
Given a partial main.py and PlaneQueue class in PlaneQueue.py, write the push() and pop() methods for PlaneQueue. Then complete main.py to read in whether flights are arriving or have landed at an airport.
- An "arriving" flight is pushed onto the queue.
- A "landed" flight is popped from the front of the queue.
Output the queue after each plane is pushed or popped. Entering -1 exits the program.
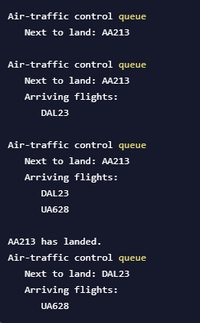
Ex: If the input is:
arriving AA213
arriving DAL23
arriving UA628
landed
-1
the output is: (see image attached)
main.py
from PlaneQueue import PlaneQueue
from PlaneNode import PlaneNode
if __name__ == "__main__":
plane_queue = PlaneQueue()
# TODO: Read in arriving flight codes and whether a flight has landed.
# Print the queue after every push() or pop() operation. If the user
# entered "landed", print which flight has landed. Continue until -1
# is read.
PlaneNode.py
class PlaneNode:
def __init__(self, flight_code='0'):
self.flight_code = flight_code
self.next = None
def print_node_data(self):
print(self.flight_code, end='')
PlaneList.py
class PlaneList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def append(self, new_node):
if self.head == None:
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
else:
self.tail.next = new_node
self.tail = new_node
def prepend(self, new_node):
if self.head == None:
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
else:
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def insert_after(self, current_node, new_node):
if self.head == None:
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
elif current_node is self.tail:
self.tail.next = new_node
self.tail = new_node
else:
new_node.next = current_node.next
current_node.next = new_node
def remove_after(self, current_node):
# Special case, remove head
if (current_node == None) and (self.head != None):
succeeding_node = self.head.next
self.head = succeeding_node
if succeeding_node == None: # Remove last item
self.tail = None
elif current_node.next != None:
succeeding_node = current_node.next.next
current_node.next = succeeding_node
if succeeding_node == None: # Remove tail
self.tail = current_node
def search(self, key):
position = 1
cur_node = self.head
while cur_node != None:
if cur_node.data == key:
cur_node.node_pos = position
return cur_node
cur_node = cur_node.next
position += 1
def print_list(self):
cur_node = self.head
while cur_node != None:
cur_node.print_node_data()
print()
cur_node = cur_node.next
PlanbeQueue.py
from PlaneList import PlaneList
class PlaneQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.plane_list = PlaneList()
self.length = 0
# TODO: Write push() and pop() methods. push() adds an item to the queue
# and adds 1 to length. pop() removes and returns the first item in
# the queue and subtracts 1 from length.
def is_empty(self):
return self.length == 0
def print_queue(self):
print('Air-traffic control queue')
if not self.is_empty():
print(' Next to land:', end=' ')
cur_node = self.plane_list.head
cur_node.print_node_data()
print()
if self.length > 1:
print(' Arriving flights:')
cur_node = cur_node.next
while cur_node is not None:
print(' ', end='')
cur_node.print_node_data()
print()
cur_node = cur_node.next
else:
print('Queue is empty.')
print()
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

- Write a program that performs a survey on beverages. The program should prompt for the next person until a lookout value of -1 is entered to terminate the program. Each person participating in the survey should choose their favorite beverage from the following list? 1. Coffee 2. Tea 3. Coke 4. Orange Juice.arrow_forwardJava Given main(), complete the SongNode class to include the printSongInfo() method. Then write the Playlist class' printPlaylist() method to print all songs in the playlist. DO NOT print the dummy head node.arrow_forwardA for construct is a loop that goes over a list of objects. Consequently, it runs indefinitely if there are items to process. What do you think about this?arrow_forward
- Implement a “To Do” list. Tasks have a priority between 1 and 9, and a description (which you can come up with on your own, say, “wash dishes”). The program is going to prompt the user to enter the tasks by running the method add_priority_description, the program adds a new task and prints the current list with priority 1 tasks on the top, and priority 9 tasks at the bottom. The program will continue to ask the user if they want to add another tasks, and repeat the add_priority_description method, or enters Q to run the quit method to quit the program. Sample output (not limited to) 1. Study for the final 1. Take the final 2. Watch Justice League with friends 3. Play ball 9. Wash Dishes 9. Clean room. There is a possibility of two tasks having the same priority. If so, the last task that was entered gets to be printed first. Use HEAP in your solution.arrow_forwardI need help coding this in Java language pleasearrow_forward
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY





