
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Convert Newton’s method for approximating square roots in Project 1 to a recursive function named newton. (Hint: The estimate of the square root should be passed as a second argument to the function.)
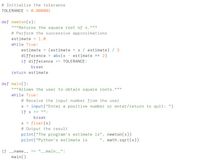
Transcribed Image Text:# Initialize the tolerance
TOLERANCE = 0.000001
def newton(x):
""Returns the square root of x.""
# Perform the successive approximations
estimate = 1.0
while True:
estimate = (estimate + x / estimate) / 2
difference = abs(x - estimate ** 2)
if difference <= TOLERANCE:
break
return estimate
def main():
"Allows the user to obtain square roots."""
while True:
# Receive the input number from the user
x = input("Enter a positive number or enter/return to quit: ")
%3D
if x
== ":
break
x = float (x)
# Output the result
print("The program's estimate is", newton (x))
print("Python's estimate is
", math.sqrt(x))
if --name_-- :
"__main__":
main()
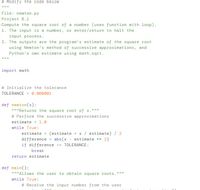
Transcribed Image Text:# Modify the code below
II II I|
File: newton.py
Project 6.1
Compute the square root of a number (uses function with loop).
1. The input is a number, or enter/return to halt the
input process.
2. The outputs are the program's estimate of the square root
using Newton's method of successive approximations, and
Python's own estimate using math.sqrt.
II II II
import math
# Initialize the tolerance
TOLERANCE = 0.000001
def newton(x):
""Returns the square root of x."""
# Perform the successive approximations
estimate = 1.0
while True:
estimate = (estimate + x / estimate) / 2
difference = abs(x - estimate ** 2)
if difference <= TOLERANCE:
break
return estimate
def main():
II I"Allows the user to obtain square roots."II"
while True:
# Receive the input number from the user
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Write a recursive function (Java) called Fac which takes one positive integer argument (n) and returns n! You may not use a built-in factorial method or function.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statement(s) is/are correct about recursion? Group of answer choices A.indication of good use of recursion: difficulty to trace down the sequence of recursive calls B.gives cleaner code but has high cost C.never be used as substitute for a simple ‘for’ loop D.bad idea to use it to evaluate simple mathematical functions. E.All of the abovearrow_forwardRecursion is a technique that calls the function by itself. Demonstrate and write a program to find the GCD of two numbers using recursion and mention the advantages of recursion.arrow_forward
- in kotlin Write two versions of a recursive palindrome check function. One version should have a block body, and the other should have an expression body. Review the lecture slide about the substring function first. Use this algorithm: if the length of the string is less than 2, return true else if the first and last characters are not equal (!=) return false else return the result of a recursive call with the substring from the second character (the one at index 1) to the second to last character. Use a main that uses a loop to test the palindrome function using this list of strings: val ss = listOf("", "A", "AA", "AB", "AAA", "ABA", "ABB", "AAAA", "AABA", "ABBA", "ABCBA", "ABCAB")arrow_forwardWrite a recursive function that displays a string reversely on the console using the following header: def reverseDisplay(value):For example, reverseDisplay("abcd") displays dcba. Write a test programthat prompts the user to enter a string and displays its reversal.arrow_forwardHi, I need a recursive function, not the one that iterates through the string and count the 'x' :)arrow_forward
- Write a recursive function to sort an array of integers into ascending order using the following idea: the function must place the smallest element in the first position, then sort the rest of the array by a recursive call. This is a recursive version of the selection sort. (Note: You will probably want to call an auxiliary function that finds the index of the smallest item in the array. Make sure that the sorting function itself is recursive. Any auxiliary function that you use may be either recursive or iterative.) Embed your sort function in a driver program to test it. Turn in the entire program and the output.arrow_forwardWrite a recursive algorithm with the following prototype: int divide (int x, int y); that returns x/y (integer division). You need not test for divide by 0. THE FUNCTION MUST BE RECURSIVE. (hint: base case should be when xarrow_forwardWhat is the purpose of the base case in a recursive function? A. The base case starts off the recursive process. B. The base case defines the basis for the function calling itself. C. The base case is what stops the recursive process. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above are true.arrow_forward
- How do I calculate the minimum velocity and maximum height using recursion and code to ask the user to guess a minimum velocity and maximum height, which the code should use as start pointsarrow_forwardT/F 9. As loop variables and recursive solutions are also not used for iterative solutions, the recursive solution generally makes memorization more effective (use fewer stored) than the corresponding iterative solution.arrow_forwardWrite a recursive algorithm with the following prototype: int add (int x, int y); that returns x if y is 0; and adds x to y otherwise. THE FUNCTION MUST BE RECURSIVE. (hint: the base case should involve a test for y being 0; recursive case should reduce y towards 0)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY