption (c). Tess and Lex both have the utility function c. Both could experience an adverse event that results in earnings of $0 per year. Tess has a 1% chance of experiencing an adverse event and Lex has a 12% chance of experiencing an adverse event. Tess and Lex are both aware of their risk of an adverse event. 1. Suppose the actuarially fair premium charge is 2600, Calculate Tess’ expected utility with full insurance if she is charged the premium. Round to two decimal places. 2. What is the premium that private insurance companies will charge for full insurance? Round to two decimal places. 3.Assume the social welfare function is the sum of the Tess’ and Lex’s utility functions. Select the correct statement regarding the explanation for what has happened in the private market and the role of social insurance. a.Adverse section has lead to market failure. The government could improve social welfare by…

