Consider a perfectly competitive market for wheat in New York City. There are 110 firms in the industry, each of which has the cost curves shown on the following graph: The following graph shows the market demand for wheat. Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve for the wheat industry. Specifically, place an orange point at the lowest point of the supply curve and another orange point at the highest point of the supply curve. (Note: You can disregard the portion of the supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output, since this is the industry supply curve. Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.) Then, place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the short-run equilibrium price and quantity in this market. (Note: Dashed drop lines will automatically extend to both axes.) At the current short-run market price, firms will________ in the short run. In the long run,some _______ the market given the current market price.
Consider a perfectly competitive market for wheat in New York City. There are 110 firms in the industry, each of which has the cost curves shown on the following graph: The following graph shows the market demand for wheat. Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve for the wheat industry. Specifically, place an orange point at the lowest point of the supply curve and another orange point at the highest point of the supply curve. (Note: You can disregard the portion of the supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output, since this is the industry supply curve. Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.) Then, place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the short-run equilibrium price and quantity in this market. (Note: Dashed drop lines will automatically extend to both axes.) At the current short-run market price, firms will________ in the short run. In the long run,some _______ the market given the current market price.
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter8: Perfect Competition
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7SCQ: If new technology in a perfectly competitive market brings about a substantial reduction in costs of...
Related questions
Question
Consider a perfectly competitive market for wheat in New York City. There are 110 firms in the industry, each of which has the cost curves shown on the following graph:
The following graph shows the market demand for wheat.
Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve for the wheat industry. Specifically, place an orange point at the lowest point of the supply curve and another orange point at the highest point of the supply curve. (Note: You can disregard the portion of the supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output, since this is the industry supply curve. Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.) Then, place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the short-run equilibrium price and quantity in this market. (Note: Dashed drop lines will automatically extend to both axes.)
At the current short-run market price, firms will________ in the short run. In the long run,some _______ the market given the current market price.
**Has not been answered. Only plugged in what I thought was the answer.**
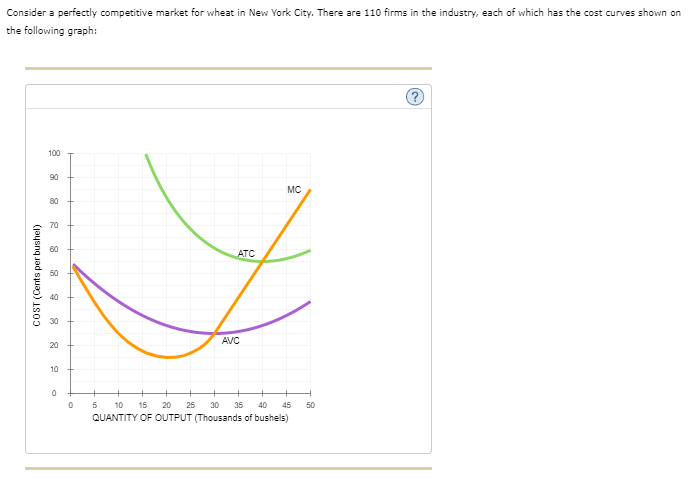
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a perfectly competitive market for wheat in New York City. There are 110 firms in the industry, each of which has the cost curves shown on
the following graph:
COST (Cents per bushel)
100
90
80
70
60
8
40
30
20
10
0
0
ATC
AVC
MC
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Thousands of bushels)
45
50
?
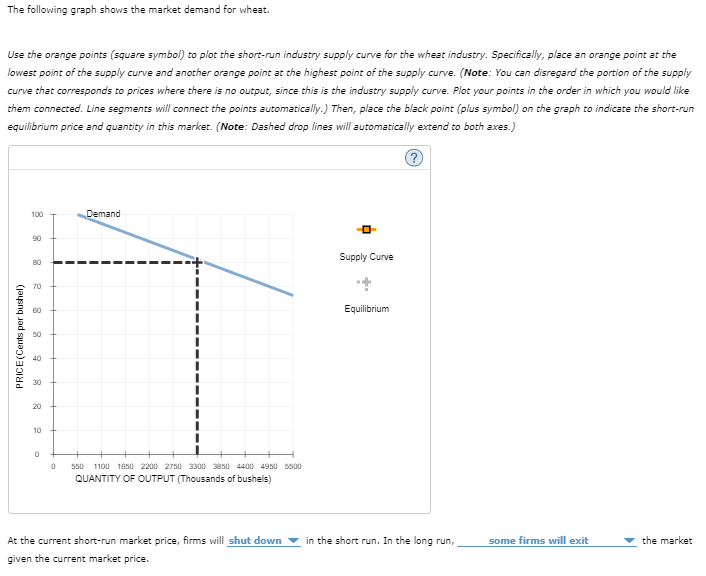
Transcribed Image Text:The following graph shows the market demand for wheat.
Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve for the wheat industry. Specifically, place an orange point at the
lowest point of the supply curve and another orange point at the highest point of the supply curve. (Note: You can disregard the portion of the supply
curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output, since this is the industry supply curve. Plot your points in the order in which you would like
them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.) Then, place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the short-run
equilibrium price and quantity in this market. (Note: Dashed drop lines will automatically extend to both axes.)
100
90
80
70
8
PRICE (Cents per bushel)
50
40
30
20
10
0
Demand
0 550 1100 1650 2200 2750 3300 3850 4400 4950 5500
QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Thousands of bushels)
At the current short-run market price, firms will shut down
given the current market price.
-0-
Supply Curve
+
Equilibrium
in the short run. In the long run,
some firms will exit
the market
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning