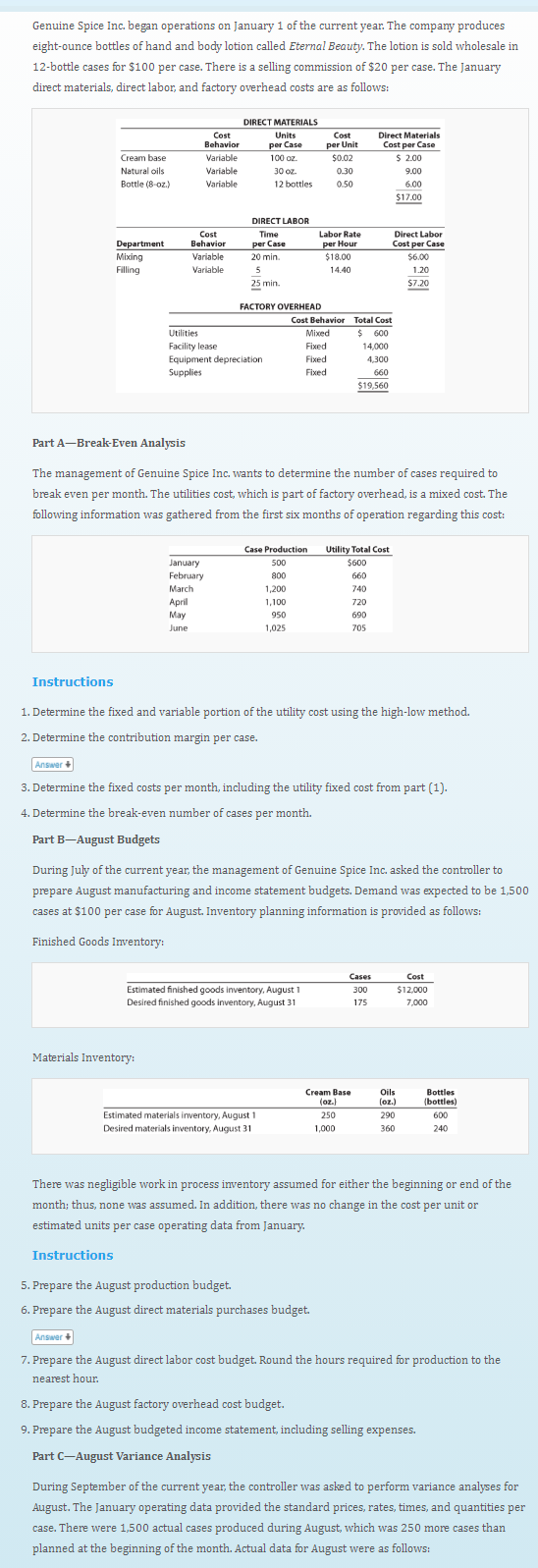
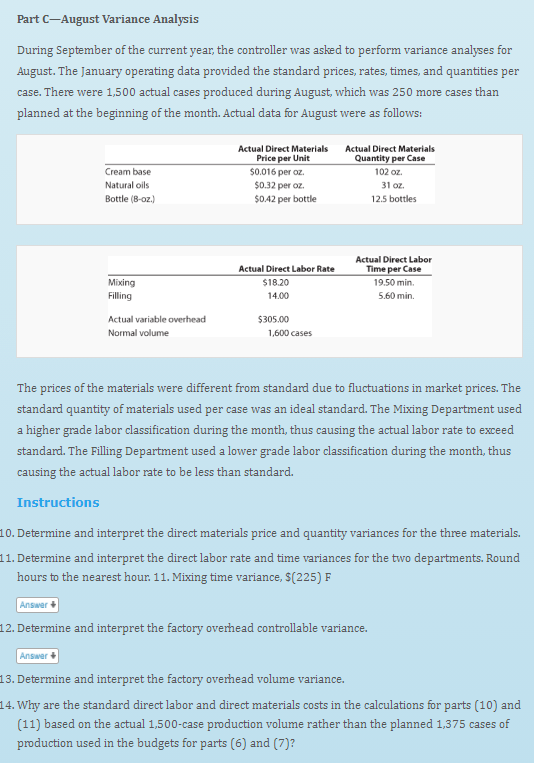
Genuine Spice Inc. began operations on January 1 of the current year. The company produces eight-ounce bottles of hand and body lotion called Eternal Beauty. The lotion is sold wholesale in 12-bottle cases for $100 per case. There is a selling commission of $20 per case. The January direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead costs are as follows: DIRECT MATERIALS Cost Behavior Units per Case Cost per Unit $0.02 Direct Materials Cost per Case $ 2.00 Cream base Variable 100 oz. Natural oils Variable 30 oz. 0.30 9.00 Bottle (8-oz.) Variable 12 bottles 0.50 6.00 $17.00 DIRECT LABOR Time per Case Labor Rate Cost Behavior Direct Labor Department Mixing Filling Cost per Case $6.00 per Hour Variable 20 min. $18.00 Variable 14.40 1.20 25 min. $7.20 FACTORY OVERHEAD Cost Behavior Total Cost Utilities Mixed $ 600 Facility lease Fixed 14,000 Equipment depreciation Supplies Fixed 4,300 Fixed 660 $19,560 Part A-Break-Even Analysis The management of Genuine Spice Inc. wants to determine the number of cases required to break even per month. The utilities cost, which is part of factory overhead, is a mixed cost. The following information was gathered from the first six months of operation regarding this cost: Case Production Utility Total Cost $600 January February 500 800 660 March 1,200 740 April May 1,100 720 950 690 June 1,025 705 Instructions 1. Determine the fixed and variable portion of the utility cost using the high-low method. 2. Determine the contribution margin per case. Answer 4 3. Determine the fixed costs per month, including the utility fixed cost from part (1). 4. Determine the break-even number of cases per month. Part B-August Budgets During July of the current year, the management of Genuine Spice Inc. asked the controller to prepare August manufacturing and income statement budgets. Demand was expected to be 1,500 cases at $100 per case for August. Inventory planning information is provided as follows: Finished Goods Inventory: Cases Cost Estimated finished goods inventory, August 1 Desired finished goods inventory, August 31 300 $12.000 175 7,000 Materials Inventory: Cream Base Oils (oz.) Bottles (oz.) (bottles) Estimated materials inventory, August 1 250 290 600 Desired materials inventory, August 31 1,000 360 240 There was negligible work in process inventory assumed for either the beginning or end of the month; thus, none was assumed. In addition, there was no change in the cost per unit or estimated units per case operating data from January. Instructions 5. Prepare the August production budget. 6. Prepare the August direct materials purchases budget. Answer + 7. Prepare the August direct labor cost budget. Round the hours required for production to the nearest hour. 8. Prepare the August factory overhead cost budget. 9. Prepare the August budgeted income statement, including selling expenses.
The Effect Of Prepaid Taxes On Assets And Liabilities
Many businesses estimate tax liability and make payments throughout the year (often quarterly). When a company overestimates its tax liability, this results in the business paying a prepaid tax. Prepaid taxes will be reversed within one year but can result in prepaid assets and liabilities.
Final Accounts
Financial accounting is one of the branches of accounting in which the transactions arising in the business over a particular period are recorded.
Ledger Posting
A ledger is an account that provides information on all the transactions that have taken place during a particular period. It is also known as General Ledger. For example, your bank account statement is a general ledger that gives information about the amount paid/debited or received/ credited from your bank account over some time.
Trial Balance and Final Accounts
In accounting we start with recording transaction with journal entries then we make separate ledger account for each type of transaction. It is very necessary to check and verify that the transaction transferred to ledgers from the journal are accurately recorded or not. Trial balance helps in this. Trial balance helps to check the accuracy of posting the ledger accounts. It helps the accountant to assist in preparing final accounts. It also helps the accountant to check whether all the debits and credits of items are recorded and posted accurately. Like in a balance sheet debit and credit side should be equal, similarly in trial balance debit balance and credit balance should tally.
Adjustment Entries
At the end of every accounting period Adjustment Entries are made in order to adjust the accounts precisely replicate the expenses and revenue of the current period. It is also known as end of period adjustment. It can also be referred as financial reporting that corrects the errors made previously in the accounting period. The basic characteristics of every adjustment entry is that it affects at least one real account and one nominal account.
I already finish 1-4 I just need the rest
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









