
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
I need help constructing graph I m not sure where to put values
On the graph paper plot a graph of your reaction rates vs. concentration by using
vertical scale or Y-axis representing reaction rate and a horizontal scale or X-axis
representing mls of solution #1(KIO3).
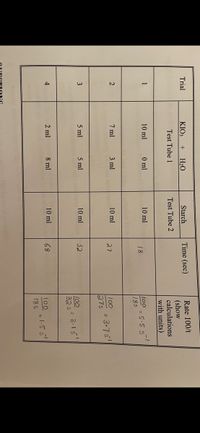
Transcribed Image Text:I1
Rate 100/t
(show
calculations
with units)
Trial
KIO3
H20
Starch
Time (sec)
Test Tube 1
Test Tube 2
10 ml
0 ml
10 ml
l00
18
= 5.5 S
185
7 ml
3 ml
10 ml
100
= 3-75
27
27s
3
5 ml
5 ml
10 ml
32
100
32 s= 3-15
4
2 ml
8 ml
10 ml
68
100
= 1-55
18S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How would you combine reactions A-C, shown below, to obtain the overall reaction: NH₂(g) +BH₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2H₂O(g) + HBNH(s) Please select all that apply. A. 2H₂(g) + O₂(g) →→→ 2H₂O(g) - B. H,BNH,(s) C. - NH3(g) +BH₂(g) H₂BNH3 (s) — 2H₂(g) + HBNH(s) Choose one or more: DA. reverse B OB. add resulting equations together OC. divide B by 2 D. reverse A OE. multiply B by 2 OF. reverse C OG. multiply C by 2 OH. divide C by 2 OI. multiply A by 2 OJ. divide A by 2arrow_forwardThe reaction C(s) + CO2(g) ⇔ 2CO(g) occurs at high temperatures. At 700 0C, a 200.0 L tank contains 1.0 mol CO, 0.20 mol CO2 and 0.40 mol of C at equilibrium. Calculate Kc for the reaction at 700 0C. Type your final answer to 3 decimal places and not as scientific notation.arrow_forwardEquilibria involving Silver Ions (Ag+) Addition of conc. ammonia (Observation and Write the Net Ionic Chemical Equilibrium Addition of Nitric Acid (Observation and Write the Net Ionic Chemical Equilibrium) Addition of Excess conc. ammonia (Observation) Addition of KI (Observation and Write the Net Ionic Chemical Equilibrium)arrow_forward
- Consider the equilibrium system described by the chemical reaction below. Determine the concentration of O2 at equilibrium by writing the equilibrium constant expression and solving it. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer. 2 H2O(g) 2 H2(g) + O2(g) 1 2 NEXT At this temperature, the Kc = 2.4 × 10-3 and the equilibrium concentrations of H2O and H2 are 0.11 M and 0.019 M, respectively. If [×] represents the equilibrium concentration of O2, set up the equilibrium expression for Kc to solve for the concentration. Each reaction participant must be represented by one tile. Do not combine terms. Ко = = 2.4 × 10-3 RESET [0.11] [0.019] 2[0.11] 2[0.019] [0.11]² [0.019]² [x] [x]² [2x] [2x]2arrow_forward4arrow_forwardExplain How did you get your answerarrow_forward
- Indicate how the concentration of each species in the chemical equation will change to reestablish equilibrium after reactant or product is added. An up arrow indicates an increase in concentration, a down arrow indicates a decrease in concentration, and leaving it blank means there is no change in the concentration. 2CO(g) + 0,(g) 2CO,(g) 88 increasing the concentration of CO increasing the concentration of CO, Answer Bankarrow_forwardH PAP Cheistry-29 X PAP Chemistry-29 X G diagram showing x b ar-2903012.agilixbuzz.com/student/135113422/activity/c412d902 Mastery Assess It 8 PAP Chemistry-2903012-42100P-1/ Le Chatelier's Principle /Lesson 128 1. Which of the following would not add stress to an equilibrium reaction shown below? A+B+C+D increasing the pressure removing product C changing the order of reactants A and B adding reactant Aarrow_forwardImage # 2 is the question.arrow_forward
- QUESTION 4 Identify all parameters that will change the equilibrium constant (K) of a solution-based chemical reaction? None of the above will change the equilbirium constant (K) for a given solution-based reaction Addition/removal of catalyst O Changing solvent O Temperature O Change in atmospheric pressure O Adding/removing products O Adding/removing reactantsarrow_forwardX OY2 OXY 2. The particle diagram above shows the system represented by the equation 2X(g)+Y2(g)=2XY(g) . Which of the following explains whether the particle diagram indicates that the system is at equilibrium? a. The particle diagram does not indicate that the system is at equilibrium because it shows the system only at one point in time. b. The particle diagram does not indicate that the system is at equilibrium because the ratio [XY]eq /[X]eq is not equal to 1. c. The particle diagram indicates that the system is at equilibrium because the value of K is small. d. The particle diagram indicates that the system is at equilibrium because [X]eq=2x[Y2]eq.arrow_forwardCan I get an easy explanation on how to balance the following reactionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY