compoundS In a neutral compound, the sum of the oxidation states is zero. Note that the sign of the oxidation states and the number of atoms associated with each oxidation state must be considered. In H2O, for example, each hydrogen atom has an oxidation state of +1 and each oxygen atom has an oxidation state of –2 for a total of 2(+1) + (-2) = 0. Part A What is the oxidation state of an individual sulfur atom in BaSO4? Express the oxidation state numerically (e.g., +1). • View Available Hint(s) Submit Part B What is the oxidation state of an individual nitrogen atom in HNO3 ? Express the oxidation state numerically (e.g., +1). • View Available Hint(s)
compoundS In a neutral compound, the sum of the oxidation states is zero. Note that the sign of the oxidation states and the number of atoms associated with each oxidation state must be considered. In H2O, for example, each hydrogen atom has an oxidation state of +1 and each oxygen atom has an oxidation state of –2 for a total of 2(+1) + (-2) = 0. Part A What is the oxidation state of an individual sulfur atom in BaSO4? Express the oxidation state numerically (e.g., +1). • View Available Hint(s) Submit Part B What is the oxidation state of an individual nitrogen atom in HNO3 ? Express the oxidation state numerically (e.g., +1). • View Available Hint(s)
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter4: Energy And Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 84QRT: Oxygen is not normally found in positive oxidation states, but when it is combined with fluorine in...
Related questions
Question
Please answer question 14 Part B, C, and D
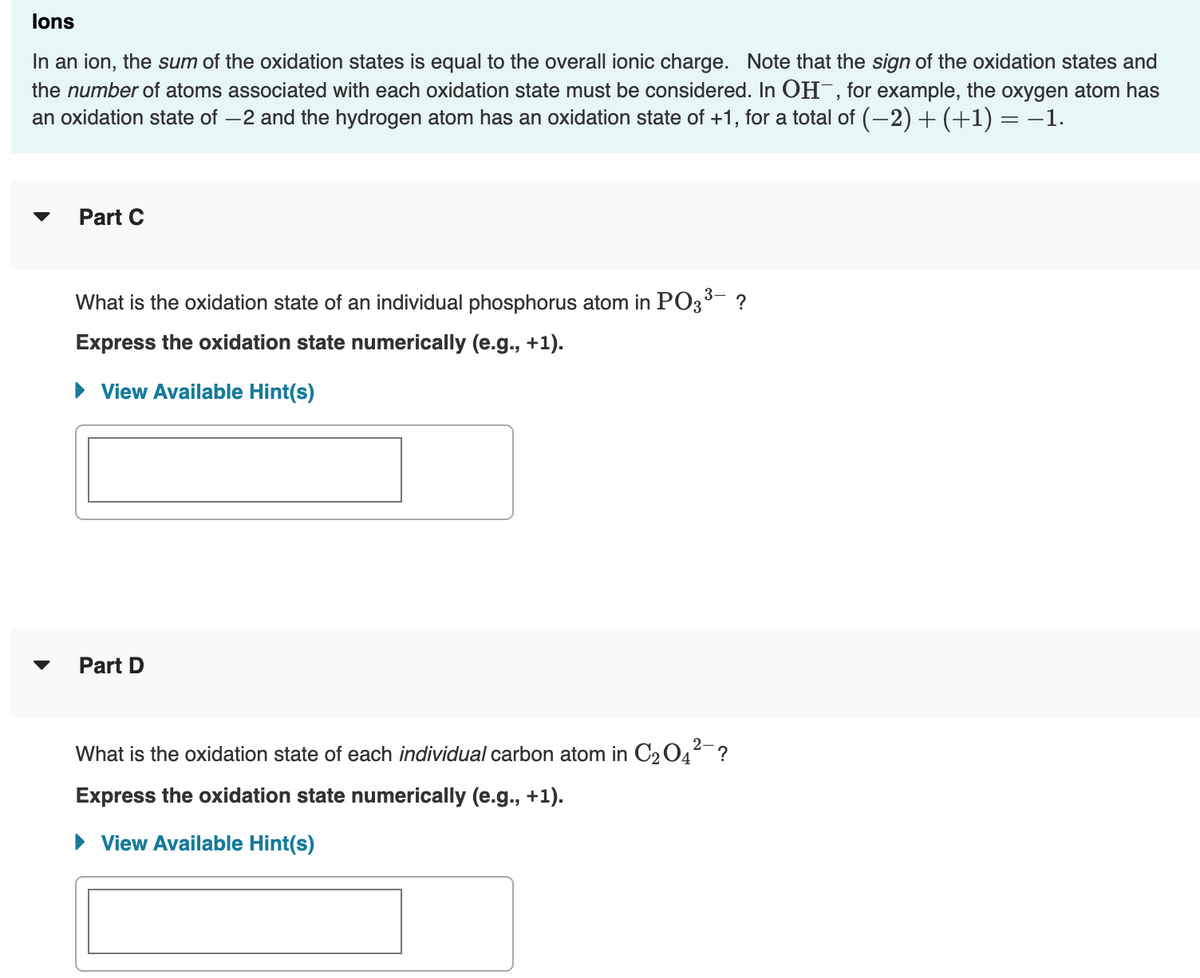
Transcribed Image Text:lons
In an ion, the sum of the oxidation states is equal to the overall ionic charge. Note that the sign of the oxidation states and
the number of atoms associated with each oxidation state must be considered. In OH¯, for example, the oxygen atom has
an oxidation state of –2 and the hydrogen atom has an oxidation state of +1, for a total of (-2) + (+1) = –1.
Part C
What is the oxidation state of an individual phosphorus atom in PO3- ?
Express the oxidation state numerically (e.g., +1).
• View Available Hint(s)
Part D
What is the oxidation state of each individual carbon atom in C2 04-?
Express the oxidation state numerically (e.g., +1).
• View Available Hint(s)
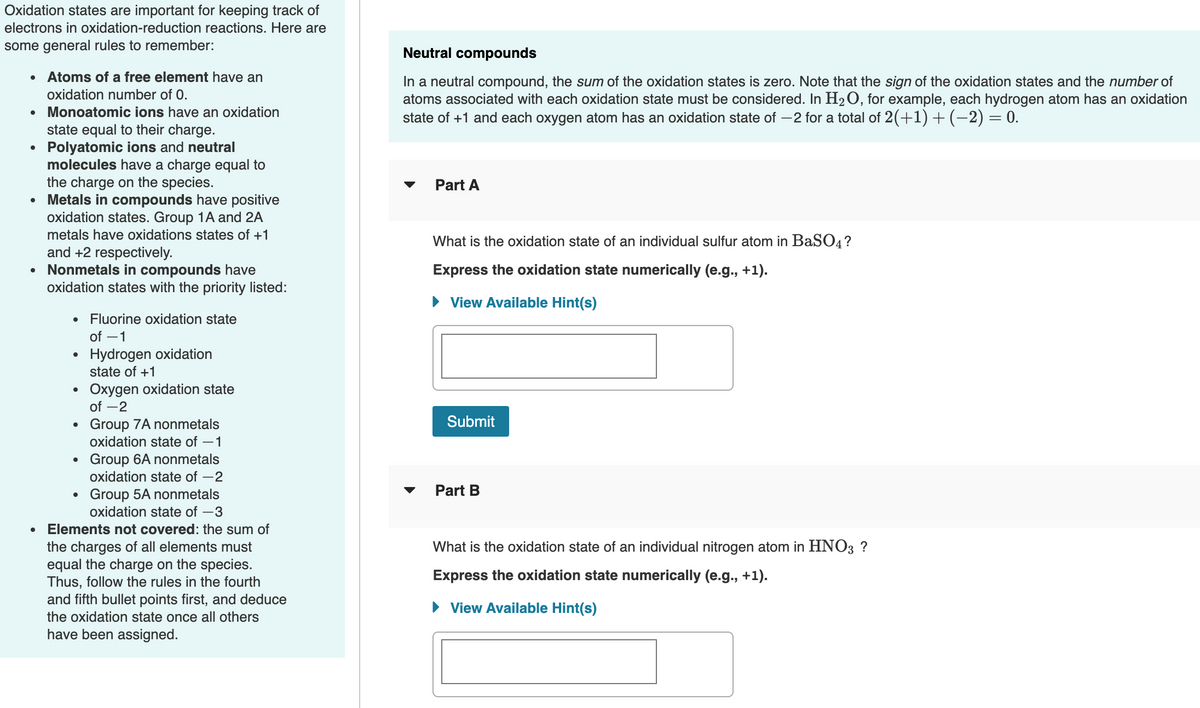
Transcribed Image Text:Oxidation states are important for keeping track of
electrons in oxidation-reduction reactions. Here are
some general rules to remember:
Neutral compounds
Atoms of a free element have an
In a neutral compound, the sum of the oxidation states is zero. Note that the sign of the oxidation states and the number of
atoms associated with each oxidation state must be considered. In H2 O, for example, each hydrogen atom has an oxidation
state of +1 and each oxygen atom has an oxidation state of -2 for a total of 2(+1) +(-2) = 0.
oxidation number of 0.
• Monoatomic ions have an oxidation
state equal to their charge.
• Polyatomic ions and neutral
molecules have a charge equal to
the charge on the species.
Metals in compounds have positive
oxidation states. Group 1A and 2A
Part A
metals have oxidations states of +1
What is the oxidation state of an individual sulfur atom in BaSO4?
and +2 respectively.
Nonmetals in compounds have
oxidation states with the priority listed:
Express the oxidation state numerically (e.g., +1).
• View Available Hint(s)
Fluorine oxidation state
of -1
• Hydrogen oxidation
state of +1
Oxygen oxidation state
of -2
Submit
Group 7A nonmetals
oxidation state of –1
Group 6A nonmetals
oxidation state of -2
Group 5A nonmetals
Part B
oxidation state of -3
Elements not covered: the sum of
the charges of all elements must
equal the charge on the species.
Thus, follow the rules in the fourth
and fifth bullet points first, and deduce
the oxidation state once all others
What is the oxidation state of an individual nitrogen atom in HNO3 ?
Express the oxidation state numerically (e.g., +1).
• View Available Hint(s)
have been assigned.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning