Erhan and Panikos produce hamburgers (H) and steaks (S). Suppose that the Erhan's PPF is defined by 950QH+425Qs = 1900. What is the opportunity cost of one hamburger? O A. 2 steaks. O B. 1/2 steak. O C. 3 steaks. O D. It depends on which axis the quantity of hamburgers is located. O E. None of the above.
Erhan and Panikos produce hamburgers (H) and steaks (S). Suppose that the Erhan's PPF is defined by 950QH+425Qs = 1900. What is the opportunity cost of one hamburger? O A. 2 steaks. O B. 1/2 steak. O C. 3 steaks. O D. It depends on which axis the quantity of hamburgers is located. O E. None of the above.
Chapter13: General Equilibrium And Welfare
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13.3P
Related questions
Question
Hi can you please answer this question thank you
Transcribed Image Text:Erhan and Panikos produce hamburgers (H) and steaks (S). Suppose that the Erhan's PPF is
defined by 950QH+425Qs = 1900. What is the opportunity cost of one hamburger?
O A. 2 steaks.
OB. 12 steak.
O C. 3 steaks.
O D. It depends on which axis the quantity of hamburgers is located.
O E. None of the above.
Erhan and Panikos produce hamburgers (H) and steaks (S). Suppose that Erhan's PPF is flatter
than Panikos' PPF, with the quantity of hamburgers on the horizontal axis. Given this
information, which of the following can you conclude?
O A. The opportunity cost of hamburgers is lower for Erhan than for Panikos.
O B. The relative price of hamburgers is lower for Erhan than for Panikos.
O C. Erhan has a comparative advantage in hamburgers.
O D. Panikos has a comparative advantage in hamburgers.
O E. Both statements A and C are correct.
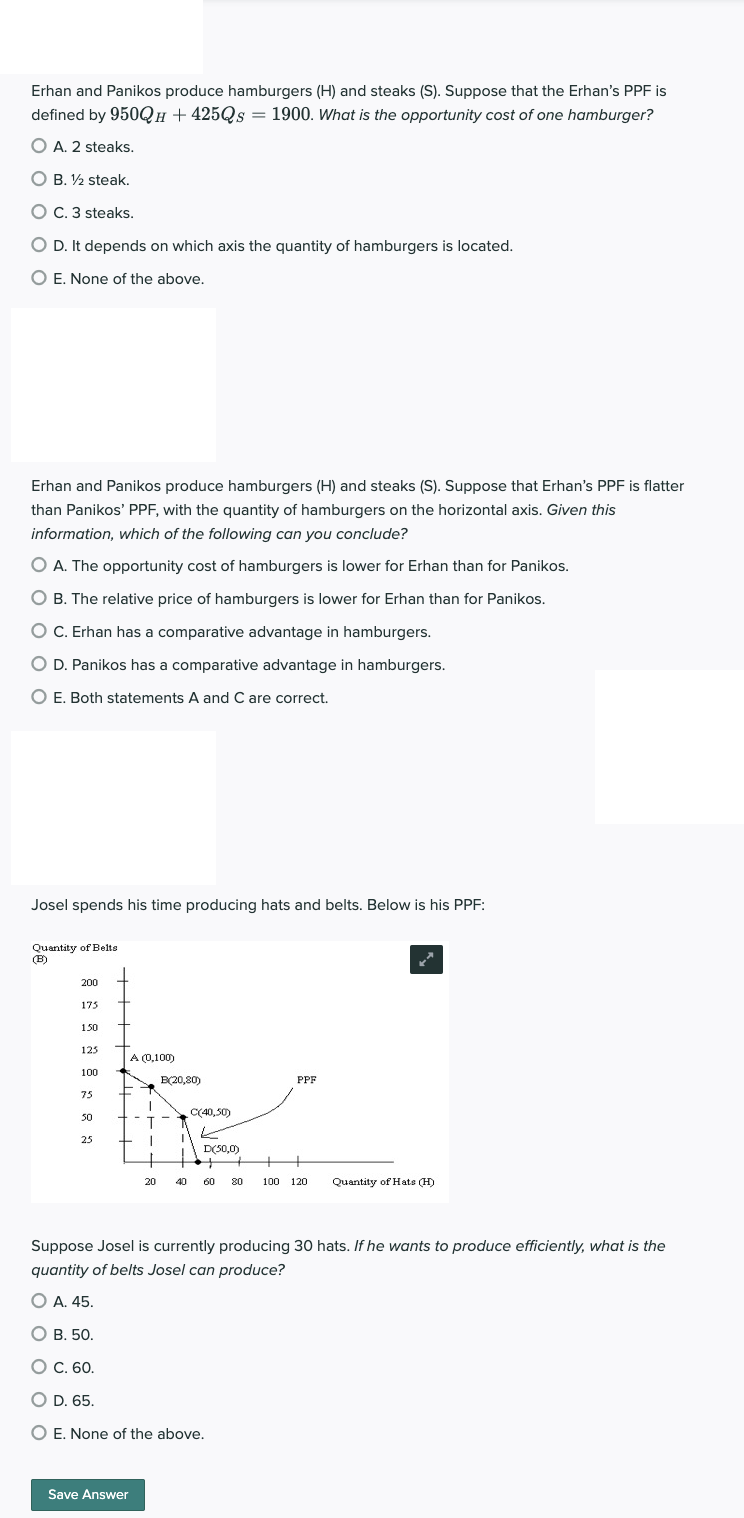
Josel spends his time producing hats and belts. Below is his PPF:
Quantity of Belts
(B)
200
175
150
125
100
75
50
25
A (0,100)
1
+ I
Save Answer
20
B(20,80)
C(40,50)
D(50,0)
PPF
40 60 80 100 120 Quantity of Hats (H)
Suppose Josel is currently producing 30 hats. If he wants to produce efficiently, what is the
quantity of belts Josel can produce?
O A. 45.
O B. 50.
O C. 60.
O D. 65.
O E. None of the above.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc


Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc