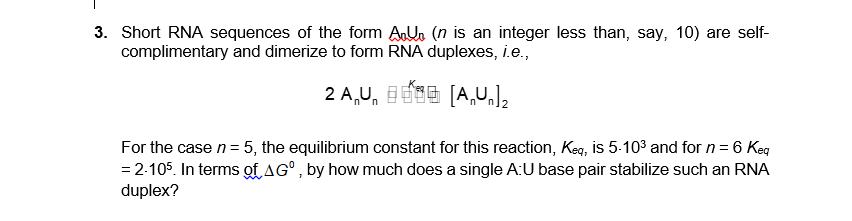
For the case n = 5, the equilibrium constant for this reaction, Keg, is 5-10³ and for n= 6 Keg = 2-105. In terms ofAG°, by how much does a single A:U base pair stabilize such an RNA duplex? %3D
Q: If you set up an in vitro translation reaction containing poly(ACGU), as template, which of the…
A: A three-letter codon is a sequence of DNA or RNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid. These…
Q: Imagine two DNA duplexes X and Y. According to calculations using the nearest neighbor method the…
A: Given two DNA duplexes. X and Y Standard enthalpy of helix formation is same for both. Standard…
Q: Snake venom phosphodiesterase hydrolyzes nucleotides from the 3' end of any oligonucleotide and…
A: The monomeric units of nucleic acids are called nucleotides. Nucleotides are generally…
Q: Ribonuclease A cannot catalyze the hydrolysis of DNA. which of the following statements explains…
A: Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polymer made up of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each…
Q: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic protein initiation is that eukaryotes' initiator…
A: Translation is the process of Synthesis of proteins from amino acids by peptide bond formation. It…
Q: snip
A: The study of how temperature affects the nucleic acid structure of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) is…
Q: At which solvent is yeast RNA very soluble? Explain why. At which solvent/s is yeast RNA insoluble?…
A: RNA are ribose nucleic acids containing ribose sugar, nitrogenous bases, and phosphate group. These…
Q: An RNA polymer is made by using the enzyme polynucleotide phosphorylase with equal quantities of CTP…
A: Answer : glycine, proline, alanine, arginine, The possible codons can be CCG CGC GCC GGC GCG CGG
Q: what percentage of the total amino acids in the protein would be made up of proline (Pro)?
A: Proline is an amino acid codded by the codons CCG, CCC, CCU, and CCA. Any one of these codons can…
Q: Different sigma factors in E. coli cells share Select one: O a. same core RNA polymerase O b. same…
A: 7.) Answer is option c
Q: Given the following mismatch (highlighted in red), which base will be replaced after mismatch repair…
A: Normal metabolic activities and environmental exposure can cause DNA damage. DNA damage in human…
Q: Consider the following coding 71 nucleotide DNA template sequence (It does not contain a…
A: In cell protein formed according to the sequence on mRNA. mRNA is formed from DNA sequence by the…
Q: Assume that the translational error frequency, d, is 1 * 10–4. (a) Calculate the probability of…
A: The probability that a protein molecule is completely error free is (1-δ)n, where n is the number of…
Q: why hot water is slightly soluble in yeast rna?
A: The RNA or ribonucleic acid which is collected from yeast is usually the total RNA that is obtained…
Q: A small section of bacterial enzyme has the amino acid sequence threonine, valine, glycine, and…
A: The process of formation of amino acids from the mRNA sequence is known as translation. mRNA…
Q: The antibiotic paromomycin binds to a ribosome and induces the same conformational changes in 16S…
A: Ribosomes are complex molecules that are composed of ribosomal RNA molecules where photosynthesis…
Q: Why is Sanger sequencing referred to as the chain termination method? Select one: a. Sugars on ddNTP…
A: Sanger sequencing also known as the "chain termination method", is a method for determining the…
Q: Shown below is an R loop prepared for electron microscopy by annealing a purified eukaryotic…
A: An R-loop refers to a structure formed by a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and an RNA molecule. As a…
Q: Shown below is an R loop prepared for electron microscopy by annealing a purified eukaryotic…
A: An exon is any part of a gene that will encode a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene…
Q: As stated in the text, bacteriophages have been discovered with the following base substitutions in…
A: (a) it is possible for dUMP to be completely substituting for dTMP if the viral genome is able to…
Q: The following polynucleotide was synthesized and used as a template for peptide synthesis in a…
A: The DNA template is used to form an mRNA polynucleotide by the process of transcription. The mRNA…
Q: For a protein-DNA binding reaction with ΔH = 0, sketch the van’t Hoff plot, label both axes.
A: Van't hoff equation gives the relationship between equilibrium constant, temperature, and enthalpy…
Q: With in vitro translation of an RNA into a polypep-tide chain, the translation can begin anywhere…
A: A cell "reads" the information in a messenger RNA (mRNA) during translation and uses it to create a…
Q: How do you seal sequence 2 (from 5' end) to the 3' end of the sequence 1 in vitro condition? Design…
A: Sealing is the joining of two DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segments under in-vitro conditions. The…
Q: The wobble pairing rule states that a 'U' in teh anticodon wobble position can pair with 'A' or 'G',…
A: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a nucleic acid found in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. It can be genetic…
Q: (i) (.. From the diagram to the right of the trp repressor in its approximate binding relationship…
A: Tryptophan (trp) repressor: It's a transcription factor that regulates amino acid metabolism. The…
Q: Like a helices, B sheets often have one side facing the surface of the protein and one side facing…
A: Option D is the correct answer.
Q: In the given segment 3 ’ C A G T T A C G G C T C C T A G G T T A T A A T T C G T T T C 5 ’…
A: DNA replication occurs with the help of several enzymes and is always synthesized in 5' to 3'…
Q: Shown in the following table are several amino acid substitutionsin the a and b chains of human…
A: Globins are considered an ancient and varied superfamily of proteins. Hemoglobin is an major protein…
Q: Diagram the enol form of cytosine following a tautomeric shift. Include in the diagram how this…
A: The bases of nucleotides can undergo spontaneous structural alterations known as tautomerization;…
Q: . The following data represent the base compositions of double-stranded DNA from two different…
A: A gene is the essential physical and functional unit of heredity. They are comprised of DNA…
Q: Why is yeast RNA insoluble with dilute HCl, ethanol, cold water, and slightly insoluble with hot…
A: Nucleic acids are known as the molecules that carry information in the cell. They are also involved…
Q: A random-sequence polyribonudeotide produced by polynudleotide phosphorylase, with CDP and ADP in a…
A: Amino acids are coded by a tripeptide sequence called codons. The first two positions of the codon…
Q: Why is yeast RNA insoluble in ethanol, dil. HCl, cold water and soluble in dil. NaOH and hot water?
A: Yeast is a single celled eukaryotic microorganism that belongs to the kingdom Fungi. The yeast cells…
Q: An RNA polymer is made by using the enzyme polynucleotide phosphorylase with equal quantities of CTP…
A: The amino acids are coded by the group of three bases called base triplets and codons.
Q: Given the following sequence of a coding DNA strand: AGTTGCGCATGCCAGAGAGGTTCGAGTGCACATAACTTGAG The…
A: DNA is a double stranded molecule with coding strand and template strand. Template strand is the one…
Q: From the diagram to the right of the trp repressor in its (i) approximate binding relationship to a…
A: Given Figure shown trp repressor protein bond to DNA double strand. Protein is mainly comprised of…
Q: which of the following sequences would most likely be able to bind a cyclic amp dna binding protein?…
A: Introduction: Nucleotides are the nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and phosphate group. Nucleotides…
Q: . The following synthetic polynucleotide is synthesized and used as a template for peptide synthesis…
A: Polypeptide is made up of chain of amino acids linked together. Polypeptides are connected together…
Q: Polyglycine, a simple polypeptide, can form a helix with φ = -80°, ψ = +150°. From the Ramachandran…
A: A protein can arrange itself according to requirements. It can be primary, secondary, tertiary and…
Q: An RNA polymer is made by using the enzyme polynucleotide phosphorylase with equal quantities of CTP…
A: Question - An RNA polymer is made by using the enzyme polynucleotide phosphorylase with equal…
Q: Low-resolution X-ray diffraction analysis of a protein composed of long stretches of the sequence…
A: Fibroins are insoluble proteins that are present in silk produced by insects, such as the larvae of…
Q: Why is RNA very soluble in diluted NaOH solution and insoluble in cold water?
A: RNA are macromolecules found abundant in tissues possessing closed packaged cells with big nuclei…
Q: A double-stranded fragment of viral DNA, one of whose strands is shown below, encodes two peptides,…
A: A double-stranded fragment of viral DNA, one of whose strands is shown below, encodes two peptides,…
Q: Bradford technique makes use of the Coomassie blue dye that binds to the protein, with the complex…
A: Three different versions of the Coomassie bright blue G-250 dye are available: cationic (blue),…
Q: Consider the wobble rules listed in Table 15.2. Which of the following mRNA codons will bind to the…
A: Protein translation is the process of molecular biology in which the mRNA synthesized by the process…
Q: Determine the sequence of amino acids specified by the codons in the following information strand.…
A:

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

- 2. A mixture of the following amino acids (glu, leu, val, arg, ser, phe) was obtained upon complete hydrolysis of a hexapeptide. a. Edman’s reagent releases leucine b. Hexapeptide with carboxypeptidase releases serine. c. Hexapeptide with trypsin forms a tripeptide A with leucine at the N terminal and tripeptide B with valine at the N terminal. d. Tripeptide A with carboxypeptidase releases arginine and a dipeptide with glutamic acid at C terminal. e. Tripeptide B with chymotrypsin form releases serine and another dipeptide. Give: 1. the amino acid sequence of tripeptide A and B. 2. the amino acid sequence in the above hexapeptide.1. A certain polypeptide was treated with trypsin and yielded the following Fragments: Leu-Glu Gly-Tyr-Asn-Arg Gln-Ala-Phe-Val-Lys The same polypeptide was treated with chymotrypsin and yielded the following fragments: Gln-Ala-Phe Asn-Arg-Leu-Glu Val-Lys-Gly-Tyr What is the amino acid sequence of this polypeptide? Instructions Make use of the table below to determine the sequence of the mystery protein.1. Considering the following nucleotide sequence in an mRNA molecule: 5’ AUG UUA CGU AAU GCU GUC GAA UCU AUU UGC UUU ACA UAA 3' d) Write the amino acid sequence of the peptide synthesized from the given mRNA nucleotide sequence. e) Draw the structure of the pertide fragment made up of the first five (5) amino acids in the given polypeptide.
- Which of the following statements is false? a. GTP is an energy source during various stages of translation. b. In the ribosome, peptidyl transferase catalyzes peptide bondformation between amino acids. c. When the mRNA code UAA reaches the ribosome, there isno tRNA to bind to it. d. A long polypeptide is cut off the tRNA in the A site so its Metamino acid links to the amino acid in the P site. e. Forty-two amino acids of a protein are encoded by 126nucleotides of the mRNA.1.Draw these phosphorylated structures as they would be connected in a polinucleotide (e.g.RNA) in the order A-B. / Show how they combine to form the polynuleotide (i.e. only the end product). Show at any one of these structures where the glycosidic bond occurs 2.Sanger sequencing revealed the sequence of an oligonucleotide to be: d-AGATGCCTGACT. Draw a diagram of the gel banding pattern post capillary electrophoresis i.e. where on the gel would the fragments feature1. The figure above shows some of the more common modifications, such as phosphorylation (1), acetylation or methylation (2), adding sugars or lipids (3,4), or adding another polypeptide (5). There are many other possibilities as well.Find and label each of these on the diagram. How might these modifications affect the protein?
- 2 Please draw the arrow-pushing mechanism to create the polyketide backbone chain of TYLOSIN. If two or more extension rounds are exactly the same, you do not need to draw them more than once. However, please clearly indicate which steps are being repeated. Please draw the complete “business end” of any cofactors you use in a step6. Which of the following statements concerning the BLOSUM62 substitution matrix is correct?a. Ala is aligned with Arg more often than expected by chance.b.Ala is never substituted by Cys.c. Tryptophan is substituted less frequently than any other amino acid.3) The ACE2 receptor protein in humans has been getting a lot of press these days, as it apparently serves as a "receptor" for the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus in addition to its normal functions. This protein has an isoelectric pH of 5.36. Suppose you want to purify this protein to study its properties, with the goal of developing a drug that would block it from binding the virus. Once you have purified the cell surface proteins from your cultured human lung cells away from all the other types of molecules in the cell, and all the cytoplasmic proteins, you might decide to use ion exchange chromatography to separate the ACE2 proteins from other proteins in your sample. If you plan to load your protein mixture onto your ion exchange column in a buffer at pH 7.4 (approximately physiological pH) and you want the ACE2 proteins to bind to the column, should you use a resin with a positive charge or a negative charge? Briefly explain why you chose the resin you selected.
- 6a) Transcribe the following DNA sequence into codons. TACGCGACATTACATGAATCGTTTGGAGATTAGCCCTATTTCTCTAAGAACACGACTb) Excise(cut out) codons numbered 5, 6, and 7. Leave the remaining codons. c) Now translate the sequence . d) Explain how many amino acids are now in your polypeptide? e) What would happen to your polypeptide if either of your cysteine amino acids near the start or end of thepolypeptide were translated incorrectly. f) Based on your final polypeptide can you make the original DNA strand by doing reverse translation andtranscription? g) Explain if your polypeptide similar to your template strand or the complementary strand?2) When DNA is placed in distilled water, which is pH 7.0, it denatures (i.e., the two strands separate). The pH inside a cell is generally 7.2-7.5, depending on the organism, but DNA is generally double-stranded under physiological conditions. Briefly explain, in your own words, why DNA denatures when placed in distilled water but not when it is inside a cell. [Reminder: the pKa for the phosphate groups in the sugar-phosphate backbone of a strand of DNA is 2.14]1. Use the info of this molecule as well as the attached addendum to demonstrate the flow of genetic information to protein sequence as described by the so-called “Central Dogma” . Clearly indicate the direction of your polynucleotide strands and peptide/protein. ATG GCA TGC AAT AGC TCA TGC 2. What would happen to the amino acid sequence if the underlined nucleotide (C) would change to an A?

