Construct the wavefunction V(r, 0, ø) for an H atoms' electron in the state 2p,. Please note that in order to have a real-valued wavefunction of p, orbital(see below), you need to do a linear superposition of the corresponding spherical harmonics for the angular part. Use the spherical harmonics table below. Show that the superposition you selected indeed results in a real orbital; however, you do not need to simplify the expressions further or normalize the wavefunction.
Construct the wavefunction V(r, 0, ø) for an H atoms' electron in the state 2p,. Please note that in order to have a real-valued wavefunction of p, orbital(see below), you need to do a linear superposition of the corresponding spherical harmonics for the angular part. Use the spherical harmonics table below. Show that the superposition you selected indeed results in a real orbital; however, you do not need to simplify the expressions further or normalize the wavefunction.
Physical Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Chapter10: Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.28E: A particle on a ring has a wavefunction =eim, where =0to2 and m is a constant. a Normalize the...
Related questions
Question
100%
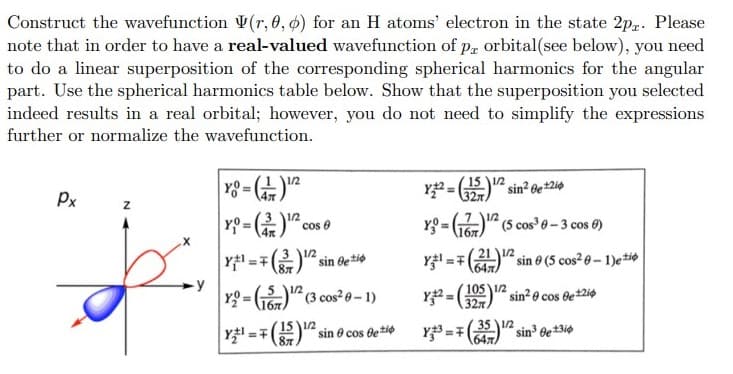
Transcribed Image Text:Construct the wavefunction V(r, 0, ø) for an H atoms' electron in the state 2p. Please
note that in order to have a real-valued wavefunction of p, orbital(see below), you need
to do a linear superposition of the corresponding spherical harmonics for the angular
part. Use the spherical harmonics table below. Show that the superposition you selected
indeed results in a real orbital; however, you do not need to simplify the expressions
further or normalize the wavefunction.
y8 = )
Y =
1/2
%3D
Px
3 12
1/2
cos 0
YO = G6)" (5 cos 0-3 cos 0)
%3D
4x
Y1 =7()2 sin Be*io
Y =7(2112 sin 0 (5 cos 6-1)etio
%3D
647)
-y
Yg = G)" (3 cos²0- 1)
Y = " sin? o cos de2i¢
105 1/2
!3!
327
1бл
Y =7
(15 1/2
87
35 12
sin 6e*3i0
1647
sin e cos detie
%3D
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning