I Review | Constants | Periodic Table involving transition of the electron from two energy states ny to ng is given as ΔΕ=-(2.18 x 10-18 J) x (-) Niels Bohr is credited with deriving this form of the Rydberg equation, which is sometimes called Bohr's equation Part B What is the change in energy, AE, in kilojoules per mole of hydrogen atoms for an electron transition from n-4 to n= 2? Express your answer in kilojoules per mole to three significant figures. > View Available Hint(s) x" X•10" AE = - 301 kJ/mol
I Review | Constants | Periodic Table involving transition of the electron from two energy states ny to ng is given as ΔΕ=-(2.18 x 10-18 J) x (-) Niels Bohr is credited with deriving this form of the Rydberg equation, which is sometimes called Bohr's equation Part B What is the change in energy, AE, in kilojoules per mole of hydrogen atoms for an electron transition from n-4 to n= 2? Express your answer in kilojoules per mole to three significant figures. > View Available Hint(s) x" X•10" AE = - 301 kJ/mol
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter5: Quantum Mechanics And Atomic Structure
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5P: Estimate the probability of finding an electron which is excited into the 2s orbital of the H atom,...
Related questions
Question
100%
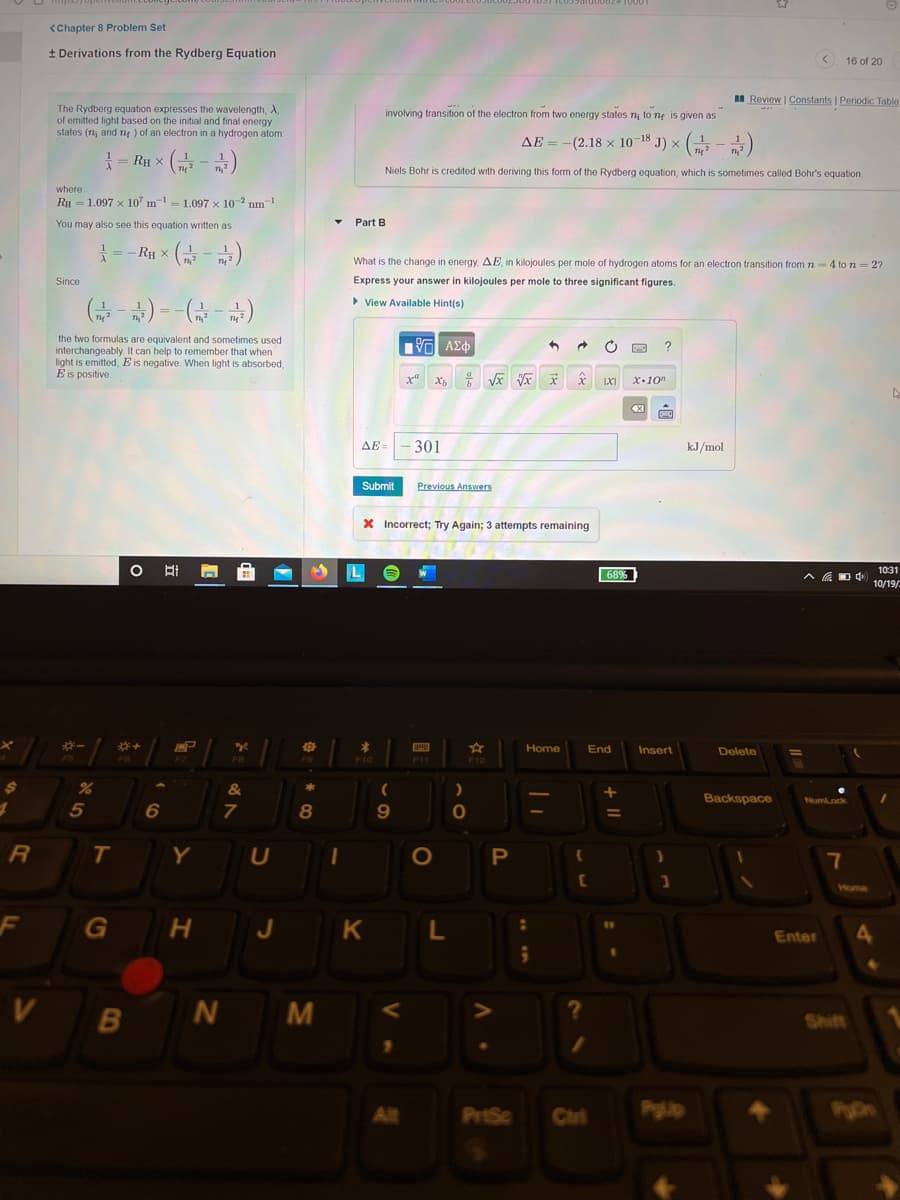
Transcribed Image Text:<Chapter 8 Problem Set
+ Derivations from the Rydberg Equation
< 16 of 20
I Review | Constants | Periodic Table
The Rydberg equation expresses the wavelength,
of emitted light based on the initial and final energy
states (ny and ny ) of an electron in a hydrogen atom:
involving transition of the electron from two energy states ny to ng is given as
AE = -(2.18 x 10-18 J) × (
Ru x (금-)
Niels Bohr is credited with deriving this form of the Rydberg equation, which is sometimes called Bohr's equation.
where
RH = 1.097 x 10" m- 1.097 x 10-2 nm-1
You may also see this equation written as
Part B
=-Ry x
What is the change in energy, AE, in kilojoules per mole of hydrogen atoms for an electron transition from 7n-4 to n = 2?
Since
Express your answer
kilojoules per mole to three significant figures.
G ) --)
> View Available Hint(s)
the two formulas are equivalent and sometimes used
interchangeably. It can help to remember that when
light is emitted, E is negative. When light is absorbed,
É is positive.
x"
X•10"
AE =
301
kJ/mol
Submit
Previous Answers
X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining
10:31
68%
ヘ D中
10/19/
*-
Home
End
Insert
Delete
F10
&
Backspace
NumLock
5
6
7
9.
Y
U
P
7
Home
G
н
J
4
Enter
B
N M
Shift
PriSc
Ciri
Pup
PDn
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning