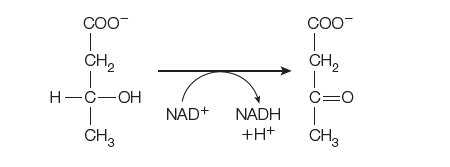
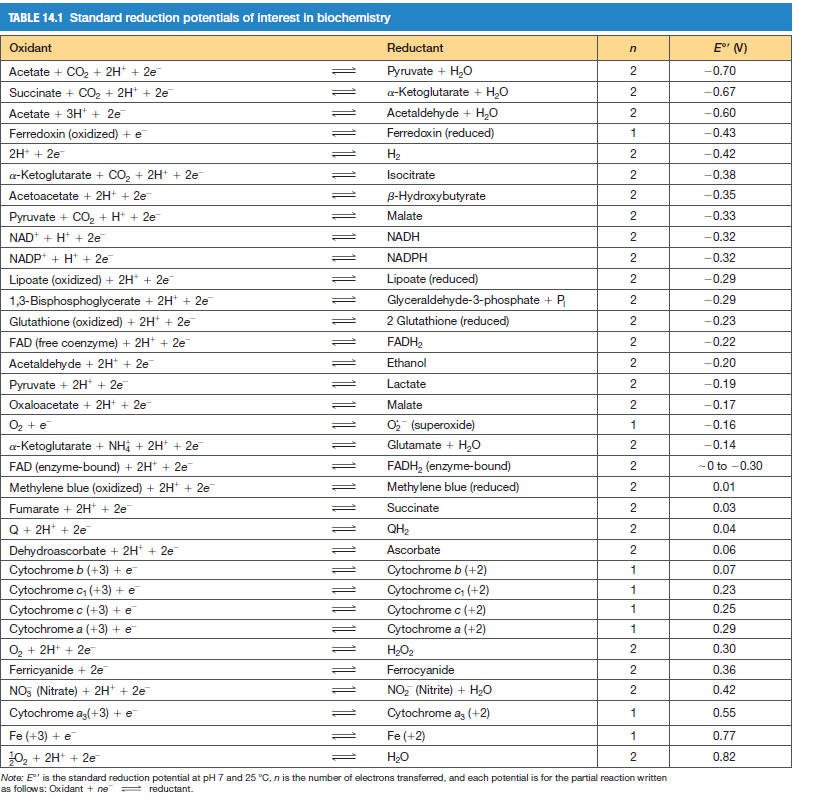
CO0- CH, CH, Н-С—ОН C=0 NAD+ NADH +H+ CH3 CH3 TABLE 14.1 Standard reduction potentials of interest in biochemistry Oxidant Reductant E" (V) Acetate + CO2 + 2H* + 2e Pyruvate + H20 -0.70 Succinate + CO2 + 2H* + 2e a-Ketoglutarate + H,0 -0.67 Acetate + 3H* + 2e -0.60 Acetaldehyde + H,0 Ferredoxin (reduced) 2 Ferredoxin (oxidized) + e 1 -0.43 2H* + 2e H2 2 -0.42 a-Ketoglutarate + CO, + 2H+ + 2e Isocitrate -0.38 Acetoacetate + 2H+ + 2e B-Hydroxybutyrate -0.35 Pyruvate + CO, + H* + 2e Malate -0.33 NAD+ + H* + 2e NADH -0.32 NADP* + H* + 2e NADPH 2 -0.32 Lipoate (oxidized) + 2H* + 2e Lipoate (reduced) -0.29 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate + 2H* + 2e Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + P -0.29 Glutathione (oxidized) + 2H* + 2e 2 Glutathione (reduced) -0.23 FAD (free coenzyme) + 2H* + 2e FADH2 2 -0.22 Acetaldehyde + 2H + 2e Pyruvate + 2H + 2e Ethanol 2 -0.20 Lactate 2 -0.19 Oxaloacetate + 2H* + 2e Malate -0.17 O2 + e a-Ketoglutarate + NHị + 2H + 2e O (superoxide) Glutamate + H,0 1 -0.16 -0.14 FAD (enzyme-bound) + 2H* + 2e FADH, (enzyme-bound) -0 to -0.30 Methylene blue (oxidized) + 2H* + 2e Methylene blue (reduced) 0.01 Fumarate + 2H* + 2e Succinate 2 0.03 Q + 2H* + 2e Dehydroascorbate + 2H* + 2e Cytochrome b (+3) + e QH2 2 0.04 Ascorbate 0.06 Cytochrome b (+2) 0.07 Cytochrome c, (+3) + e Cytochrome c, (+2) 1 0.23 Cytochrome c (+3) + e Cytochrome c (+2) 1 0.25 Cytochrome a (+3) + e Cytochrome a (+2) 1 0.29 O2 + 2H+ + 2e H2O2 0.30 Ferricyanide + 2e Ferrocyanide 2 0.36 NO, (Nitrate) + 2H* + 2e NO, (Nitrite) + H2O 2 0.42 Cytochrome a,(+3) + e Cytochrome a, (+2) 0.55 Fe (+3) + e Fe (+2) 1 0.77 0, + 2H* + 2e H20 0.82 Note: E" is the standard reduction potential at pH 7 and 25 °C, n is the number of electrons transferred, and each potential is for the partial reaction written as follows: Oxidant + ne = reductant.
Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain, also known as the electron transport system, is a group of proteins that transfer electrons through a membrane within mitochondria to create a gradient of protons that drives adenosine triphosphate (ATP)synthesis. The cell uses ATP as an energy source for metabolic processes and cellular functions. ETC involves series of reactions that convert redox energy from NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) + hydrogen (H)) and FADH2(flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)) oxidation into proton-motive force(PMF), which is then used to synthesize ATP through conformational changes in the ATP synthase complex, a process known as oxidative phosphorylation.
Metabolism
Picture a campfire. It keeps the body warm on a cold night and provides light. To ensure that the fire keeps burning, fuel needs to be added(pieces of wood in this case). When a small piece is added, the fire burns bright for a bit and then dies down unless more wood is added. But, if too many pieces are placed at a time, the fire escalates and burns for a longer time, without actually burning away all the pieces that have been added. Many of them, especially the larger chunks or damp pieces, remain unburnt.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the cellular process involved in the generation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules from the organic nutritional source obtained from the diet. It is a universal process observed in all types of life forms. The glucose (chemical formula C6H12O6) molecules are the preferred raw material for cell respiration as it possesses a simple structure and is highly efficient in nature.
Freshly prepared mitochondria were incubated with β-hydroxybutyrate, oxidized cytochrome c, ADP, Pi, and cyanide. β-hydroxybutyrate is oxidized by an NAD+-dependent dehydrogenase.
The experimenter measured the rate of oxidation of β-hydroxybutyrate and
the rate of formation of ATP.
(a) Indicate the probable flow of electrons in this system.
(b) How many moles of ATP would you expect to be formed per mole of
β-hydroxybutyrate oxidized in this system?
(c) Why is b-hydroxybutyrate added rather than NADH?
(d) What is the function of the cyanide?
(e) Write a balanced equation for the overall reaction occurring in this
system (electron transport and ATP synthesis).
(f) Calculate the net standard free energy change (ΔG°') in this system,
using E'0 values from Table 14.1 and a ΔG°' value for ATP hydrolysis
of -32.2 kJ/mol.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









