
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
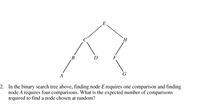
Transcribed Image Text:### Binary Search Tree Diagram
#### Diagram Explanation:
The diagram illustrates a binary search tree structure, which is a data structure used to maintain a sorted sequence of elements, allowing for efficient insertion, deletion, and lookup operations.
- **Nodes:**
- E (root)
- C, H (children of E)
- B, D (children of C)
- A (child of B)
- F (child of H)
- G (child of F)
- **Levels of Nodes:**
- Level 1: Node E
- Level 2: Nodes C, H
- Level 3: Nodes B, D, F
- Level 4: Nodes A, G
Each node in the tree has 0, 1, or 2 children. In this structure, left children are typically smaller than their parent nodes, while right children are larger.
### Text:
2. In the binary search tree above, finding node E requires one comparison and finding node A requires four comparisons. What is the expected number of comparisons required to find a node chosen at random?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- If a binary search tree has n nodes, what are the lowest and highest nodes? Your answer should be supported by mathematical logic.arrow_forwardA worst-case scenario for a binary tree sort that uses a self-balancing binary search tree is O(n log n) time. The merge sort method is much faster than this one.arrow_forwardIn a binary search tree, to remove a node N that has left child C1 and right child C2, we do the following: Group of answer choices We make C1 the left child of N’s parent and C2 the right child of N’s parent We make C1 the right child of N’s parent and C2 the left child of N’s parent We find the largest item L in N’s left subtree, copy the contents of L to N, and remove L We find the smallest item S in N’s right subtree, copy the contents of S to N, and remove N We find the largest item L in N's right subtree, copy the contents of L to N, and remove Larrow_forward
- TREE C: 1. Is tree Ca binary search tree? 2. If tree C is a binary search tree, is it balanced or skewed? If it is not a binary search tree, why not?arrow_forwardBACKTRACKINGarrow_forwardQuestion in image. No need for the code. Please explain the algorithm in a simple way with the answer. Thank youarrow_forward
- In the binary search tree, write a function that takes in a root, p, and checks whether the tree rooted in p is a binary search tree or not. What is the time complexity of your function? def is_bst(self, p: Node):arrow_forwardLet T be a binary search tree with n nodes, in which n > 0. When T is linear, the search algorithm makes key comparisons, in the unsuccassful case.arrow_forwardThe minimum height of a binary search tree win n keys is log2 n. Select one: True or Falsearrow_forward
- In a binary search tree, to remove a node N that has parent P and one child C, we do the following: Group of answer choices If C is the right child of N, we make C the right child of P, and if C is the left child of N, we make C the left child of P If C is the right child of N, we make C the left child of P, and if C is the left child of N, we make C the right child of P If N is the left child of P, we make C the left child of P and if N is the right child of P, we make C the right child of P If N is the left child of P, we make C the right child of P and if N is the right child of P, we make C the left child of P none of the abovearrow_forwardIn the worst-case situation, binary tree sort using a self-balancing binary search tree requires O(n log n) time, which is slower than merge sort.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education